Chapter 8
Procedure Coding (HCPCS and ICD-10-PCS)
1. Define terms, phrases, abbreviations, and acronyms.
2. Demonstrate an understanding of the history and purpose of procedure coding systems.
3. Discuss how procedure coding data are used for research, education, and administrative purposes.
4. Provide an explanation of the relationship between procedure coding and documentation, medical necessity, claim forms, and reimbursement.
5. Discuss the relationship between procedure coding and diagnosis coding.
6. Identify variations in the use of coding systems for outpatient, non-patient, and inpatient services.
7. Outline the standard code set requirements for reporting procedures under HIPAA.
8. List the two levels of HCPCS and discuss the content of each system.
9. Explain the reasons why ICD-10 was implemented and discuss the transition to ICD-10.
10. Outline the content of the ICD-10-PCS coding system.
11. Demonstrate an understanding of the steps to coding using the HCPCS and ICD-10-PCS procedure coding systems and basic coding principles.
Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS)
Local Coverage Determinations (LCD)
Local Medical Review Policy (LMRP)
National Coverage Determinations (NCD)
American Academy of Professional Coders
American Health Information Management Association
Ambulatory Payment Classifications
Center for Disease Control and Prevention
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
Current Procedural Terminology
Health Care Financing Administration
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification
International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification
International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Procedure Coding System
Medicare Administrative Contractor
Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Groups
National Coverage Determinations
National Center for Health Statistics
National Uniform Billing Committee
Hospital coding and billing professionals are required to have an understanding of the ICD-9-CM coding system and will need to transition to ICD-10. In an effort provide current and future knowledge required for hospital professionals, this text presents concepts on coding using ICD-9-CM and ICD-10. The prior chapters presented concepts regarding coding medical conditions and significant procedures using ICD-9-CM. This chapter will focus on coding procedures, services, and items using HCPCS and the ICD-10-PCS coding system. A discussion of the history and purpose of procedure coding will highlight the importance of procedure coding in the health care industry. A brief review of how procedure coding relates to documentation, medical necessity, claim forms, reimbursement, and diagnosis coding will further demonstrate the importance of procedure coding. Variations in coding system utilization are outlined to illustrate appropriate code usage for outpatient, non-patient, and inpatient services. The content, format, and conventions of the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) and the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) is reviewed to provide an overview of coding using these systems. The chapter will close with a discussion of the basic steps to coding using HCPCS and ICD-10-PCS codes.
History of Procedure Coding
The classification and coding of procedures, services, and items constitute a newer development than the coding of conditions, which began in the 17th century. Procedure coding systems were developed in the 1960s to provide a standardized system for providers to report procedures to third-party payers for reimbursement. The system also allows for collection of data to be used for statistical purposes. Historically, physicians and other providers submitted a written description of procedures and services rendered on the claim form to explain charges. Payers experienced difficulty in processing claims submitted with the written descriptions. Additionally, tracking, monitoring, and statistical analysis using the written descriptions was a very complex process. The need for a standardized system of reporting procedures and services was first addressed when the American Medical Association (AMA) developed the Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) coding system. Other procedure coding systems were later introduced such as HCPCS Medicare National Codes and the International Classifications of Diseases (ICD) Procedure Coding System, as illustrated in Figure 8-1.
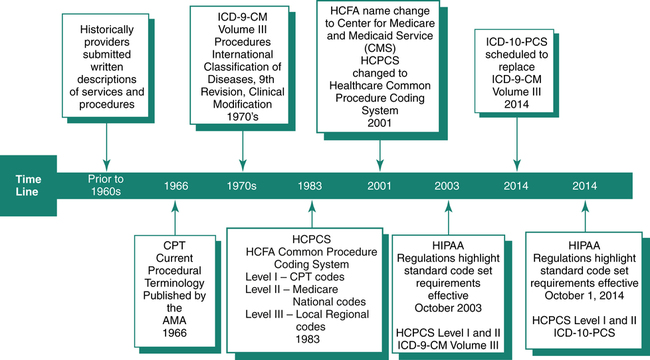
Legislative intervention, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996, laid the foundation for the standardization of transactions. HIPAA regulations highlighted standard procedure code sets required for submission of claims to payers effective October 2003 as the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) for reporting services, procedures, and items and the International Classifications of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) for coding patient conditions and significant procedures. In accordance with HIPAA provisions, effective October 1, 2014, the standard code set for reporting hospital diagnoses and procedure will be Heath Care Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS), National Drug Codes (NDC), and the International Classifications of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10), as illustrated in Figure 8-2.
Development of ICD-10
• The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) diagnosis coding system is the system scheduled to replace ICD-9-CM Volumes I-II for coding patient conditions (reasons for health services) in all health care settings. ICD-10-CM is the clinical modification of the World Health Organization’s ICD-10.
• The International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) is the procedure coding system scheduled to replace ICD-9-CM Volume III in accordance with HIPAA provisions. The ICD-10-PCS was developed by 3M Health Information System under contract with CMS.
• Completeness – a unique code should be created for all procedures that are substantially different.
• Expansion – the system should allow codes to be added as new procedures are developed.
• Multiaxial – codes contain characters that are independent with each individual component axis retaining its meaning across broad ranges of codes.
• Standardized terminology – the system should not include multiple meanings for terms. Each term should have a specific meaning.
Other principals followed in the development of ICD-10-PCS:
• Diagnostic information is not included in procedure descriptions.
• Not otherwise specified (NOS) options are restricted.
• Limited use of not elsewhere classified (NEC) option.
• Level of specificity for procedures performed today is included.
Differences ICD-9-CM Volume III versus ICD-10-PCS
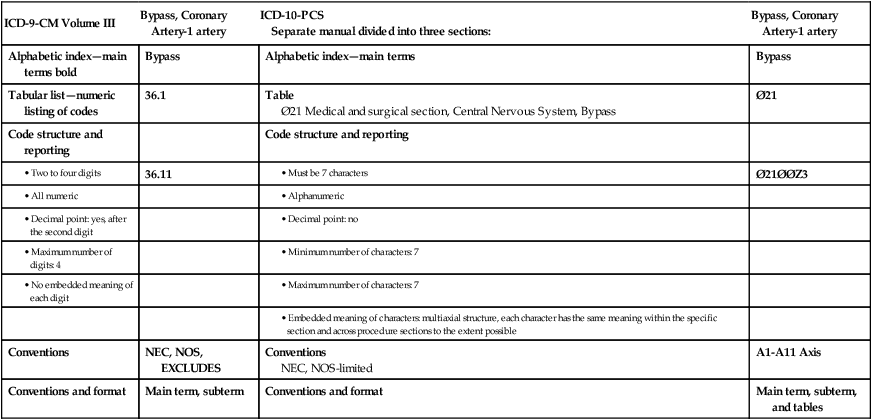
A significant difference between ICD-9-CM Volume III and ICD-10-PCS is the manual content and the code format. The indexes contained in both systems outline procedures alphabetically by main term and subterms. Codes are listed in the index to provide direction to the appropriate code section. The tabular list in ICD-9-CM Volume III is a numeric list of codes. ICD-10-PCS provides alphanumeric tables that are used to construct a valid code. A valid code in ICD-9-CM Volume III is 2 to 4 digits. A valid code in ICD-10-PCS is 7 alphanumeric characters. Table 8-1 illustrates some of the differences between ICD-9-CM Volume III and ICD-10-PCS.
TABLE 8-1
Differences in ICD-9-CM Volume III versus ICD-10-PCS
| ICD-9-CM Volume III | Bypass, Coronary Artery-1 artery | ICD-10-PCS Separate manual divided into three sections: | Bypass, Coronary Artery-1 artery |
| Alphabetic index—main terms bold | Bypass | Alphabetic index—main terms | Bypass |
| Tabular list—numeric listing of codes | 36.1 | Table Ø21 Medical and surgical section, Central Nervous System, Bypass | Ø21 |
| Code structure and reporting | Code structure and reporting | ||
| 36.11 | Ø21ØØZ3 | ||
| Conventions | NEC, NOS, EXCLUDES | Conventions NEC, NOS-limited | A1-A11 Axis |
| Conventions and format | Main term, subterm | Conventions and format | Main term, subterm, and tables |
(Data from Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Web site, ICD-10 Development, https://www.cms.gov/ICD10/.)
Procedure Coding Defined
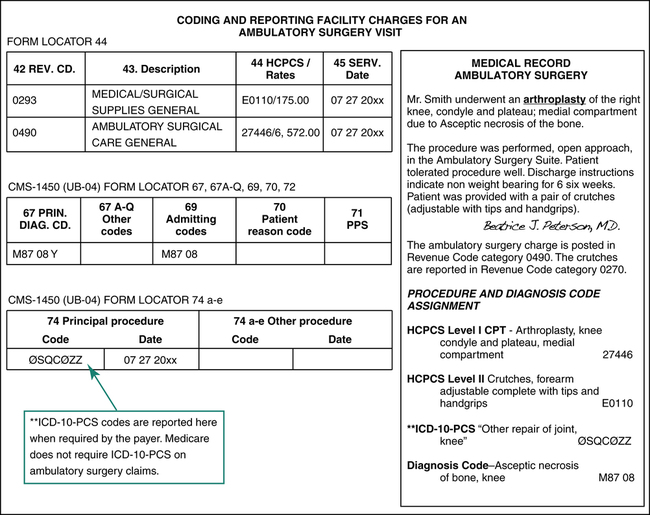
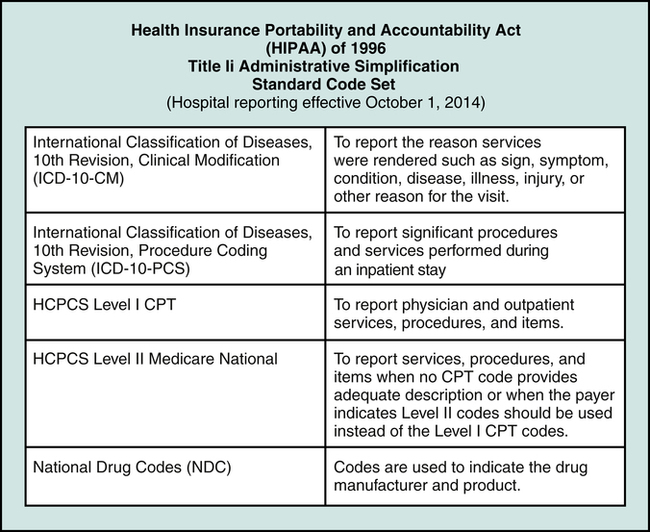
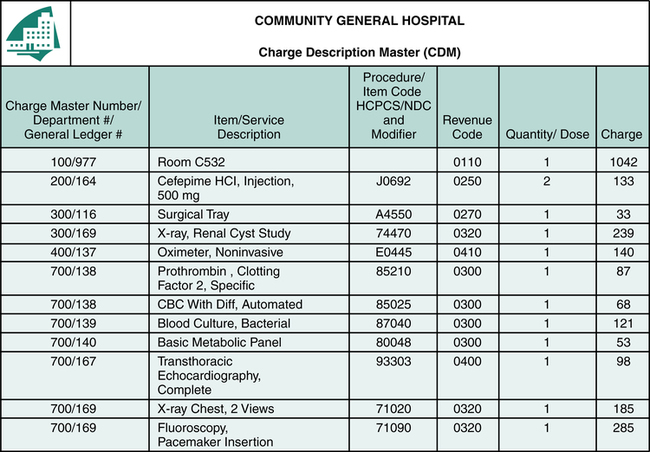
The definition of coding is the assignment of numeric or alphanumeric codes to all health care data elements of outpatient and inpatient care. Procedure coding is the process of translating written descriptions of procedures, services, and items documented in the patient’s medical record into numeric or alphanumeric codes. Procedure coding is an essential component of the billing process (Figure 8-3). The description of procedures, services, and items provided during a hospital visit is communicated to payers using procedure coding systems. The process begins when the patient presents at the hospital with a health care issue that requires attention, or for a service that involves health care status. The physician or other provider reviews the history, performs an examination, and prepares a plan of care. Patient care services are rendered in accordance with physician’s orders and the plan of care. Written descriptions of health care services, procedures, and items are documented in the patient’s medical record. Charges are posted by various departments through the Charge Description Master (CDM), also called the chargemaster. All procedures, services, and items listed in the chargemaster are associated with a code from the appropriate procedure coding system (Figure 8-4). Heath Information Management (HIM) personnel are responsible for coding patient conditions and significant procedures documented in the patient medical record that are not posted through the chargemaster.
Procedure Code Data Usage
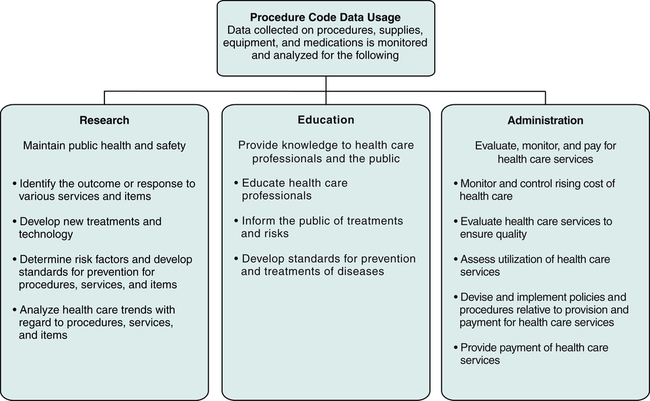
Procedure coding systems allow for the collection of data regarding procedures and services performed and the various items used to diagnose and treat patient conditions. The data gathered through the use of these coding systems can be monitored, tracked, and retrieved for various purposes such as research, education, and administration, as illustrated in Figure 8-5.
Procedure Coding Relationships
Procedure coding relates to all aspects of the billing process. The process of procedure coding is dependent on information documented in the medical record. Charges for services are described on the claim form using procedure codes. Payers conduct medical necessity reviews and payment determination based on the procedure and diagnosis codes submitted. In essence, procedure coding is the key to obtaining reimbursement for services rendered. It is important for hospital coding and billing professionals to understand how procedure coding relates to documentation, medical necessity, claim forms, and reimbursement, as illustrated in Figure 8-6.
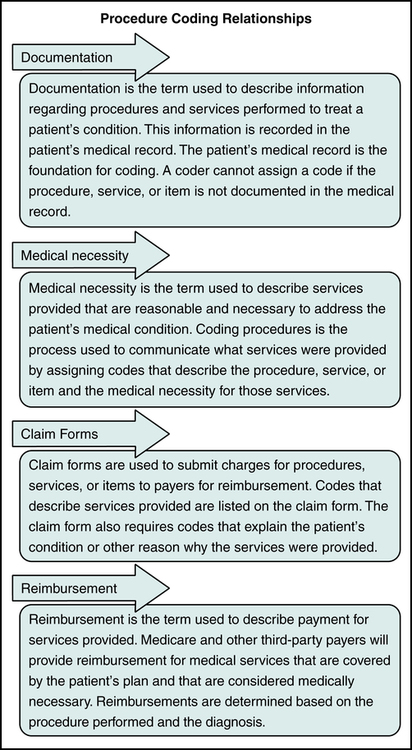
Documentation
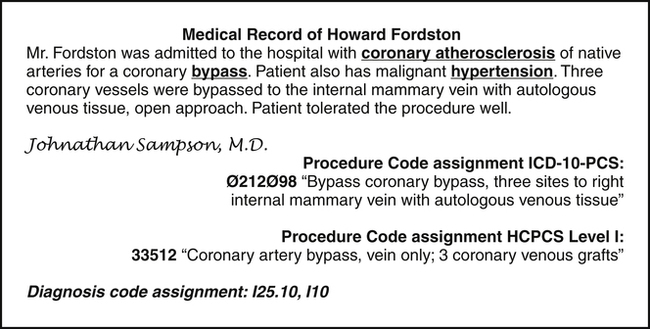
Documentation is the term used to describe information recorded in the medical record regarding patient conditions, procedures, services, supplies, equipment, and medications provided as part of the patient’s care. The patient’s medical record is the foundation for coding. When coding procedures, services, and items it is necessary to read the record to identify the service or item that must be coded for billing purposes. A code from HCPCS or ICD-10-PCS is assigned to accurately describe the service or item documented in the medical record. Figure 8-7 illustrates an example showing the assignment of HCPCS Level I and ICD-10-PCS procedure codes to describe a coronary bypass procedure performed during the hospital inpatient stay.
Medical Necessity
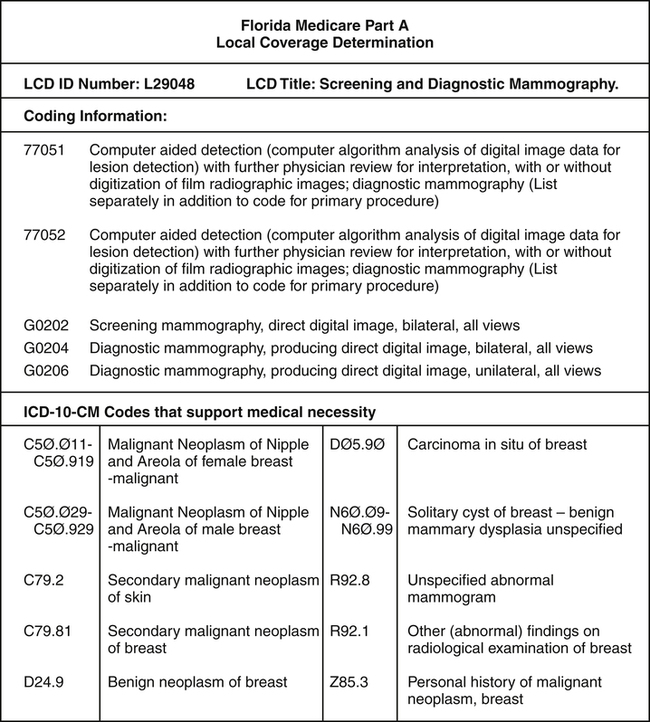
It is critical for coders to review LCD policies to understand medical necessity requirements for services, procedures, and items. Payers will not provide reimbursement for services that are not medically necessary. It is also critical for coders to understand coding and payer specific guidelines. Figure 8-8 illustrates the Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for mammography. NCD policies can be found on the CMS Web site at https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database.
Claim Forms
CMS-1450 (UB-04)
The fields used to record diagnosis and procedure codes on the CMS-1450 (UB-04) are highlighted in Figure 8-9. Procedure codes are reported on the claim form in FL 44 and FL 74a-e. Diagnosis codes that describe the medical reason for services are reported in FL 67A-Q, 69, 70, and 72. HCPCS Level I and II codes are reported in FL 44 in accordance with payer guidelines. ICD-10-PCS codes are recorded in FL 74a-e to describe significant procedures performed during an inpatient stay.
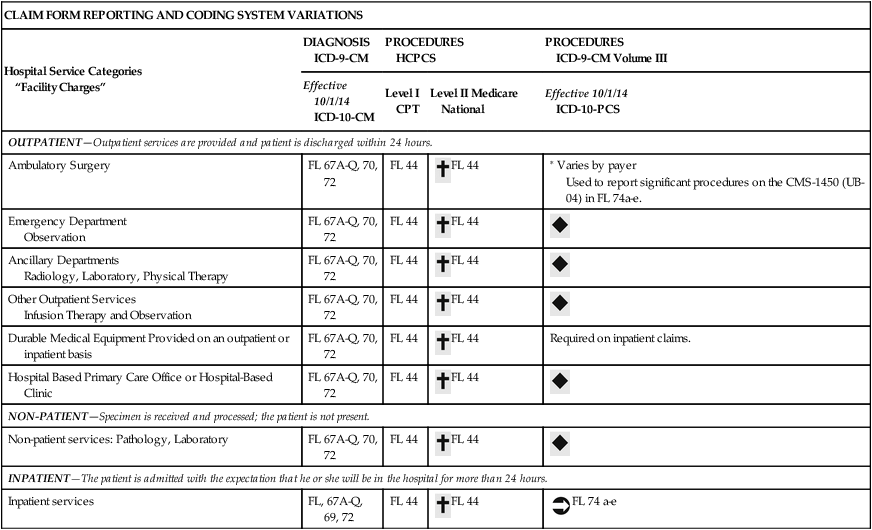
Procedure Coding System Variations
Procedure coding systems are used to communicate with payers regarding services, procedures, and items provided for the purpose of obtaining reimbursement. As discussed in previous chapters, the ICD-9-CM diagnosis coding system is currently used to report the medical reason why services, procedures, and items are provided. The ICD-10-CM diagnosis coding system will replace ICD-9-CM effective October 1, 2014. The chapters also highlighted coding system variations based on service category, which illustrates diagnosis coding systems used for all service categories as illustrated in Table 8-2. Unlike diagnosis code usage, procedure code utilization varies by service category. Service categories include outpatient, non-patient, and inpatient. The following section presents procedure coding system variations using HCPCS and ICD-10-PCS based on services provided on an outpatient, non-patient, or inpatient basis.
TABLE 8-2
CMS-1450 (UB-04) Claim Form Reporting of Coding Systems Based on the Level of Service
| CLAIM FORM REPORTING AND CODING SYSTEM VARIATIONS | ||||
| Hospital Service Categories “Facility Charges” | DIAGNOSIS ICD-9-CM | PROCEDURES HCPCS | PROCEDURES ICD-9-CM Volume III | |
| Effective 10/1/14 ICD-10-CM | Level I CPT | Level II Medicare National | Effective 10/1/14 ICD-10-PCS | |
| OUTPATIENT—Outpatient services are provided and patient is discharged within 24 hours. | ||||
| Ambulatory Surgery | FL 67A-Q, 70, 72 | FL 44 |  FL 44 FL 44 | ∗ Varies by payer Used to report significant procedures on the CMS-1450 (UB-04) in FL 74a-e. |
| Emergency Department Observation | FL 67A-Q, 70, 72 | FL 44 |  FL 44 FL 44 |  |
| Ancillary Departments Radiology, Laboratory, Physical Therapy | FL 67A-Q, 70, 72 | FL 44 |  FL 44 FL 44 |  |
| Other Outpatient Services Infusion Therapy and Observation | FL 67A-Q, 70, 72 | FL 44 |  FL 44 FL 44 |  |
| Durable Medical Equipment Provided on an outpatient or inpatient basis | FL 67A-Q, 70, 72 | FL 44 |  FL 44 FL 44 | Required on inpatient claims. |
| Hospital Based Primary Care Office or Hospital-Based Clinic | FL 67A-Q, 70, 72 | FL 44 |  FL 44 FL 44 |  |
| NON-PATIENT—Specimen is received and processed; the patient is not present. | ||||
| Non-patient services: Pathology, Laboratory | FL 67A-Q, 70, 72 | FL 44 |  FL 44 FL 44 |  |
| INPATIENT—The patient is admitted with the expectation that he or she will be in the hospital for more than 24 hours. | ||||
| Inpatient services | FL, 67A-Q, 69, 72 | FL 44 |  FL 44 FL 44 |  FL 74 a-e FL 74 a-e |
∗Some payers may require on ambulatory surgery claims.
 Not required on outpatient and non-patient claims.
Not required on outpatient and non-patient claims.
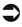 Used to report significant procedures on the CMS-1450 (UB-04) in FL 74 a-e.
Used to report significant procedures on the CMS-1450 (UB-04) in FL 74 a-e.
Outpatient Services
Outpatient procedures, services, or items are recorded in the patient’s medical record. Charges are posted through the chargemaster by the departments involved in the patient’s care. The Health Information Management Department (HIM) receives the medical record after the patient is discharged. HIM personnel assign codes for patient diagnoses and procedures that are not posted through the chargemaster. The procedure and diagnosis codes are used for the appropriate Ambulatory Payment Classification (APC) assignment. It is important to remember hospital services that are considered outpatient services, which include emergency room, observation, ambulatory surgery, and a hospital-based primary care clinic visit. The reporting of diagnosis and procedure codes for an ambulatory surgery case on CMS-1450 (UB-04) is illustrated in Figure 8-10.
Non-Patient Services
Non-patient services are those involving tests or procedures performed on a specimen when the patient is not present. Laboratory testing on a specimen sent to the hospital from the physician’s office is an example of a non-patient service. Department personnel post non-patient services through the chargemaster. Non-patient services are coded using HCPCS Level I and Level II codes (Table 8-2). Most hospital non-patient services are submitted on the CMS-1450 (UB-04).
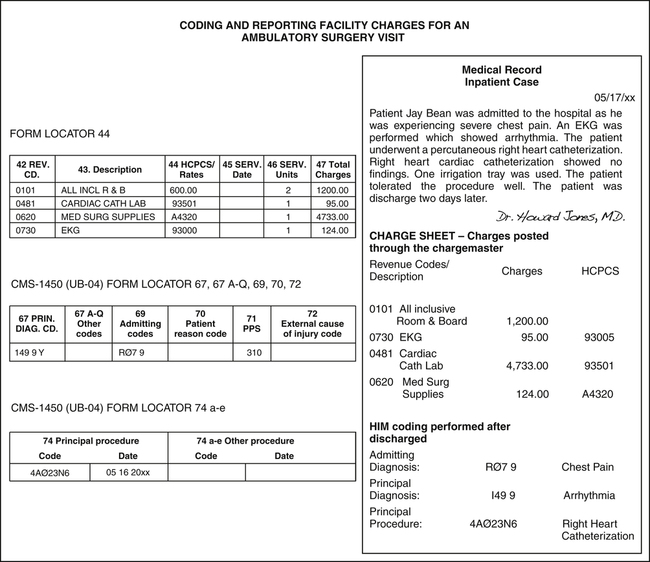
Inpatient Services
Other Procedures
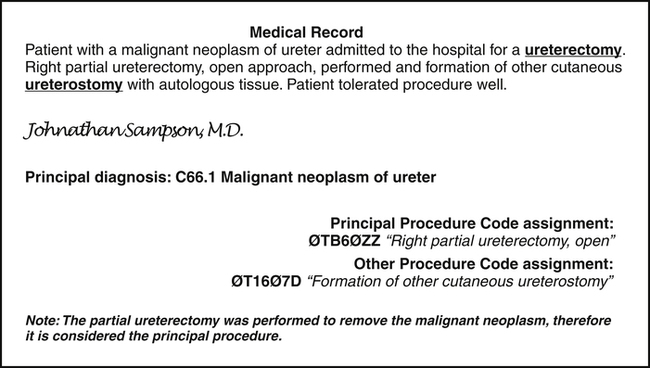
Other significant procedures performed during the stay are recorded in FL 74a-e as illustrated in Figure 8-11. It is important to remember that payers will compare the principal and other procedures codes with the principal and other diagnosis codes to determine medical necessity.
After the patient is discharged, the medical record is forwarded to HIM for coding of patient conditions and procedures not posted through the chargemaster. The principal diagnosis and procedure codes are used to determine the Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Groups (MS-DRG) assignment. Figure 8-12 illustrates an example of coding an inpatient case for reporting on the CMS-1450 (UB-04).



 Medicare National codes are used when a CPT code cannot be found that adequately describes the service or item or when the payer requires a Level II code.
Medicare National codes are used when a CPT code cannot be found that adequately describes the service or item or when the payer requires a Level II code.