Chapter 3 Jennifer Saylor and Linda Bucher 1. Explain the purpose, components, and techniques related to a patient’s health history and physical examination. 2. Obtain a nursing history using a functional health pattern format. 3. Select appropriate techniques of inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation for physical examination of a patient. 4. Differentiate among comprehensive, focused, and emergency types of assessment in terms of indications, purposes, and components. You will obtain a patient’s health history and perform a physical examination during the assessment phase of the nursing process. The findings of your assessment (1) contribute to a database that identifies the patient’s current and past health status and (2) provide a baseline against which future changes can be evaluated. The purpose of the nursing assessment is to enable you to make clinical judgments or diagnoses about your patient’s health status.1 Assessment is identified as the first step of the nursing process, but it is performed continually throughout the nursing process to validate nursing diagnoses, evaluate nursing interventions, and determine whether patient outcomes and goals have been met. eTABLE 3-1 RECORDING FINDINGS OF A NORMAL PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF HEALTHY ADULT *These data would be obtained from an examination of the genitalia if the nurse has the appropriate education. eTABLE 3-2 HEAD-TO-TOE (TOTAL BODY) ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST *If the nurse has the appropriate education, the speculum and bimanual examination of women and the prostate gland examination of men can be performed after this inspection. eTABLE 3-3
Health History and Physical Examination
Data Collection
Example
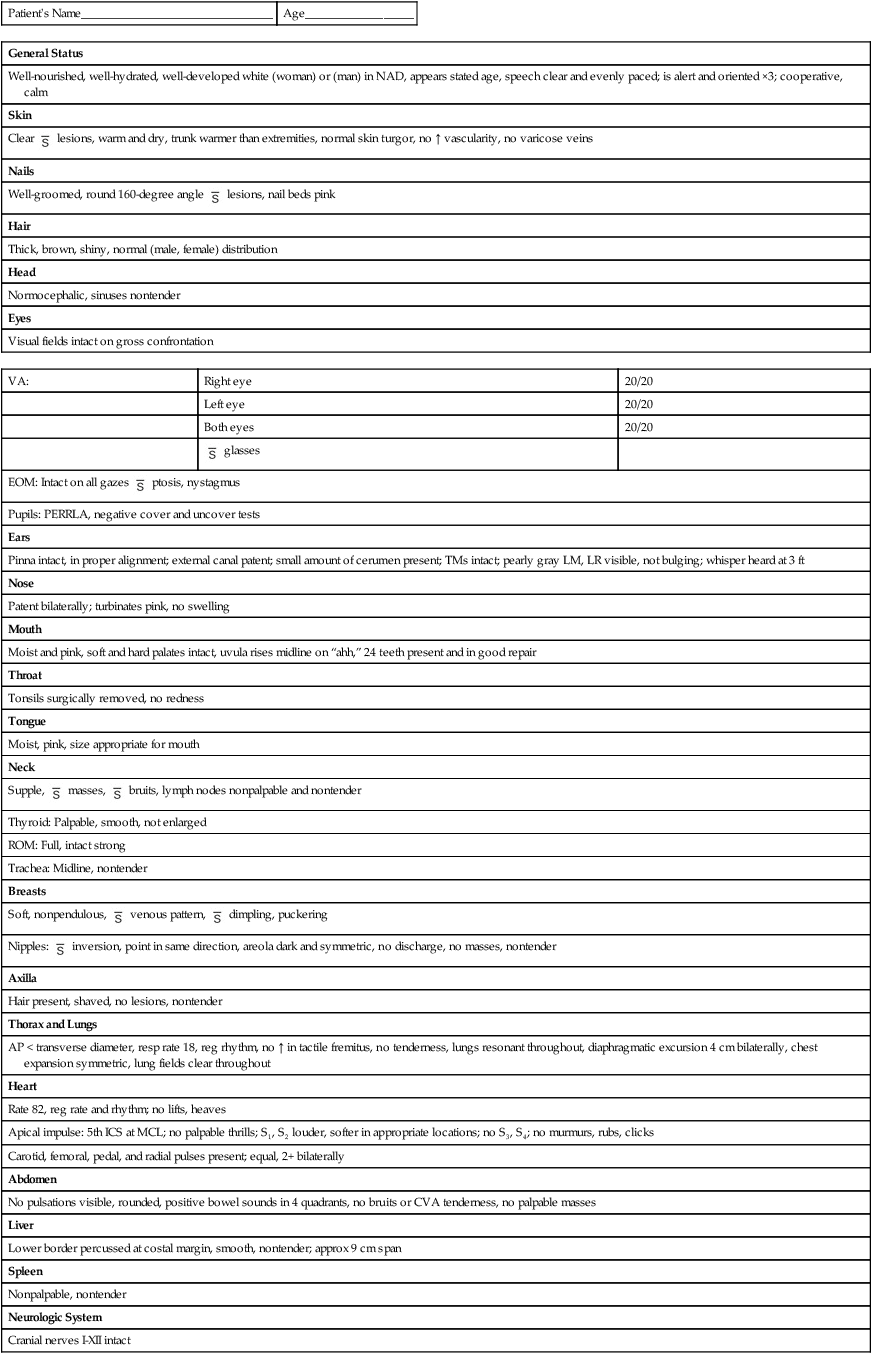
Patient’s Name________________________________
Age__________________
General Status
Well-nourished, well-hydrated, well-developed white (woman) or (man) in NAD, appears stated age, speech clear and evenly paced; is alert and oriented ×3; cooperative, calm
Skin
Clear 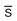 lesions, warm and dry, trunk warmer than extremities, normal skin turgor, no ↑ vascularity, no varicose veins
lesions, warm and dry, trunk warmer than extremities, normal skin turgor, no ↑ vascularity, no varicose veins
Nails
Well-groomed, round 160-degree angle 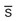 lesions, nail beds pink
lesions, nail beds pink
Hair
Thick, brown, shiny, normal (male, female) distribution
Head
Normocephalic, sinuses nontender
Eyes
Visual fields intact on gross confrontation
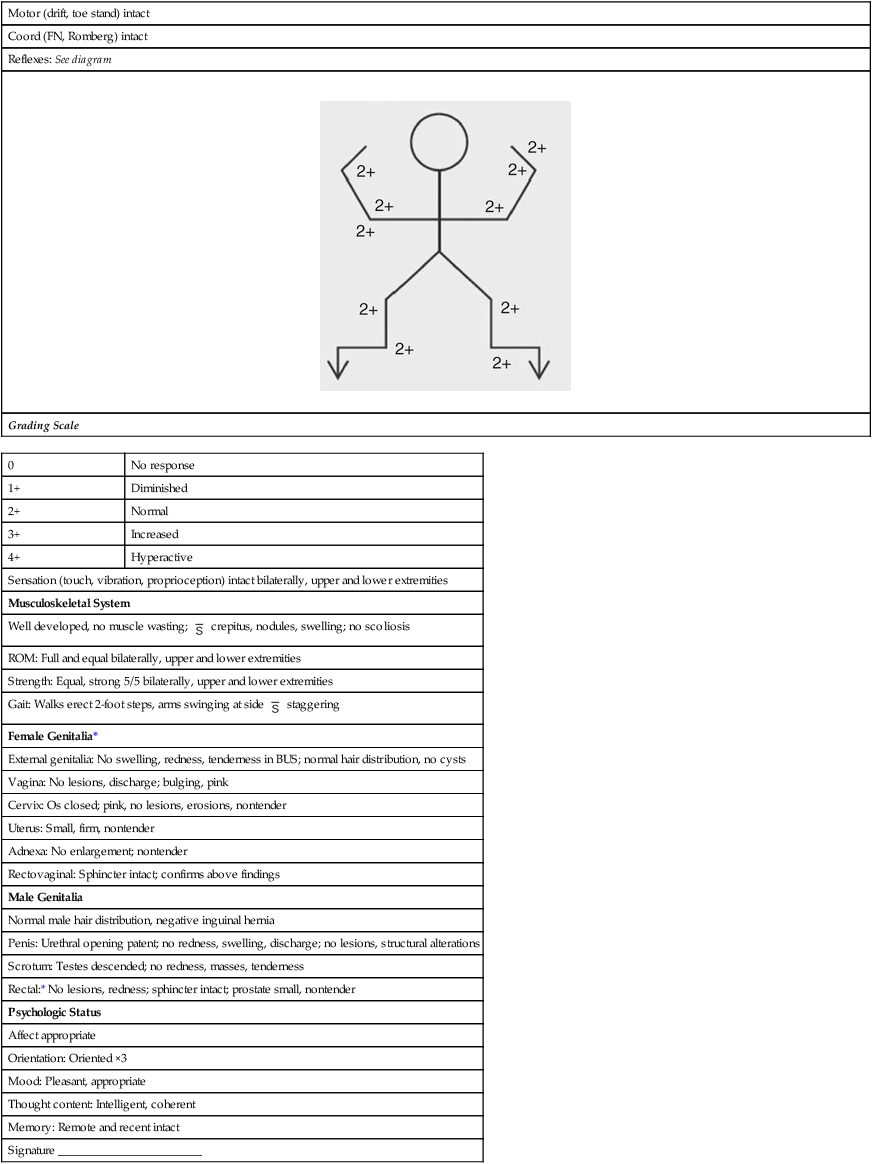
0
No response
1+
Diminished
2+
Normal
3+
Increased
4+
Hyperactive
Sensation (touch, vibration, proprioception) intact bilaterally, upper and lower extremities
Musculoskeletal System
Well developed, no muscle wasting; 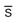 crepitus, nodules, swelling; no scoliosis
crepitus, nodules, swelling; no scoliosis
ROM: Full and equal bilaterally, upper and lower extremities
Strength: Equal, strong 5/5 bilaterally, upper and lower extremities
Gait: Walks erect 2-foot steps, arms swinging at side 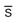 staggering
staggering
Female Genitalia*
External genitalia: No swelling, redness, tenderness in BUS; normal hair distribution, no cysts
Vagina: No lesions, discharge; bulging, pink
Cervix: Os closed; pink, no lesions, erosions, nontender
Uterus: Small, firm, nontender
Adnexa: No enlargement; nontender
Rectovaginal: Sphincter intact; confirms above findings
Male Genitalia
Normal male hair distribution, negative inguinal hernia
Penis: Urethral opening patent; no redness, swelling, discharge; no lesions, structural alterations
Scrotum: Testes descended; no redness, masses, tenderness
Rectal:* No lesions, redness; sphincter intact; prostate small, nontender
Psychologic Status
Affect appropriate
Orientation: Oriented ×3
Mood: Pleasant, appropriate
Thought content: Intelligent, coherent
Memory: Remote and recent intact
Signature ________________________
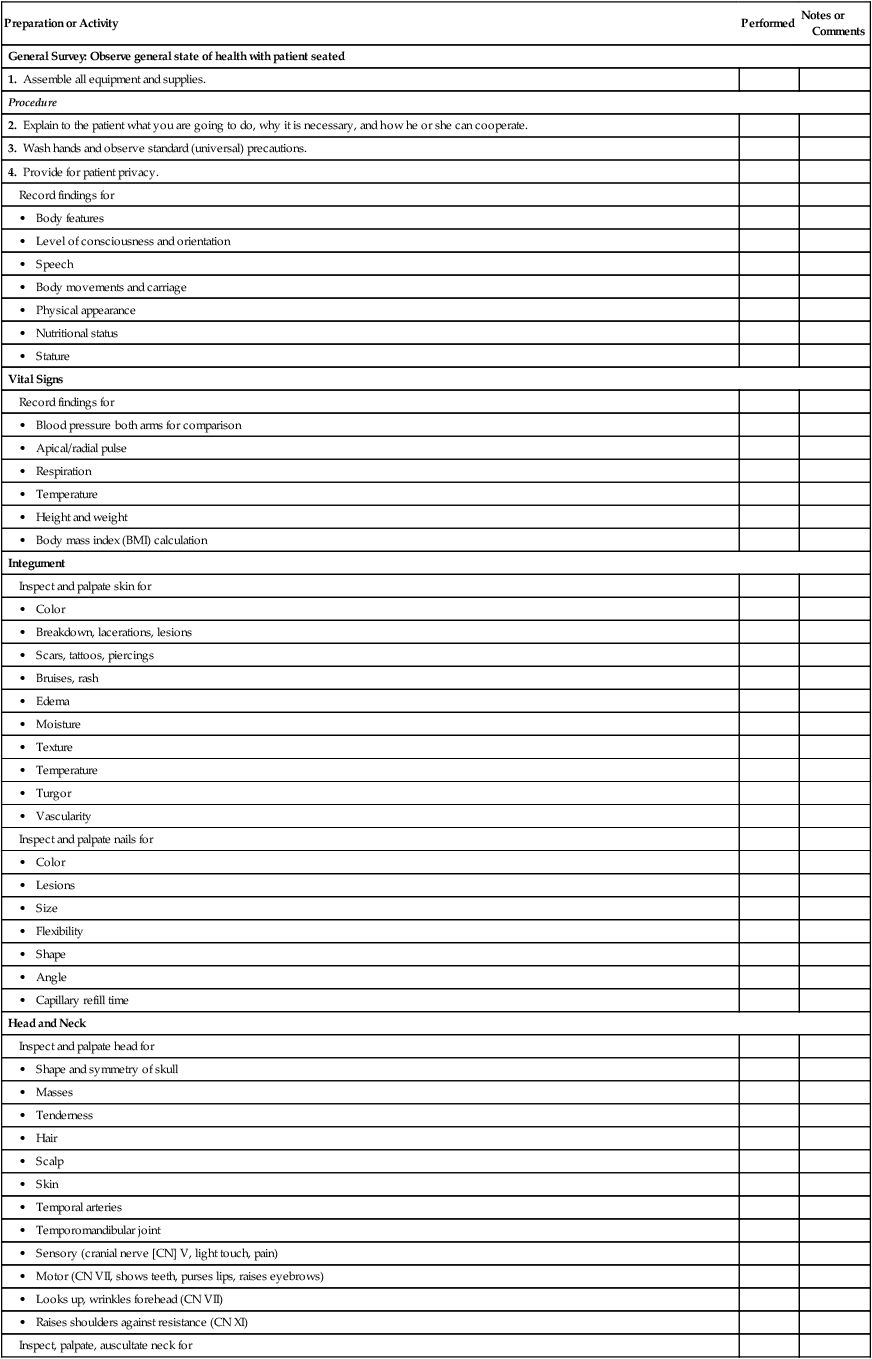
Preparation or Activity
Performed
Notes or Comments
General Survey: Observe general state of health with patient seated
1. Assemble all equipment and supplies.
Procedure
2. Explain to the patient what you are going to do, why it is necessary, and how he or she can cooperate.
3. Wash hands and observe standard (universal) precautions.
4. Provide for patient privacy.
Record findings for
• Body features
• Level of consciousness and orientation
• Speech
• Body movements and carriage
• Physical appearance
• Nutritional status
• Stature
Vital Signs
Record findings for
• Blood pressure both arms for comparison
• Apical/radial pulse
• Respiration
• Temperature
• Height and weight
• Body mass index (BMI) calculation
Integument
Inspect and palpate skin for
• Color
• Breakdown, lacerations, lesions
• Scars, tattoos, piercings
• Bruises, rash
• Edema
• Moisture
• Texture
• Temperature
• Turgor
• Vascularity
Inspect and palpate nails for
• Color
• Lesions
• Size
• Flexibility
• Shape
• Angle
• Capillary refill time
Head and Neck
Inspect and palpate head for
• Shape and symmetry of skull
• Masses
• Tenderness
• Hair
• Scalp
• Skin
• Temporal arteries
• Temporomandibular joint
• Sensory (cranial nerve [CN] V, light touch, pain)
• Motor (CN VII, shows teeth, purses lips, raises eyebrows)
• Looks up, wrinkles forehead (CN VII)
• Raises shoulders against resistance (CN XI)
Inspect, palpate, auscultate neck for
• Skin (vascularity and visible pulsations)
• Symmetry
• Range of motion
• Pulses and bruits (carotid)
• Midline structure (trachea, thyroid gland, cartilage)
• Lymph nodes (preauricular, postauricular, occipital, mandibular, tonsillar, submental, anterior and posterior cervical, infraclavicular, supraclavicular)
Inspect, assess, palpate eyes for
• Visual acuity
• Eyebrows
• Position and movement of eyelids (CN VII)
• Visual fields
• Extraocular movements (CN III, IV, VI)
• Cornea, sclera, conjunctiva
• Pupillary response (CN III)
• Red reflex
Inspect, palpate nose and sinuses for
• External nose: shape, blockage
• Internal nose: patency of nasal passages, shape, turbinates or polyps, discharge
• Frontal and maxillary sinuses
Inspect, assess, palpate ears for
• Placement
• Pinna
• Auditory acuity (whispered voice, ticking watch) (CN VIII)
• Mastoid process
• Auditory canal
• Tympanic membrane
Inspect, assess, palpate mouth for
• Lips (symmetry, lesions, color)
• Buccal mucosa (Stensen’s and Wharton’s ducts)
• Teeth (absence, state of repair, color)
• Gums (color, receding from teeth)
• Tongue for strength (asymmetry, ability to stick out tongue, side to side, fasciculations) (CN XII)
• Palates
• Tonsils and pillars
• Uvular elevation (CN IX)
• Posterior pharynx
• Gag reflex (CN IX and X)
• Jaw strength (CN V)
• Moisture
• Color
• Floor of mouth
Extremities
Observe size and shape, symmetry and deformity, involuntary movements; inspect and palpate arms, fingers, wrists, elbows, shoulders for
• Strength
• Range of motion
• Joint pain
• Swelling
• Pulses (radial, brachial)
• Test reflexes
• Triceps
• Biceps
• Brachioradialis
Inspect and palpate legs for
• Strength
• Range of motion
• Joint pain
• Swelling, edema
• Hair distribution
• Sensation (light touch, pain, temperature)
• Pulses (dorsalis pedis, posterior tibialis)
• Test reflexes
• Patellar
• Achilles
• Plantar
Posterior Thorax
Inspect for muscular development, respiratory movement, approximation of anteroposterior diameter
• Palpate for symmetry of respiratory movement, tenderness of costovertebral angle, spinous processes, tumors or swelling, tactile fremitus.
• Percuss for pulmonary resonance.
• Auscultate for breath sounds.
• Auscultate for egophony, bronchophony, and whispered pectoriloquy.
Anterior Thorax
• Assess breasts for configuration, symmetry, dimpling of skin.
• Assess nipples for rash, direction, inversion, retraction.
• Inspect for apical impulse, other precordial pulsations.
• Palpate the apical impulse and the precordium for thrills, lifts, heaves, tenderness.
• Inspect neck for venous distention, pulsations, waves.
• Palpate the lymph nodes in the subclavian, central axillary, and brachial areas.
• Palpate breasts.
• Auscultate for rate and rhythm, character of S1 and S2 heart sounds in the aortic, pulmonic, Erb’s point, tricuspid, and mitral areas; bruits at carotid, epigastrium; breath sounds at right middle lobe.
Abdomen
• Inspect for scars, shape, symmetry, bulging, muscular position and condition of umbilicus, movements (respiratory, pulsations, presence of peristaltic waves).
• Auscultate for peristalsis, bruits.
• Percuss, then palpate to confirm positive findings; check liver (size, tenderness); spleen; kidney (size, tenderness); urinary bladder (distention).
• Palpate femoral pulses, inguinofemoral nodes, and abdominal aorta.
Neurologic
Observe motor status
• Gait
• Toe walk
• Heel walk
• Drift
Coordination
• Finger to nose
• Romberg sign
• Heel to opposite shin
Observe the following:
• Proprioception (position sense of great toe)
Genitalia*
Male external genitalia
• Inspect penis, noting hair distribution, prepuce, glans, urethral meatus, scars, ulcers, eruptions, structural alterations, discharge.
• Inspect epidermis of perineum, rectum.
• Inspect skin of scrotum; palpate for descended testes, masses, pain.
Female external genitalia
• Inspect hair distribution; mons pubis, labia (minora and majora); urethral meatus; Bartholin’s, urethral, and Skene’s glands (may also be palpated, if indicated); introitus; any discharge.
• Assess for presence of cystocele, prolapse.
• Inspect perineum and rectum.
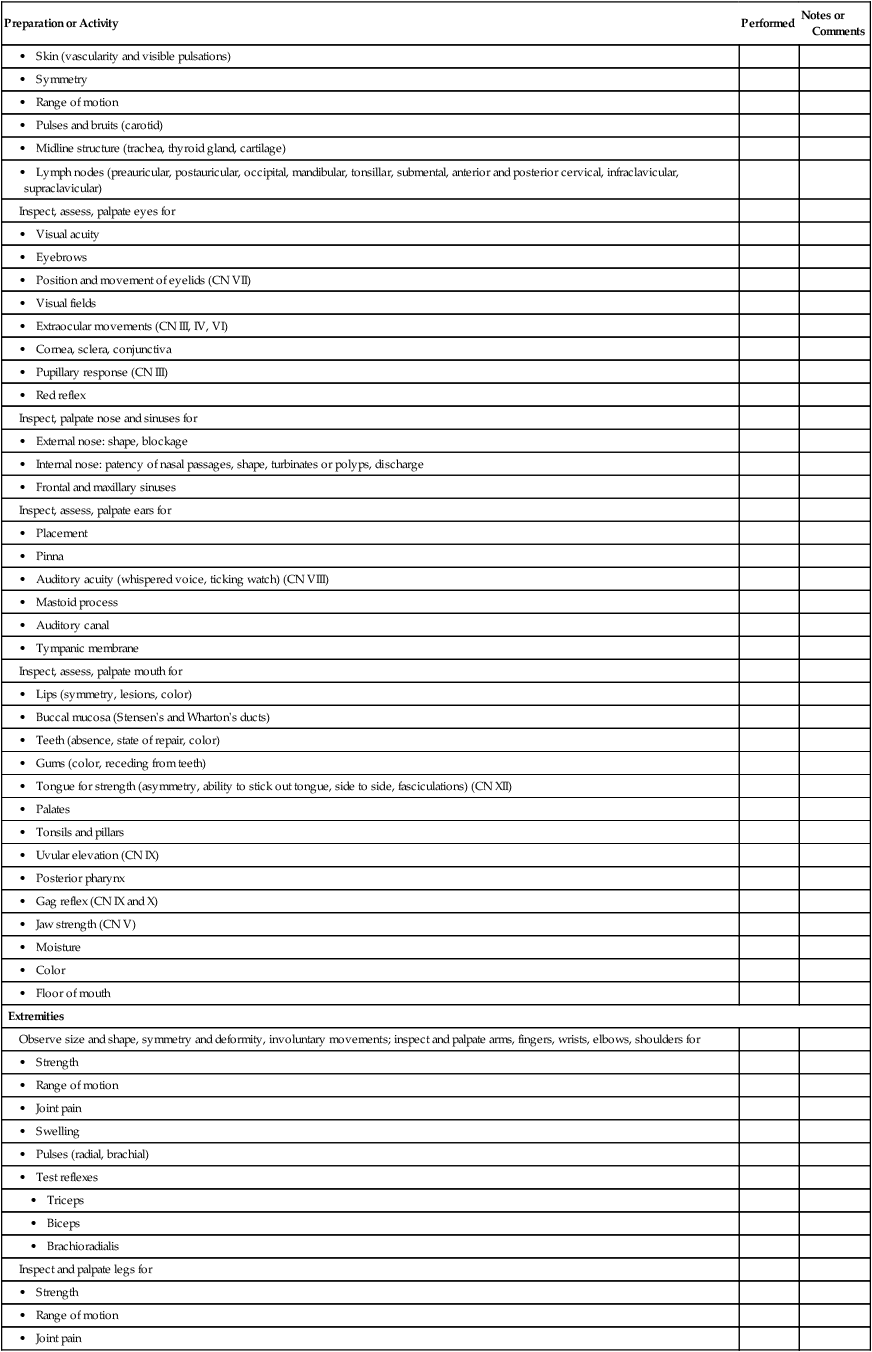
Visual System
Use this checklist to make sure that the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Changes in vision (e.g., acuity, blurred)
Y
N
Eye redness, itching, discomfort
Y
N
Drainage from eyes
Y
N
Objective: Physical Examination
Inspect
Eyes for any discoloration or drainage
Conjunctiva and sclera for color and vascularity
Lens for clarity
Eyelid for ptosis
Assess
Vision based on patient’s looking at nurse or Snellen chart
Extraocular movements
Peripheral vision
PERRLA
PERRLA, Pupils equal, round, reactive to light and accommodation.
Integumentary System
Use this checklist to make sure that the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Hair loss (unusual or rapid)
Y
N
Changes in skin (e.g., lesions, bruising)
Y
N
Nail discoloration
Y
N
Objective: Diagnostic
Check the following for results and critical values.
Biopsy results
Albumin
Objective: Physical Examination
Inspect
Skin for color, integrity, scars, lesions, signs of breakdown
Facial and body hair for distribution, color, quantity, hygiene
Nails for shape, contour, color, thickness, cleanliness
Dressings if present
Palpate
Skin for temperature, texture, moisture, thickness, turgor, mobility
Respiratory System
Use this checklist to make sure that the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Shortness of breath
Y
N
Wheezing
Y
N
Sputum production (color, quantity)
Y
N
Pain with breathing
Y
N
Cough
Y
N
Objective: Diagnostic
Check the following laboratory results for critical values.
Arterial blood gases
Chest x-ray
Hct, Hgb
Objective: Physical Examination
Observe
Respirations for rate, quality, and pattern
Inspect
Skin and nails for integrity and color
Neck for position of trachea
Shape, symmetry, and movement of chest wall
Palpate
Chest and back for masses
Auscultate
Lung (breath) sounds
Hematologic System
Use this checklist to make sure that the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Unusual bleeding or bruising
Y
N
Black, tarry stool
Y
N
Blood in vomitus
Y
N
Swelling in neck, armpits, or groin
Y
N
Dark-colored urine
Y
N
Fatigue
Y
N
Heart palpitations
Y
N
Objective: Diagnostic
Check the following laboratory results for critical values.
CBC
White blood cell count with differential
Clotting: PT, INR, aPTT, platelets
Hgb, Hct
Objective: Physical Examination
Inspect
Skin for lesions or color changes
Auscultate
BP for alteration or orthostasis
Palpate
Pulse for tachycardia
Liver and spleen for enlargement
Lymph nodes for lymphadenopathy
aPTT, Activated partial thromboplastin time; INR, international normalized ratio; PT, prothrombin time.
Cardiovascular System
Use this checklist to make certain that the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Chest pain
Y
N
Palpitations
Y
N
Shortness of breath (especially when lying down or at rest)
Y
N
Edema in legs or any part of body
Y
N
Leg pain during exercise
Y
N
Excess urination at night
Y
N
Objective: Diagnostic
Check the following for critical values or changes.
Cardiac biomarkers (troponin, CK-MB)
Hematocrit and hemoglobin
Electrocardiogram
Objective: Physical Examination
Inspect and Palpate
Anterior chest wall for pulsations and heaves
Pulses for symmetry, quality, and rhythm
Auscultate
Blood pressure
Heart for rate, rhythm, and sounds
CK-MB, Creatine kinase–MB.
Gastrointestinal System
Use this checklist to make sure that the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Loss of appetite
Y
N
Abdominal pain
Y
N
Changes in stools. If so, color, blood, consistency, frequency, etc.
Y
N
Nausea, vomiting
Y
N
Painful swallowing
Y
N
Objective: Diagnostic
Check the following laboratory results for critical values.
Endoscopy: colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, esophagogastroduodenoscopy
CT scan
Radiologic series: upper GI, lower GI
Stool for occult blood or ova and parasites
Liver function tests
Objective: Physical Examination
Inspect
Skin for color, lesions, scars, petechiae, etc.
Abdominal contour for symmetry and distention
Anus and rectum for intact skin, hemorrhoids
Auscultate*
Bowel sounds
Palpate
Abdominal quadrants using light touch
Abdominal quadrants using a deep technique
*Note: Do auscultation before palpation.
Urinary System
Use this checklist to make sure that the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Painful urination
Y
N
Changes in color of urine (blood, cloudy)
Y
N
Change in characteristics or urination (diminished, excessive)
Y
N
Problems with frequent nighttime urination (nocturia)
Y
N
Objective: Diagnostic
Check the following laboratory results for critical values.
Blood urea nitrogen
Serum creatinine
Urinalysis
Urine culture and sensitivity
Objective: Physical Examination
Inspect
Abdomen
Urinary meatus for inflammation or discharge
Palpate
Abdomen for bladder distention, masses, or tenderness
Percuss
Costovertebral angle for tenderness
Auscultate
Renal arteries for bruits
Endocrine System
Use this checklist to ensure that the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Excessive or increased thirst
Y
N
Excessive or decreased urination
Y
N
Excessive hunger
Y
N
Intolerance to heat or cold
Y
N
Excessive sweating
Y
N
Recent weight gain or loss
Y
N
Objective: Diagnostic
Check the following laboratory results for critical values.
Potassium
Glucose
Sodium
Glycosylated hemoglobin (Hb A1C)
Thyroid studies: TSH, T3, T4
Objective: Physical Examination
Inspect/Measure
Body temperature
Height and weight
Alertness and emotional state
Skin for changes in color and texture
Hair for changes in color, texture, and distribution
Auscultate
Heart rate, blood pressure
Palpate
Extremities for edema
Skin for texture and temperature
Neck for thyroid size, shape
T3, Triiodothyronine; T4, thyroxine; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Reproductive System
Use this checklist to ensure that the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Vaginal discharge/itching, unusual bleeding
Y
N
Penile pain, lesions, discharge
Y
N
Medications: oral contraceptives, antihypertensives, psychotropics, hormones
Y
N
Self-examinations (breast or testicular examination) and results
Y
N
Clinical examinations of reproductive systems (breast, pelvis, testicular, prostate) and results
Y
N
Pain in the abdomen, pelvis, or genitalia
Y
N
Objective: Diagnostic
Check the following for results and critical values.
Serum hCG
Serum PSA
Culture and sensitivity test results
Hormone levels (testosterone, progesterone, estrogen) if done
Screen for STIs (e.g., chlamydia, gonorrhea)
Laboratory reports: wet mounts, dark-field microscopy
X-ray of pelvis or breasts
Ultrasound of prostate
Objective: Physical Examination
Inspect
External genitalia for redness, swelling, drainage
Breasts for swelling, dimpling, retraction, drainage
Palpate
Breast tissue for masses or inflammation
hCG, Human chorionic gonadotropin; PSA, prostate-specific antigen.
Neurologic System
Use this checklist to make sure the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Blackouts/loss of memory
Y
N
Weakness, numbness, tingling in arms or legs
Y
N
Headaches, especially new onset
Y
N
Loss of balance/coordination
Y
N
Orientation to person, place, and time
Y
N
Objective: Diagnostic
Check the following laboratory results for critical values.
Lumbar puncture
CT or MRI of brain
EEG
Objective: Physical Examination
Inspect/Observe
General level of consciousness/orientation
Oropharynx for gag reflex and soft palate movement
Peripheral sensation of light touch and pinprick (face, hands, feet)
Smell with an alcohol wipe
Eyes for extraocular movements, PERRLA, peripheral vision, nystagmus
Gait for smoothness and coordination
Palpate
Strength of neck, shoulders, arms, and legs full and symmetric
Percuss
Reflexes
PERRLA, Pupils equal, round, and reactive to light and accommodation.
Musculoskeletal System
Use this checklist to make sure that the key assessment steps have been done.
Subjective
Ask the patient about any of the following and note responses.
Joint pain or stiffness
Y
N
Muscle weakness
Y
N
Bone pain
Y
N
Objective: Diagnostic
Check the results of the following diagnostic studies.
X-ray results
Bone scans
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Objective: Physical Examination
Inspect and Palpate
Skeleton and extremities (and compare sides) for alignment, contour, symmetry, size, and gross deformities
Joints for range of motion, tenderness or pain, heat, crepitus, and swelling
Muscles (and compare sides) for size, symmetry, tone, and tenderness or pain
Bones for tenderness or pain
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Health History and Physical Examination
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

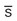 glasses
glasses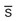 ptosis, nystagmus
ptosis, nystagmus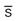 masses,
masses, 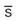 bruits, lymph nodes nonpalpable and nontender
bruits, lymph nodes nonpalpable and nontender venous pattern,
venous pattern,  dimpling, puckering
dimpling, puckering inversion, point in same direction, areola dark and symmetric, no discharge, no masses, nontender
inversion, point in same direction, areola dark and symmetric, no discharge, no masses, nontender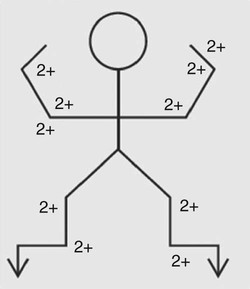
 , without; S1, S2, S3, and S4, heart sounds; TM, tympanic membrane; VA, visual acuity.
, without; S1, S2, S3, and S4, heart sounds; TM, tympanic membrane; VA, visual acuity.