Urinary Catheters
Objectives
• Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter.
• Explain why urinary catheters are used.
• Describe 2 types of urinary catheters.
• Explain the purpose and rules for catheter care.
• Describe how to use 2 urine drainage systems.
• Explain how to remove an indwelling catheter.
• Explain how to apply a condom catheter.
• Perform the procedures described in this chapter.
• Explain how to promote PRIDE in the person, the family, and yourself.
Key Terms
Key Abbreviations
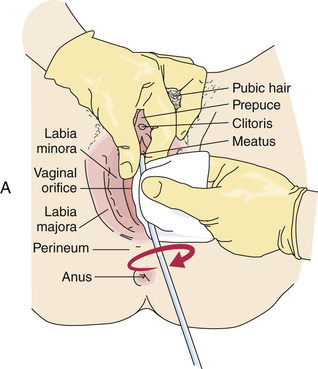
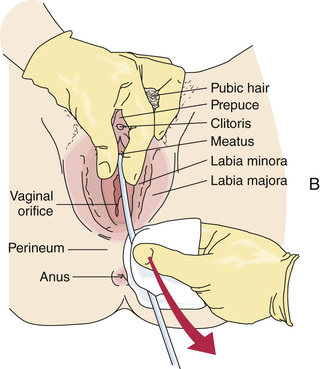
A catheter is a tube used to drain or inject fluid through a body opening. Inserted through the urethra into the bladder, a urinary catheter drains urine. Catheterization is the process of inserting a catheter. With proper training and supervision, some states and agencies let nursing assistants insert and remove urinary catheters.
See Focus on Surveys: Urinary Catheters.
See Promoting Safety and Comfort: Urinary Catheters.
Purposes and Types of Catheters
These types of catheters are common.
• A straight catheter drains the bladder and then is removed.
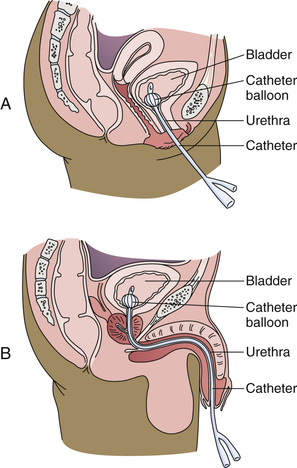
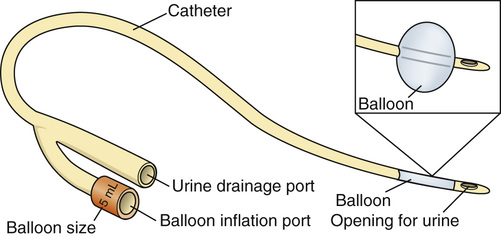
• An indwelling catheter (retention or Foley catheter) is left in the bladder. Urine drains constantly into a drainage bag. A balloon near the tip is inflated with sterile water after the catheter is inserted. The balloon prevents the catheter from slipping out of the bladder (Fig. 25-1).
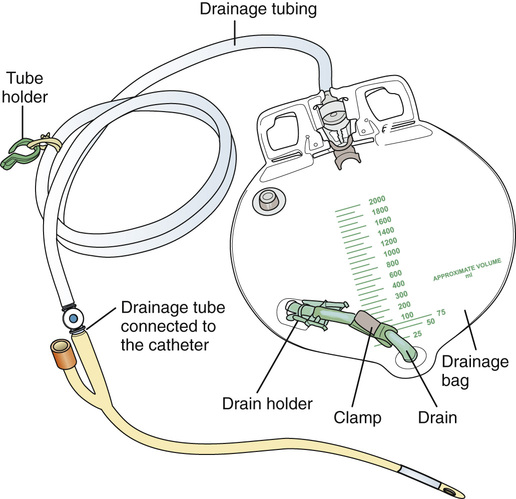
See Figure 25-2 for parts of an indwelling catheter. Tubing connects the catheter to the urine drainage bag. See Figure 25-3 for the parts of the urine drainage system.
Catheters create a risk for UTIs. However, they are used:
• To protect wounds and pressure ulcers from contact with urine.
• For hourly urine output measurements.
• To collect sterile urine specimens.
• To measure the amount of urine in the bladder after the person voids. This is called residual urine.
Catheters do not treat the cause of incontinence. They are a last resort for incontinence.
 Catheter Care
Catheter Care
You will care for persons with indwelling catheters. The risk of UTI is high. Follow the rules in Box 25-1 to promote safety and comfort.
See Delegation Guidelines: Catheter Care, p. 410.
See Promoting Safety and Comfort: Catheter Care, p. 410.
See procedure: Giving Catheter Care, p. 411.
 Urine Drainage Systems
Urine Drainage Systems
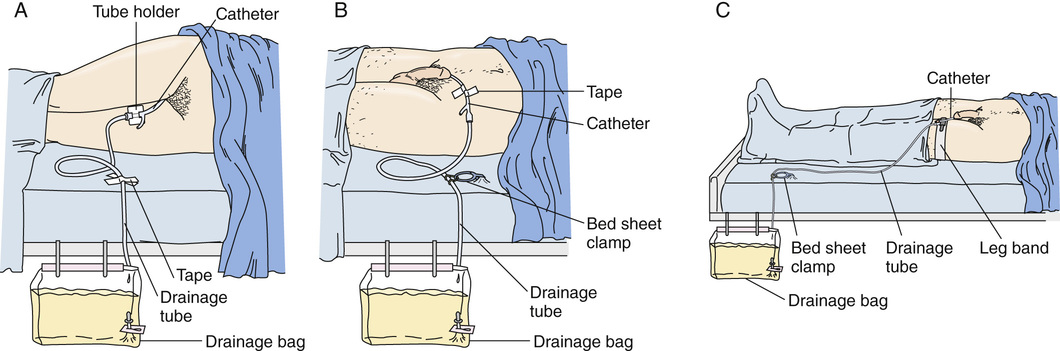
A closed drainage system is used for indwelling catheters. Only urine should enter the system from the catheter to the urine drainage bag. The urinary system is sterile. Infection can occur if microbes enter the drainage system. The microbes travel up the tubing or catheter into the bladder and kidneys. A UTI can threaten health and life. See Box 25-1 to prevent infection and for proper care of the drainage system.
There are 2 types of urine drainage bags.
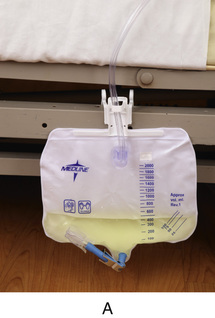
• Standard drainage bags usually hold at least 2000 mL (milliliters) of urine.
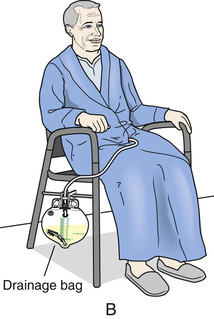
• Leg bags attach to the thigh or calf with elastic bands or Velcro (p. 418). Leg bags hold less than 1000 mL of urine. Some people wear leg bags when up.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree