1. Differentiate among the types of viral hepatitis, including etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, and collaborative care. 2. Describe the nursing management of the patient with viral hepatitis. 3. Describe the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, and collaborative care of the patient with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. 4. Explain the etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, collaborative care, and nursing management of the patient with cirrhosis of the liver. 5. Describe the clinical manifestations and management of liver cancer. 6. Differentiate between acute and chronic pancreatitis related to pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, collaborative care, and nursing management. 7. Explain the clinical manifestations, collaborative care, and nursing management of the patient with pancreatic cancer. 8. Describe the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, and collaborative care of gallbladder disorders. 9. Describe the nursing management of the patient undergoing surgical treatment of cholecystitis and cholelithiasis. 1. Maintains weight appropriate for height 2. Maintains food and fluid intake adequate to meet nutritional needs 1. Demonstrates gradual increase in activity tolerance 2. Reports ability to perform daily activities with scheduled rest periods Maintains liver function throughout infectious process adequate to meet physiologic needs Maintains skin integrity with relief of edema and pruritus 1. Experiences normalization of fluid balance as a result of medical and nursing interventions 2. Maintains blood pressure and urinary output within normal limits 1. Family confronts problems and involves family members in decision making 2. Family uses available social support for treatment of alcohol abuse **Outcomes and interventions for this nursing diagnosis for the patient with cirrhosis are presented in eNCP 44-1,the Patient With Acute Viral Hepatitis. Maintains fluid and electrolyte balance within normal limits Maintains normal electrolyte balance 1. Reports adequate pain control 2. Uses nondrug techniques of pain management to reduce need for pain medication
Nursing Management
Liver, Pancreas, and Biliary Tract Problems
![]() eNursing Care Plan 44-1 Patient With Acute Viral Hepatitis
eNursing Care Plan 44-1 Patient With Acute Viral Hepatitis
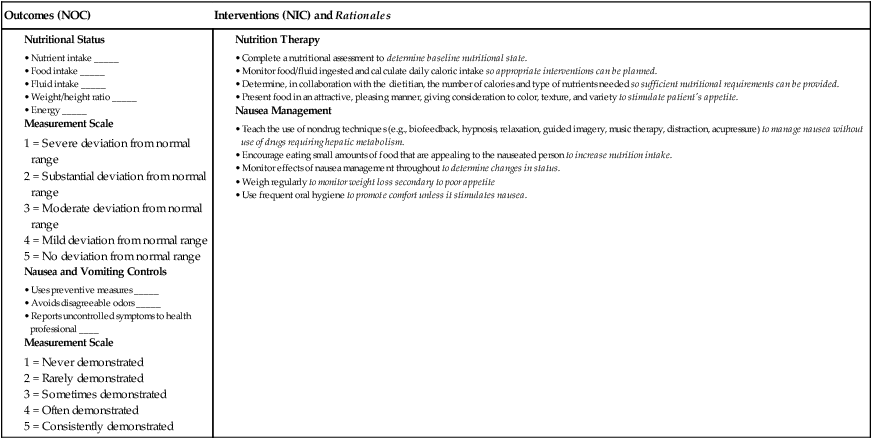
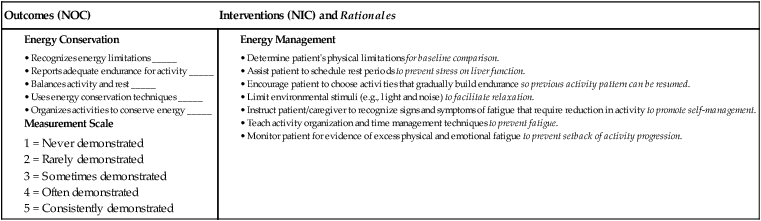

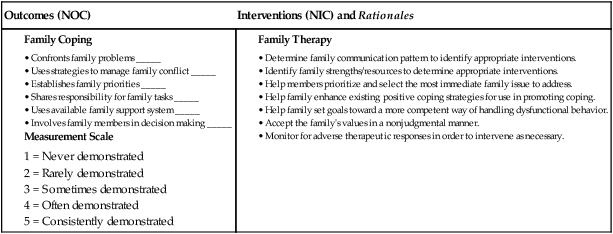
![]() eNursing Care Plan 44-2 Patient With Cirrhosis
eNursing Care Plan 44-2 Patient With Cirrhosis
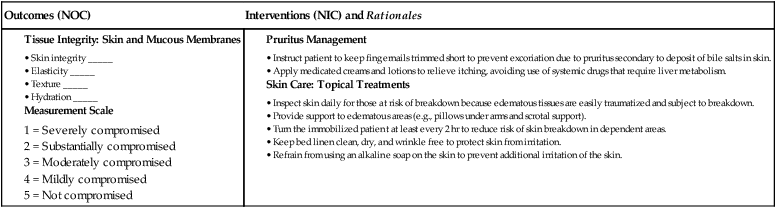
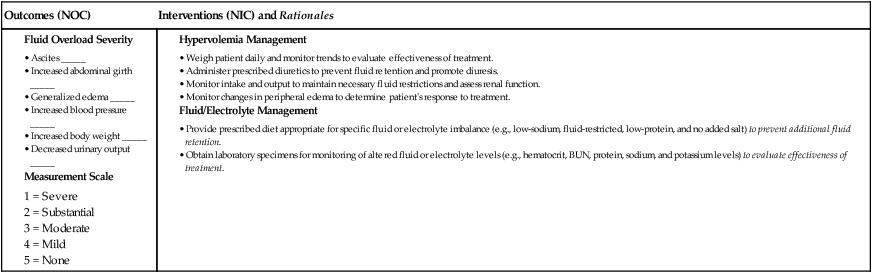
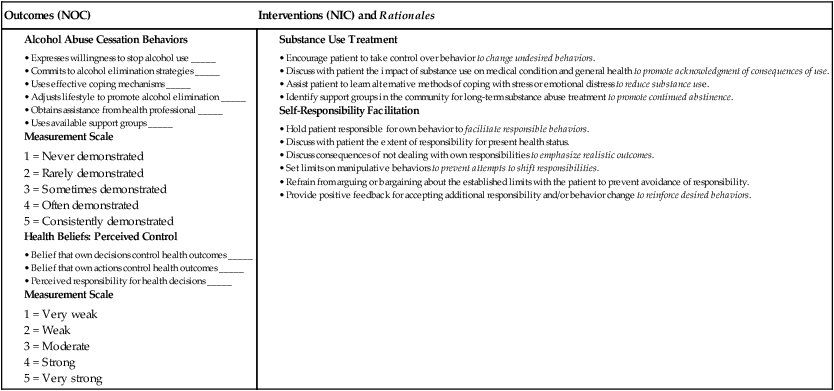


![]() eNursing Care Plan 44-3 Patient With Acute Pancreatitis
eNursing Care Plan 44-3 Patient With Acute Pancreatitis


Nursing Management: Liver, Pancreas, and Biliary Tract Problems
1. Differentiate among the types of viral hepatitis, including etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, and collaborative care. 2. Describe the nursing management of the patient with viral hepatitis. 3. Describe the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, and collaborative care of the patient with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. 4. Explain the etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, collaborative care, and nursing management of the patient with cirrhosis of the liver. 5. Describe the clinical manifestations and management of liver cancer. 6. Differentiate between acute and chronic pancreatitis related to pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, collaborative care, and nursing management. 7. Explain the clinical manifestations, collaborative care, and nursing management of the patient with pancreatic cancer. 8. Describe the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, complications, and collaborative care of gallbladder disorders. 9. Describe the nursing management of the patient undergoing surgical treatment of cholecystitis and cholelithiasis.
Nursing Management
Liver, Pancreas, and Biliary Tract Problems



