Chapter 3
Health Promotion and Risk Factor Management Care Plans
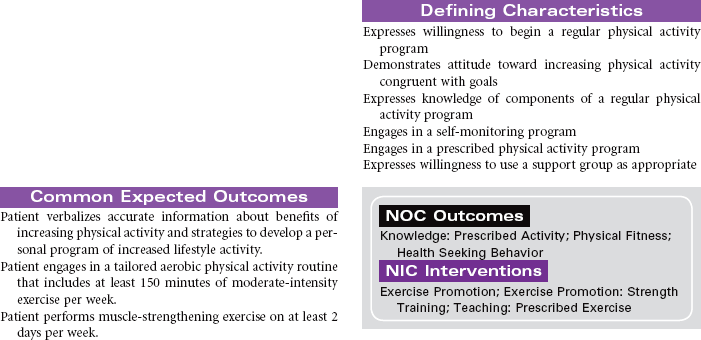
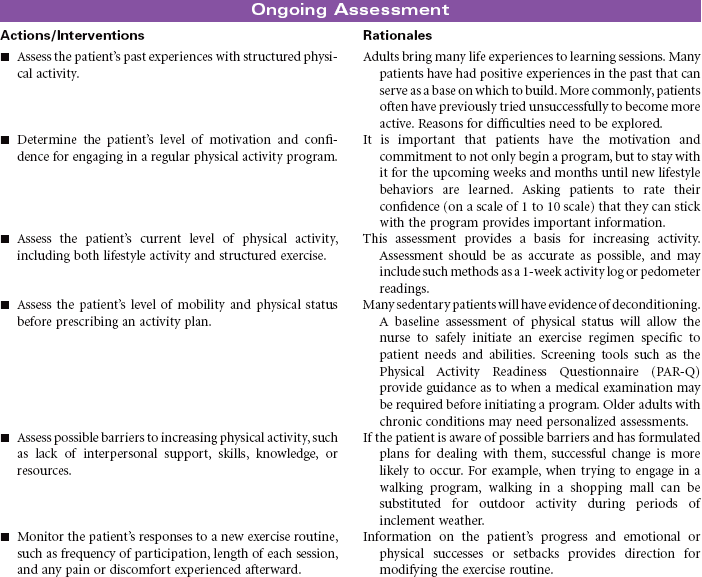
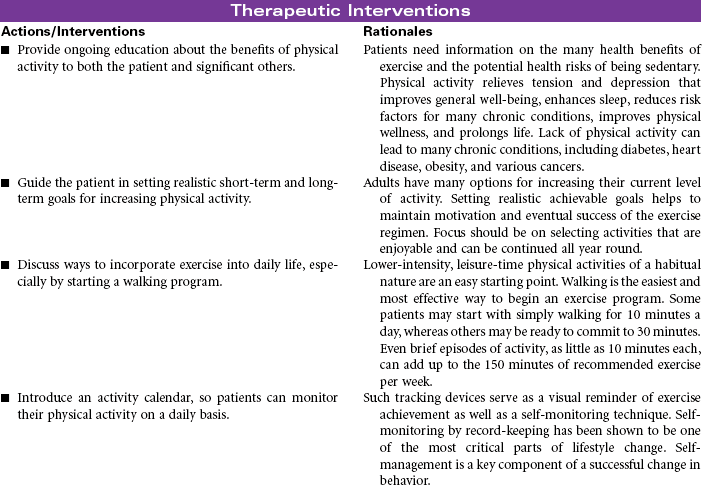
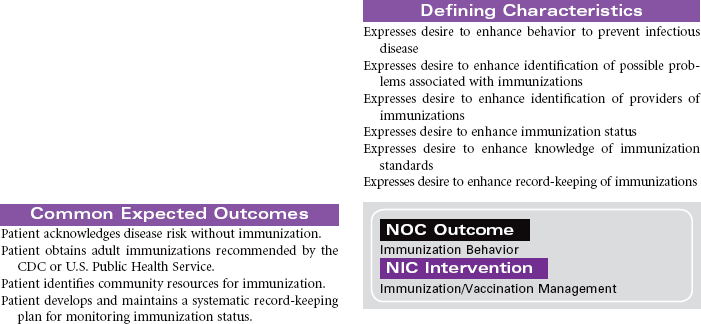
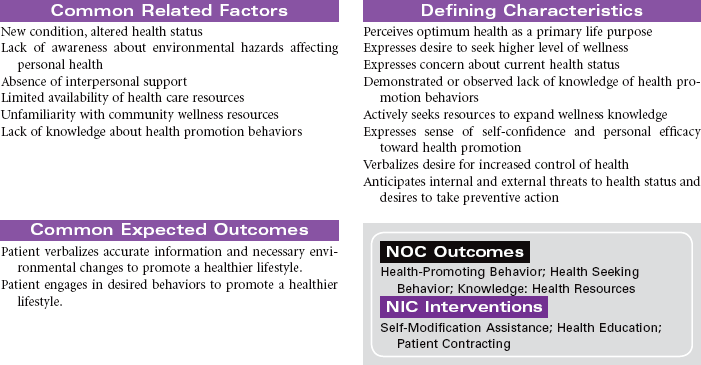
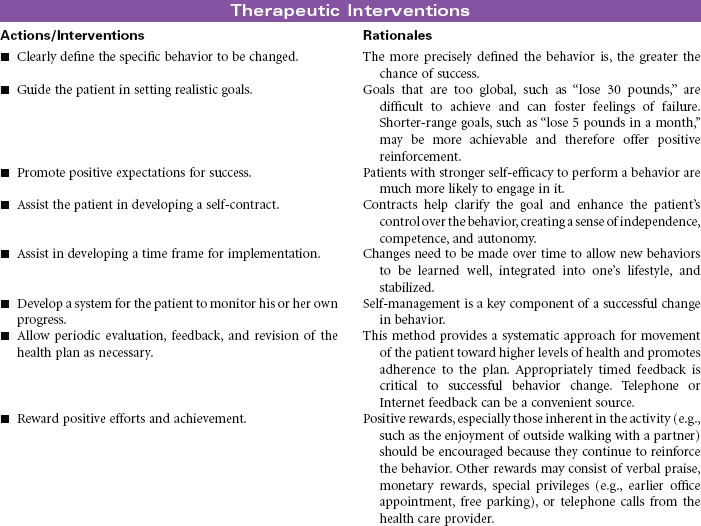
![]() Health-Seeking Behaviors
Health-Seeking Behaviors
![]() For additional care plans and an Online Care Plan Constructor, go to http://evolve.elsevier.com/Gulanick/.
For additional care plans and an Online Care Plan Constructor, go to http://evolve.elsevier.com/Gulanick/.



Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

 = Independent
= Independent  = Collaborative
= Collaborative