Chapter 5
Hospital Billing Process
1. Define terms, phrases, abbreviations, and acronyms.
2. Demonstrate an understanding of the billing process and its purpose.
3. Discuss the key provisions of participating provider agreements (PAR).
4. Identify variations in claim requirements by payer type and type of service.
5. Explain the difference between traditional, fixed, and Prospective Payment Systems (PPS) reimbursement methods.
6. Discuss the content and purpose of the Charge Description Master (CDM).
7. Differentiate between coding systems required for outpatient services versus inpatient services.
8. Discuss the purpose of the detailed itemized statement and how it relates to the claim form.
9. Explain the difference between a clean and dirty claim, and discuss the importance of submitting a clean claim.
10. Explain the significance of accounts receivable (AR) management.
11. Demonstrate an understanding of phases of the hospital revenue cycle.
Accounts receivable (A/R) management
Ambulatory Payment Classifications (APC)
Charge Description Master (CDM)
Electronic data interchange (EDI)
Inpatient Prospective Payment System (IPPS)
Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Groups (MS-DRG)
Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS)
Participating provider agreement
Prospective Payment Systems (PPS)
Resource-Based Relative Value Scale (RBRVS)
American National Standards Institute
Ambulatory Payment Classifications
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
Health Care Financing Administration
Health Care Common Procedure Coding System
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification
International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Procedure Coding System
Inpatient Prospective Payment System
Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Groups
National Uniform Billing Committee
Outpatient Prospective Payment System
Resource Based Relative Value Scale
Usual, customary, and reasonable
The role of hospital billing and coding professionals is complicated because of the ever-changing health insurance environment and variations in payer guidelines. It is essential for billing and coding professionals to understand payer guidelines to ensure that accurate reimbursement is obtained and to ensure compliance with payer guidelines. A review of several provisions of the participating provider agreement (PAR) “payer contract” will illustrate how payer guidelines vary and the significant impact they have on the billing process. A discussion of how charges are captured, coding systems, and claim forms will provide a basis for understanding the billing process. The chapter will close with an overview of the hospital revenue cycle from patient admission to collections. Many of the concepts presented in this chapter are presented to provide an overview of the hospital billing process. These concepts will be expanded upon in future chapters.
Purpose of the Billing Process
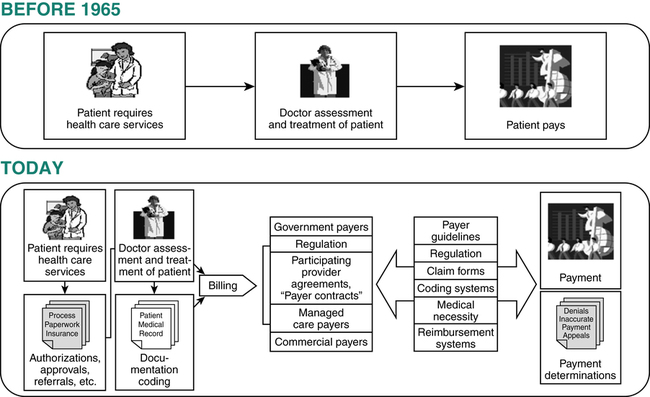
The complexity of the hospital billing process is a result of the health care industry’s evolution. Health insurance and government-funded health care benefit programs were born. Regulation of the health care industry was enhanced. Contracts between providers and payers were initiated. The process of submitting charges became more involved. It now involves authorizations and certifications, medical record documentation, coding, participating provider agreements, various payer guidelines, and different reimbursement systems (Figure 5-1). The complexity of this system makes it essential for hospital billing and coding professionals to have knowledge of key elements of the billing process to ensure that appropriate reimbursement is obtained and compliance with payer guidelines. This section will discuss key elements: payer guidelines, Charge Description Master, coding systems, and universally accepted claims forms.
Payer Guidelines
Participating Provider Agreement (PAR)
The hospital’s payer mix includes various payers that provide coverage to patients seen at the hospital. Medicare, Medicaid, TRICARE, Blue Cross/Blue Shield, Worker’s Compensation, and various managed care plans are generally part of the hospital’s payer mix. Hospitals and other providers may elect to enter into a written agreement to participate with payers, known as the participating provider agreement. A participating provider agreement (PAR) is a written agreement between the hospital and a payer that outlines the terms and conditions of participation for the hospital and the payer. Figures 5-2 and 5-3 highlight common provisions related to patient care services, patient financial responsibility, billing requirements, and reimbursement as outlined below.
Charge Submission Requirements
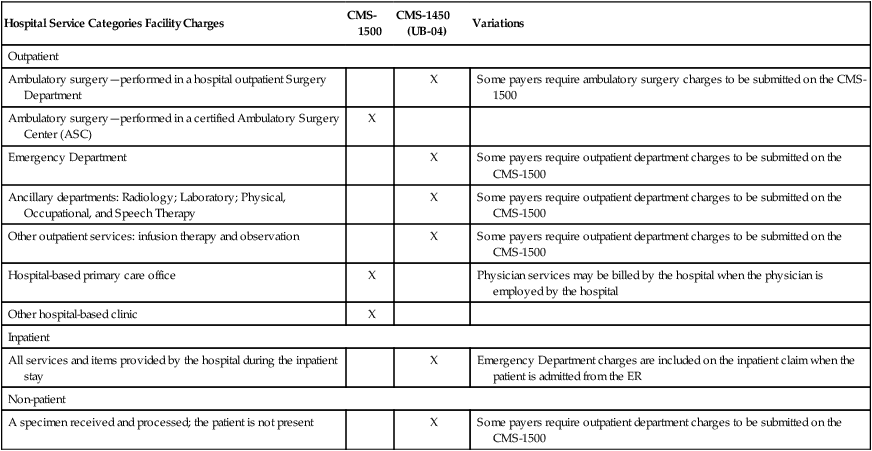
Claim form requirements vary by payer, and the participating provider agreement defines what claim form should be used to submit charges. Some payers define claim form requirements based on the part of the plan that covers specific services. For example, the CMS-1450 (UB-04) is used to submit charges covered under Medicare Part A. The CMS-1500 is used to submit charges covered under Medicare Part B. Durable medical equipment is covered under Medicare Part B; therefore, charges for these items are generally submitted on the CMS-1500. Claim form submission requirements also vary based on the following service categories: outpatient, inpatient, and non-patient. The following section provides an overview of the claim form required for these service categories, as shown in Table 5-1. Claim forms will be discussed further in the Claim Forms chapter.
TABLE 5-1
| Hospital Service Categories Facility Charges | CMS-1500 | CMS-1450 (UB-04) | Variations |
| Outpatient | |||
| Ambulatory surgery—performed in a hospital outpatient Surgery Department | X | Some payers require ambulatory surgery charges to be submitted on the CMS-1500 | |
| Ambulatory surgery—performed in a certified Ambulatory Surgery Center (ASC) | X | ||
| Emergency Department | X | Some payers require outpatient department charges to be submitted on the CMS-1500 | |
| Ancillary departments: Radiology; Laboratory; Physical, Occupational, and Speech Therapy | X | Some payers require outpatient department charges to be submitted on the CMS-1500 | |
| Other outpatient services: infusion therapy and observation | X | Some payers require outpatient department charges to be submitted on the CMS-1500 | |
| Hospital-based primary care office | X | Physician services may be billed by the hospital when the physician is employed by the hospital | |
| Other hospital-based clinic | X | ||
| Inpatient | |||
| All services and items provided by the hospital during the inpatient stay | X | Emergency Department charges are included on the inpatient claim when the patient is admitted from the ER | |
| Non-patient | |||
| A specimen received and processed; the patient is not present | X | Some payers require outpatient department charges to be submitted on the CMS-1500 | |
CMS-1450 (UB-04) is used to submit charges to Medicare Part A.
Electronic Claims
In accordance with HIPAA regulations, standard formats for electronic transactions, including submission of claims, have been adopted. The standard formats adopted were developed by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). The standard transaction format for the CMS-1500 is the ANSI X12 837 and the format for the CMS-1450 (UB-04) is the ANSI X12 837I. The standard transaction formats contain elements found on the CMS-1500 and CMS-1450 (UB-04) paper claims. The current standard format, Version 5010, was adopted and the compliance date for all HIPAA covered entities to transition to Version 5010 was January 1, 2012. Details regarding Version 5010 can be viewed on the CMS Web site at http://www.cms.gov/ICD10/11a_Version_5010.asp#TopOfPage.
Reimbursement Methods
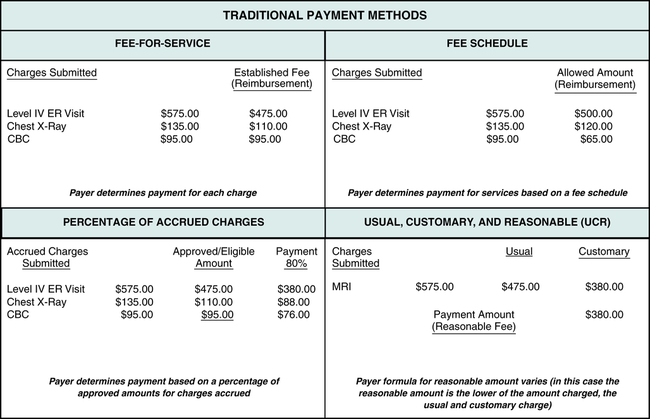
Traditional Payment Methods
• Fee-for-Service is a reimbursement method that provides payment for hospital services based on an established fee schedule for each service.
• Fee Schedule is a listing of established, allowed amounts for specific medical services and procedures.
• Percentage of Accrued Charges is a reimbursement method that calculates payment for charges accrued during a hospital stay based on a percentage of accrued charges.
• Usual, Customary, and Reasonable (UCR) is based on a review of the usual and customary fee to determine the fee that is considered reasonable.
Figure 5-4 illustrates examples of payment calculations using traditional payment methods—fee-for-service, percentage of accrued charges, fee schedule, and usual, customary, and reasonable (UCR).
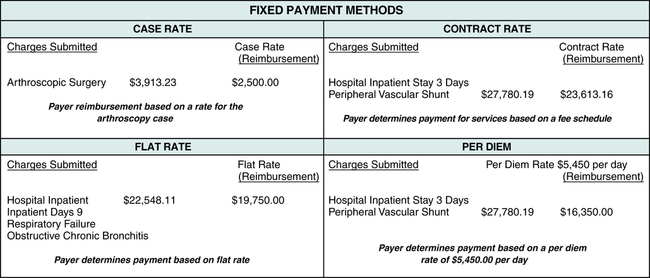
Fixed Payment Methods
Capitation is a reimbursement method that provides payment of a fixed amount, paid per member per month. Capitation methods are generally used to provide reimbursement for primary care physician services and other specified outpatient services provided to managed care plan members.
Case Rate is a set payment rate paid to the hospital for the case. The payment rate is based on the type of case and resources required to treat the patient.
Contract Rate is a set payment rate as agreed to in a contract between the hospital and the payer.
Flat Rate is a set payment rate for the hospital admission regardless of charges accrued.
Per Diem is a set payment rate per day rather than payment based on the total of accrued charges.
Relative Value Scale (RVS) assigns a relative value that represents work, practice expense, and the cost of malpractice insurance to each professional service code.
Figure 5-5 illustrates examples of some of the most common fixed payment methods used to reimburse hospitals for services (case rate, contract rate, flat rate, and per diem).
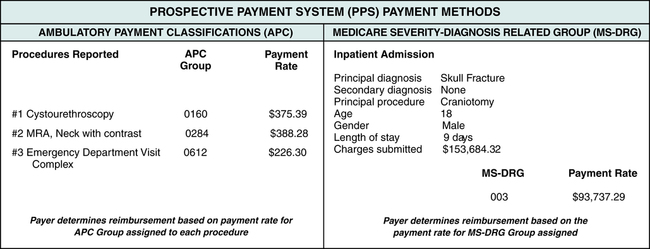
Prospective Payment Systems (PPS)
Ambulatory Payment Classifications (APC)
PPS methods were implemented to provide pre-established payment amounts for reimbursement to providers for services rendered to members of government health care programs. Figure 5-6 illustrates payment determination based on the MS-DRG and APC reimbursement systems. PPS will be discussed further in the Prospective Payment Systems (PPS) chapter.
Reimbursement Method Variations
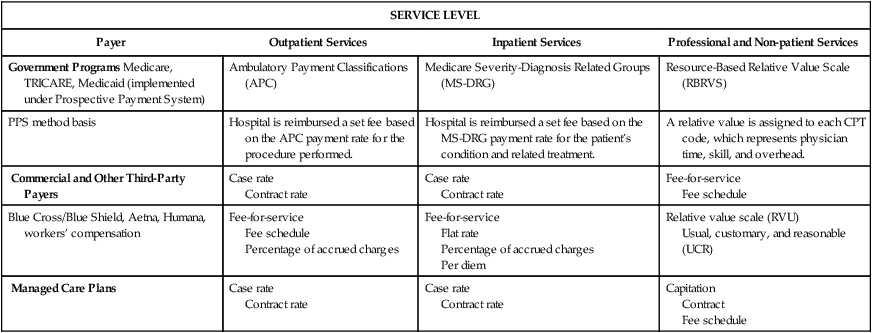
It is also important to understand guidelines relating to each of the different payment methods by payer type. Three major categories of third-party payers are government programs, commercial payers, and managed care plans. Each of the payer types listed uses various methods of reimbursement for outpatient, inpatient, non-patient, and professional services. Some of the most common reimbursement methods used by government programs, commercial payers, and managed care plans are outlined in Table 5-2 for outpatient, inpatient, non-patient, and professional services. It is important to note that many commercial and managed care payers are adopting prospective payment reimbursement methods, such as APC and MS-DRG, as a part of their contract rates. Reimbursement methods will be discussed further as they relate to each of the payer categories later in this text.
TABLE 5-2
Reimbursement Method Variations
| SERVICE LEVEL | |||
| Payer | Outpatient Services | Inpatient Services | Professional and Non-patient Services |
| Government Programs Medicare, TRICARE, Medicaid (implemented under Prospective Payment System) | Ambulatory Payment Classifications (APC) | Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Groups (MS-DRG) | Resource-Based Relative Value Scale (RBRVS) |
| PPS method basis | Hospital is reimbursed a set fee based on the APC payment rate for the procedure performed. | Hospital is reimbursed a set fee based on the MS-DRG payment rate for the patient’s condition and related treatment. | A relative value is assigned to each CPT code, which represents physician time, skill, and overhead. |
| Commercial and Other Third-Party Payers | Case rate Contract rate | Case rate Contract rate | Fee-for-service Fee schedule |
| Blue Cross/Blue Shield, Aetna, Humana, workers’ compensation | Fee-for-service Fee schedule Percentage of accrued charges | Fee-for-service Flat rate Percentage of accrued charges Per diem | Relative value scale (RVU) Usual, customary, and reasonable (UCR) |
| Managed Care Plans | Case rate Contract rate | Case rate Contract rate | Capitation Contract Fee schedule |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree