1. State six functions of the urinary system. 2. Describe the location and structural features of the kidneys. 3. Draw and label the parts of a nephron. 4. State the two parts of the juxtaglomerular apparatus. 5. Describe the location, structure, and function of the ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. 6. List and describe the three steps in urine formation. 7. Identify the hormones that affect kidney function, and explain how they do so. 8. Explain the function of renin. 9. Describe ways in which the aging of an individual affects the urinary system. The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys produce the urine. The ureters transport the urine away from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder stores the urine until it is excreted from the body. The urethra is a tubular structure that carries the urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body. The components of the urinary system are illustrated in Figure 15-1. The macroscopic internal structure of the kidney is illustrated in Figure 15-2. The outer, reddish region is the renal cortex. The renal cortex surrounds a darker reddish-brown region called the renal medulla. The renal medulla consists of a series of renal pyramids. The renal pyramids appear striated because they contain straight tubular structures and blood vessels. The wide bases of the pyramids are adjacent to the cortex. The pointed ends of the pyramids, called renal papillae, are directed toward the center of the kidney. Portions of the renal cortex extend into the spaces between adjacent pyramids to form renal columns. The cortex and medulla make up the functional tissue of the kidney.
Urinary System
Introduction to the Urinary System
Components of the Urinary System
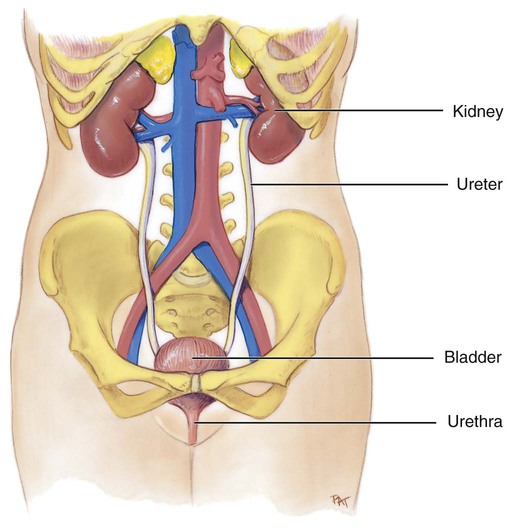
Kidneys
Macroscopic Structure
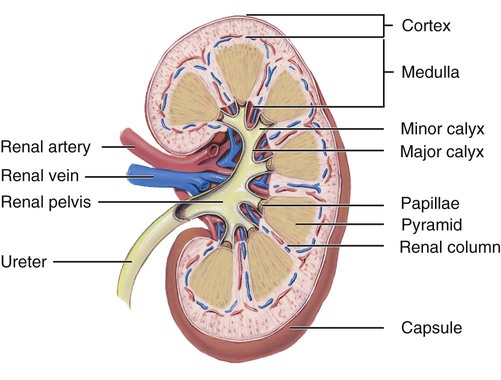
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



