Chapter 11
Health Care Payers
1. Define terms, phrases, abbreviations, and acronyms.
2. Identify and describe types of health insurance plans.
3. Discuss the differences between traditional fee-for-service and managed care plans.
4. Explain why health insurance plans and government programs implemented managed care plans.
5. Distinguish between private and government payers.
6. Describe the role of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) in government plans.
7. Discuss eligibility requirements for each government program and provide an overview of coverage for each government program.
8. Outline coordination of benefits (COB) guidelines for Medicare, Medicaid, and TRICARE.
9. Demonstrate an understanding of basic plan terms and specifications.
Advance Beneficiary Notice (ABN)
Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP)
Civilian Health and Medical Program of the Veterans Administration (CHAMPVA)
Coordination of benefits (COB)
Defense Enrollment Eligibility Reporting System (DEERS)
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO)
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO)
Hospital-Issued Notice of Non-Coverage (HINN)
Local Coverage Determination (LCD)
Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC)
Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP)
Military treatment facility (MTF)
National Coverage Determination (NCD)
Non-Availability Statement (NAS)
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
TRICARE Management Activity (TMA)
Aid to Families with Dependent Children
Ambulatory Payment Classifications
Civilian Health and Medical Program of the Uniformed Services
Civilian Health and Medical Program of the Veterans Administration
Children’s Health Insurance Program
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
Current Procedural Terminology
Defense Enrollment Eligibility Reporting System
Exclusive Provider Organization
Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnostic, and Treatment
Federally Qualified Health Center
Health Care Financing Administration
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System
Hospital-Issued Notice of Non-Coverage
Health Maintenance Organization
International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification
International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Clinical Modification
International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Procedure Coding System
Medicare Administrative Contractor
Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement Modernization Act
Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Groups
National Coverage Determination
Participating provider agreement
Preferred Provider Organization
Resource-Based Relative Value Scale
State Children’s Health Insurance Program
Usual, customary, and reasonable
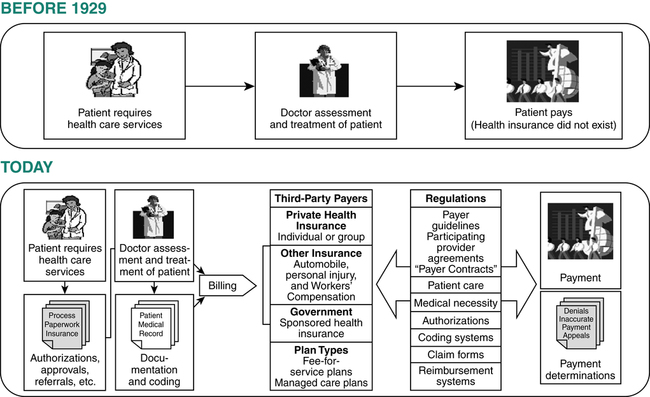
Today the health insurance industry consists of a large number of insurance companies offering a wide spectrum of coverage through many different plans and government-sponsored programs (Figure 11-1). Hospitals provide services to patients for treatment of conditions that are covered under various health insurance plans. The process of submitting claims for hospital services is complex because of variations in plan types, coverage, reimbursement, and billing requirements. It is important for hospital personnel involved in billing and coding services to have an understanding of these variations to ensure compliance with plan requirements and to obtain accurate reimbursement. A discussion of all payer plan variations is beyond the scope of this text. In fact, the insurance industry is so diverse that much of the required knowledge can only be gained through experience with the various payers. This chapter provides an overview of key elements of various types of health care coverage and payers.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Traditional Fee-for-Service Plans
Traditional health insurance plans are fee-for-service plans, also referred to as indemnity plans. A fee-for-service plan provides health insurance coverage for services rendered by providers of the patient’s choice. Reimbursement is determined for each service based on a fee schedule. Traditional health insurance plans were fee-for-service plans. Fee-for-service plans do not require referrals or preauthorizations. A claim is submitted by the hospital summarizing the total accrued charges. Accrued charges represent the total amount of all charges incurred during the patient visit. Fee-for-service plans generally pay a percentage of accrued charges, such as 80%, as outlined in the plan. The patient is generally responsible for a deductible and a coinsurance amount that is a percentage of the accrued charges, as illustrated in Figure 11-2.
Characteristics of Fee-for-Service Plans
• Health care services may be obtained from providers of the patient’s choice.
• Authorizations or referrals are not required.
• The hospital charges a fee for each service.
• Reimbursement is based on a percentage of the total charges.
• The patient is responsible for a deductible and coinsurance.
Major Medical Insurance
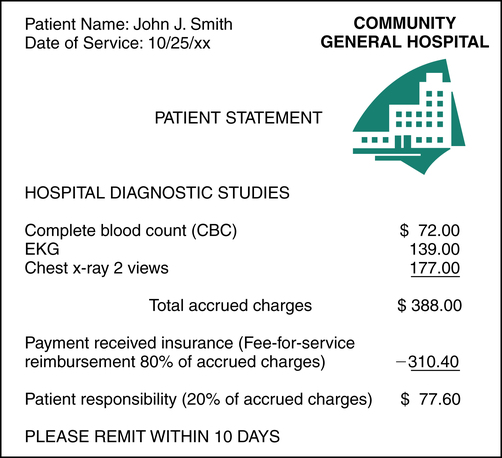
Major medical insurance provides coverage for large medical expenses incurred as a result of a catastrophic or prolonged illness. Services required for treatment of a prolonged illness can result in the accumulation of large medical expenses. The major medical plan outlines a specific dollar amount or total number of hospital days that need to be exceeded before major medical coverage becomes effective. A patient may initially require basic medical health care coverage and later require major medical benefits. For instance, John Smith received health care services required to diagnose and treat his liver failure (Figure 11-3). The expenses exceeded $35,000, as indicated on the patient’s account. According to his plan, the major medical coverage becomes effective when medical expenses exceed $30,000 or when the hospital stay exceeds 45 days. Major medical benefits are generally paid on a fee-for-service basis in accordance with the plan.
Managed Care Plans
Characteristics of Managed Care Plans
• A wide range of preventive, diagnostic, and therapeutic services are covered.
• Patient care services must be coordinated through a primary care physician (PCP).
• Health care services are provided within a network of providers as defined by the plan.
• A referral from the PCP is required for the patient to seek care from other providers.
• Reimbursement is determined on a capitation basis, which is a predetermined, fixed payment, per member, per month.
• The plan requires the patient to pay a copayment for specified services. Payment of a deductible may also be required by the plan.
• The plan contains provisions regarding cost-containment measures.
Cost-Containment Measures
Referral
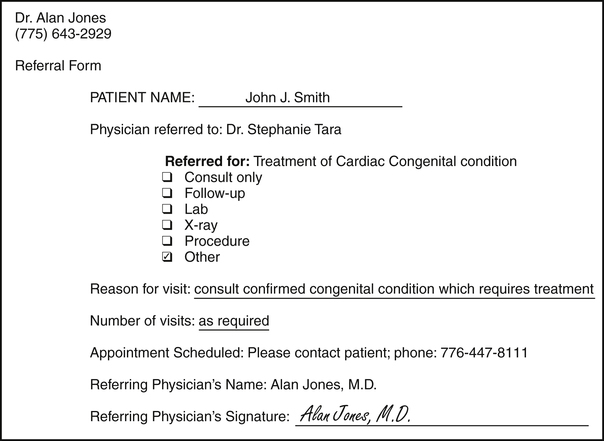
A referral is the process of one physician transferring the care of a patient for a specific illness or injury to another physician. When diagnostic, therapeutic, or specialty care is required that is beyond the scope of the primary care physician (PCP), a referral form is prepared by the PCP and forwarded to the provider. The managed care plan will not pay for services rendered without the appropriate referral. Figure 11-4 illustrates a sample referral form.
Preauthorization
Preauthorization is a process required by a managed care plan to obtain approval for a service before the service is rendered. Information regarding the patient’s condition and the plan for treatment is presented to the managed care plan by the provider’s representative. Preauthorization is granted if the plan approves the service. Services that require preauthorization are defined by the managed care plan. For example, most managed care plans require preauthorization for a hospital admission prior to the admission. If an emergency admission is necessary, an authorization must be obtained within a specified period of time after the admission as outlined by the plan. Payment for services will be denied if preauthorization is not obtained. Figure 11-5 illustrates a sample preauthorization request form.

Types of Managed Care Plans
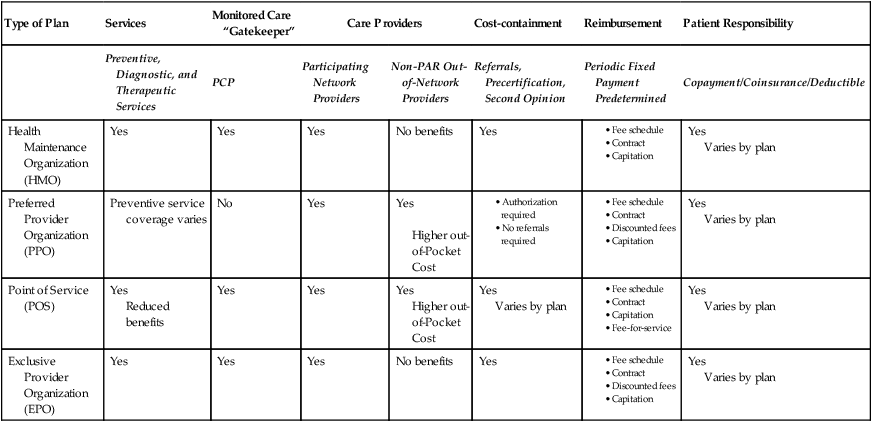
Managed care systems attempt to control health care costs by discouraging unnecessary hospitalization and overutilization of health care services. There are several types of managed care plans, including Health Maintenance Organization (HMO), Preferred Provider Organization (PPO), Point of Service (POS), and Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO). A comparison of these plans is outlined in Table 11-1.
TABLE 11-1
| Type of Plan | Services | Monitored Care “Gatekeeper” | Care Providers | Cost-containment | Reimbursement | Patient Responsibility | |
| Preventive, Diagnostic, and Therapeutic Services | PCP | Participating Network Providers | Non-PAR Out-of-Network Providers | Referrals, Precertification, Second Opinion | Periodic Fixed Payment Predetermined | Copayment/Coinsurance/Deductible | |
| Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No benefits | Yes | Yes Varies by plan | |
| Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) | Preventive service coverage varies | No | Yes | Yes Higher out-of-Pocket Cost | Yes Varies by plan | ||
| Point of Service (POS) | Yes Reduced benefits | Yes | Yes | Yes Higher out-of-Pocket Cost | Yes Varies by plan | Yes Varies by plan | |
| Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No benefits | Yes | Yes Varies by plan | |
Government Payers
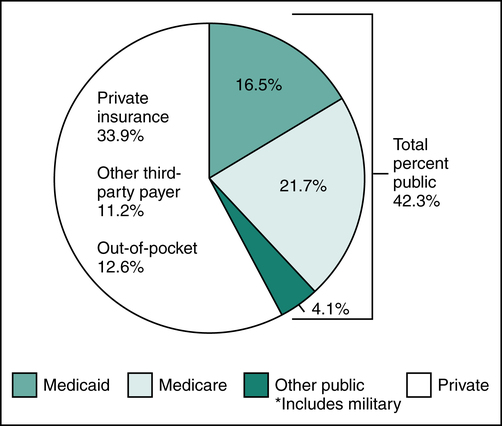
The health insurance industry has evolved over the past decade and the government has become the largest payer of health care services. In the 1960s a growing concern over the rising cost of health care and limited access to care for the poor and elderly resulted in the implementation of several federally sponsored government health insurance programs. In 1965, through an amendment of the Social Security Act of 1935, health insurance for the aged, called Medicare, was implemented. Another program, Medicaid, was implemented to provide coverage for health expenses to low-income individuals. In 1966, the U.S. Congress created the Civilian Health and Medical Program of the Uniformed Services (CHAMPUS), now known as TRICARE, to provide coverage for medical care provided to individuals in the military. Government health care expenditures have increased exponentially over the years. As the largest payer of health care services, the government sets the pace in the health care industry by establishing policies regarding provision of care, processing claims, and payment for services (Figure 11-6).
Medicare
• Individuals 65 years of age or older
• Individuals who are eligible for Social Security disability
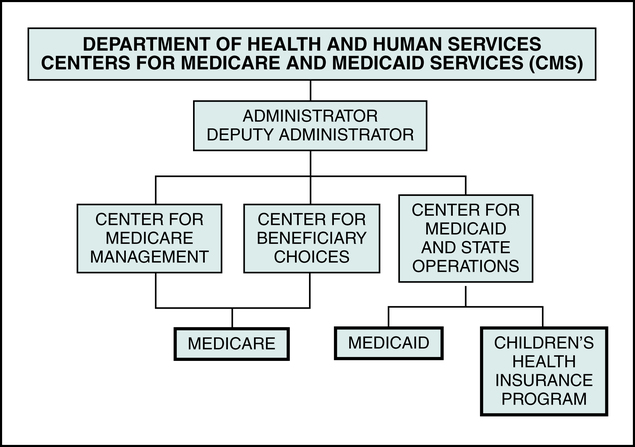
Two divisions within CMS that are chiefly responsible for the Medicare program are the Center for Medicare Management and the Center for Beneficiary Choices as illustrated in Figure 11-7. The Center for Medicare Management is responsible for the oversight of traditional fee-for-service Medicare. It serves as the focal point for all interactions with health care providers, intermediaries, and carriers for issues relating to CMS policies and operations. Responsibilities of the Center for Medicare Management include the management of fee-for-service administrative contractors and the development of policies regarding coding and payments.
Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC)
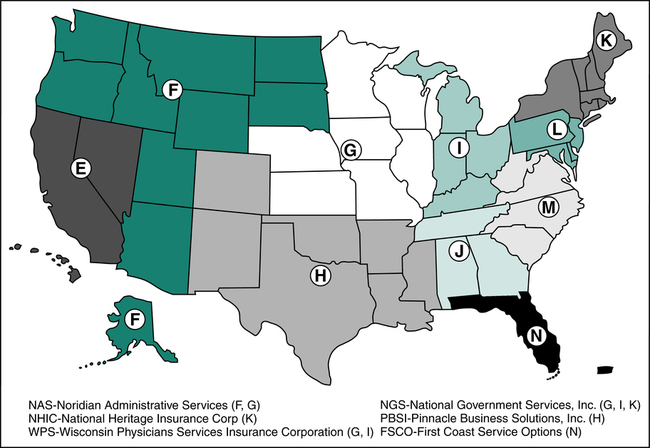
A Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) is an insurance company or other entity that contracts with the Federal government to handle functions related to enrollment and processing of claims for the Medicare program. Medicare contractors were previously known as fiscal intermediaries (FI) or Medicare carriers. CMS published a notice of change, effective October 1, 2005, stating fiscal intermediaries will be replaced with new contractors referred to as Medicare Administrative Contractors (MAC). From 2006 to today, CMS has awarded contracts through competitive procedures to MACs in 15 jurisdictions. To further improve effectiveness and efficiency, the original 15 jurisdictions are being consolidated into 10 jurisdictions. Contractors may be awarded the contract for Medicare Part A and/or Medicare Part B. Additionally, Medicare awards specialty contracts for durable medical equipment, home health, and hospice. Medicare Administrative Contractors (MAC) may vary by jurisdiction, for example First Coast Service Options, a division of Blue Cross and Blue Shield, is the MAC for jurisdiction “N,” and Noridian Administrative Services is the MAC for jurisdiction “F.” Figure 11-8 illustrates the 10 jurisdictions and provides examples of contractors for several of those jurisdictions. More information regarding MAC jurisdictions can be found on the CMS Web site.
Eligibility
• Worked for at least 10 years as a Medicare-covered employee (contributions were made for Social Security)
• Are citizens or permanent residents of the United States
• Are eligible for Social Security disability benefits or
• Have end-stage renal disease (ESRD)(permanent kidney failure requiring dialysis or transplant)
Coverage
Coverage provided under the Medicare program is defined in four parts: Medicare Part A, Part B, Part C, and Part D, as illustrated in Figure 11-9. Each part of Medicare provides benefits for specific services.
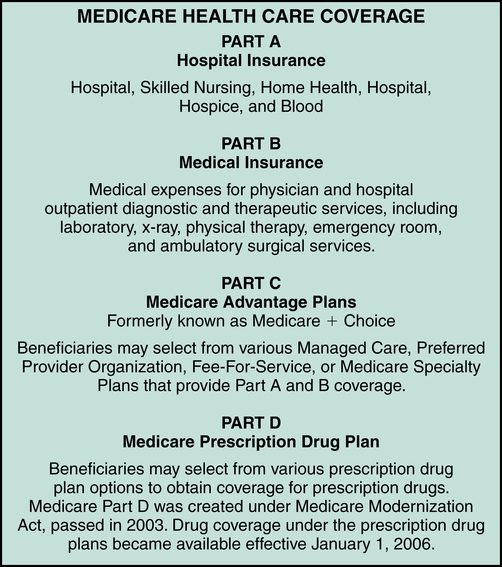
Medicare Part A
1. Inpatient hospitalization, which includes room and board (semi private), medications, supplies, nursing care, and other hospital services.
2. Skilled nursing facility care provided by a Medicare-approved nursing facility. Nursing facility services are covered when the patient is admitted to a nursing facility from a hospital after a minimum stay of 3 days in the facility.
3. Home health care provided on a part-time or intermittent skilled care basis, including home health aide services, durable medical equipment, supplies, and other services.
4. Hospice care services provided to a patient who is terminally ill for the purpose of relieving pain and symptoms.
5. Blood required during a patient stay, after the first 3 pints.
Medicare beneficiaries are required to pay a Medicare Part A deductible and coinsurance. Deductible and coinsurance amounts may change annually. The Part A deductible for 2013 is $1,184.00. The Part A coinsurance requirement is $296.00 per day for inpatient hospital days 61 to 90. The coinsurance requirement for inpatient hospital days 91 to 150 is $592.00 per day. Medicare beneficiaries are entitled to Lifetime reserve days. Lifetime reserve days are 60 days of hospitalization, per lifetime, that the beneficiary may use Reserve days at his or her discretion. Lifetime reserve days may be used to cover patient stays beyond 90 days. The patient is responsible for all hospital charges for stays over 150 days, beyond lifetime reserve days. Table 11-2 illustrates Medicare Part A covered services, amounts paid by Medicare, and the patient’s responsibility for the major classifications of coverage.
TABLE 11-2
| Services | Benefit | Medicare Pays | Patient Pays |
| Inpatient Hospitalization Semiprivate room and board, general nursing, and miscellaneous hospital services and supplies (Medicare payments are based on benefit periods) Includes: hospitalization in a hospital, psychiatric, rehabilitation, or long-term care facility | First 60 days | All but $1,184 | $1,184 deductible |
| 61st to 90th day | All but $296 a day | $296 a day | |
| 60 reserve days benefit† | All but $592 each day after 90 | $592 a day | |
| Beyond 150 days | Nothing | All costs† | |
| Skilled Nursing Facility Care Patient must have been in a hospital for at least 3 days and enter a Medicare-approved facility generally within 30 days after hospital discharge‡ (Medicare payments based on benefit periods) | First 20 days | 100% of approved amount | Nothing |
| 21st to 100th day | All but $148.00 a day | Up to $148.00 a day | |
| Beyond 100 days | Nothing | All costs | |
| Home Health Care Part-time or intermittent skilled care, home health aide services, durable medical equipment and supplies, and other services | Unlimited as long as Medicare conditions are met and services are declared “medically necessary” | 100% of approved amount; 80% of approved amount for durable medical equipment | Nothing for services; 20% of approved amount for durable medical equipment |
| Hospice Care Pain relief, symptom management, and support services for the terminally ill | If patient elects the hospice option and as long as doctor certifies need | All but limited costs for outpatient drugs and inpatient respite care | Limited cost sharing for outpatient drugs and inpatient respite care |
| Blood | Unlimited if medically necessary, after the first 3 pints | All but first 3 pints per calendar year§ | For first 3 pints |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree