Central Nervous System Depressants
Objectives
• Differentiate the types and stages of sleep.
• Explain several nonpharmacologic ways to induce sleep.
• Discuss the uses of benzodiazepines.
• Apply the nursing process for the patient taking benzodiazepines for hypnotic use.
• Compare the stages of anesthesia.
• Explain the uses for topical anesthetics.
• Differentiate general and local anesthetics and their major side effects.
Key Terms
anesthetics, p. 299
balanced anesthesia, p. 299
caudal block, p. 301
dependence, p. 293
epidural block, p. 301
hangover, p. 293
hypnotic effect, p. 292
insomnia, p. 292
nerve block, p. 301
nonrapid eye movement (NREM) sleep, p. 292
rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, p. 292
saddle block, p. 302
sedation, p. 292
spinal anesthesia, p. 301
spinal block, p. 301
tolerance, p. 293
withdrawal symptoms, p. 293
![]() http://evolve.elsevier.com/KeeHayes/pharmacology/
http://evolve.elsevier.com/KeeHayes/pharmacology/
Drugs that are central nervous system (CNS) depressants cause varying degrees of depression (reduction in functional activity) within the CNS. The degree of depression depends primarily on the drug and the amount of drug taken. The broad classification of CNS depressants includes sedative-hypnotics, general anesthetics, analgesics, opioid and nonopioid analgesics, anticonvulsants, antipsychotics, and antidepressants. The last five groups of depressant drugs are presented in separate chapters. Sedative-hypnotics and general anesthetics are discussed in this chapter.
Types and Stages of Sleep
Sleep disorders such as insomnia (inability to fall or remain asleep) occur in 10% to 30% of Americans. Insomnia occurs more frequently in women and increases with age.
People spend approximately one third of their lives, or as much as 25 years, sleeping. Normal sleep is composed of two definite phases: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and nonrapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Both REM and NREM occur cyclically during sleep at about 90- minute intervals (Figure 21-1). The four succeedingly deeper stages of NREM sleep end with an episode of REM sleep, and the cycle begins again. If sleep is interrupted, the cycle begins again with stage 1 of NREM sleep. Individuals perform better during their waking hours if they experience all types and stages of sleep.
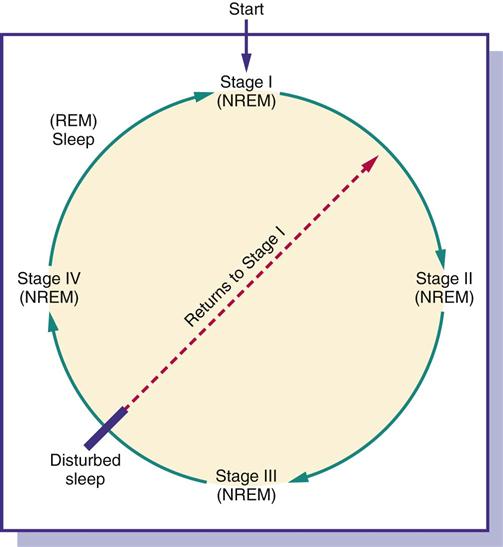
It is during the REM sleep phase that individuals experience most of their recallable dreams. Children have few REM sleep periods and have longer periods of stage 3 and 4 NREM sleep. Older adults experience a decrease in stages 3 and 4 NREM sleep and have frequent waking periods.
It is difficult to rouse a person during REM sleep. The period of REM sleep episodes becomes longer during the sleep process. Frequently if a person is roused from REM sleep, a vivid, bizarre dream may be recalled. If these dreams are unpleasant, they may be called nightmares. Sleep-walking or nightmares that occur in children take place during NREM sleep.
Nonpharmacologic Methods
Before using sedative-hypnotics or over-the-counter (OTC) sleep aids, various nonpharmacologic methods should be used to promote sleep. Once the nurse discovers why the patient cannot sleep, the following ways to promote sleep may be suggested:
1. Arise at a specific hour in the morning.
2. Take few or no daytime naps.
4. Avoid heavy meals or strenuous exercise before bedtime.
5. Take a warm bath, listen to quiet music, or perform other soothing activities before bed.
6. Decrease exposure to loud noises.
7. Avoid drinking copious amounts of fluids before sleep.
Sedative-Hypnotics
Sedative-hypnotics are commonly ordered for treatment of sleep disorders. The mildest form of CNS depression is sedation, which diminishes physical and mental responses at lower dosages of certain CNS depressants but does not affect consciousness. Sedatives are used mostly during the daytime. Increasing the drug dose can produce a hypnotic effect—not hypnosis but a form of “natural” sleep. Sedative-hypnotic drugs are sometimes the same drug; however, certain drugs are used more often for their hypnotic effect. With very high doses of sedative-hypnotic drugs, anesthesia may be achieved. An example of an ultrashort-acting barbiturate used to produce anesthesia is thiopental sodium (Pentothal).
Sedatives were first prescribed to reduce tension and anxiety. Barbiturates were initially used for their antianxiety effect until the early 1960s, when benzodiazepines were introduced. Because of the many side effects of barbiturates and their potential for physical and mental dependency, they are now less frequently prescribed.
More than $35 million is spent each year on OTC sleep aids such as Nytol, Sominex, Sleep-Eze, and Tylenol PM. The primary ingredient in OTC sleep aids is an antihistamine such as diphenhydramine (not barbiturates or benzodiazepines).
There are short-acting hypnotics and intermediate-acting hypnotics. Short-acting hypnotics are useful in achieving sleep, because they allow the patient to awaken early in the morning without experiencing lingering side effects. Intermediate-acting hypnotics are useful for sustaining sleep; however, after using one the patient may experience residual drowsiness, or hangover, in the morning. This may be undesirable if the patient is active and requires mental alertness. The ideal hypnotic promotes natural sleep without disrupting normal patterns of sleep and produces no hangover or undesirable effect. Table 21-1 lists the common side effects and adverse reactions associated with sedative-hypnotic use and abuse.
TABLE 21-1
COMMON SIDE EFFECTS AND ADVERSE REACTIONS OF SEDATIVE-HYPNOTICS
| SIDE EFFECTS AND ADVERSE REACTIONS | EXPLANATION OF THE EFFECTS |
| Hangover | A hangover is residual drowsiness resulting in impaired reaction time. The intermediate- and long-acting hypnotics are frequently the cause of drug hangover. The liver biotransforms these drugs into active metabolites that persist in the body, causing drowsiness. |
| REM rebound | REM rebound, which results in vivid dreams and nightmares, frequently occurs after taking a hypnotic for a prolonged period then abruptly stopping. However, it may occur after taking only one hypnotic dose. |
| Dependence | Dependence is the result of chronic hypnotic use. Physical and psychological dependence can result. Physical dependence results in the appearance of specific withdrawal symptoms when a drug is discontinued after prolonged use. The severity of withdrawal symptoms depends on the drug and dosage. Symptoms may include muscular twitching and tremors, dizziness, orthostatic hypotension, delusions, hallucinations, delirium, and seizures. Withdrawal symptoms start within 24 hours and can last for several days. |
| Tolerance | Tolerance results when there is a need to increase the dosage over time to obtain the desired effect. It is mostly caused by an increase in drug metabolism by liver enzymes. The barbiturate drug category can cause tolerance after prolonged use. Tolerance is reversible when the drug is discontinued. |
| Excessive depression | Long-term use of a hypnotic may result in CNS depression, which is characterized by lethargy, sleepiness, lack of concentration, confusion, and psychological depression. |
| Respiratory depression | High doses of sedative-hypnotics can suppress the respiratory center in the medulla. |
| Hypersensitivity | Skin rashes and urticaria can result when taking barbiturates. Such reactions are rare. |
Hypnotic drug therapy should usually be short-term to prevent drug dependence and drug tolerance. Interrupting hypnotic therapy can decrease drug tolerance, but abruptly discontinuing a high dose of hypnotic taken over a long period can cause withdrawal symptoms. In such cases, the dose should be tapered to avoid withdrawal symptoms. As a general rule, the lowest dose should be taken to obtain sleep. Patients with severe respiratory disorders should avoid hypnotics, which could cause an increase in respiratory depression. Usually hypnotics are contraindicated during pregnancy. Ramelteon (Rozerem) is the only major sedative-hypnotic approved for long-term use. This drug may be used for treating chronic insomnia.
The category of sedative-hypnotics includes barbiturates, benzodiazepines, and nonbenzodiazepines, among others. Each category is discussed separately. Prototype drug charts are included for benzodiazepines and nonbenzodiazepines.
Barbiturates
Barbiturates were introduced as a sedative in the early 1900s. They are classified as long-acting, intermediate-acting, short-acting, and ultrashort-acting.
• The ultrashort-acting barbiturate, thiopental sodium (Pentothal), is used as a general anesthetic.
Barbiturates should be restricted to short-term use (2 weeks or less) because of their numerous side effects, including tolerance to the drug. In the United States, barbiturates are classified in the schedule of the Controlled Substances Act as class II for short-acting, class III for intermediate-acting, and class IV for long-acting. In Canada, barbiturates are classified as schedule G. Barbiturates are listed in Table 21-2.
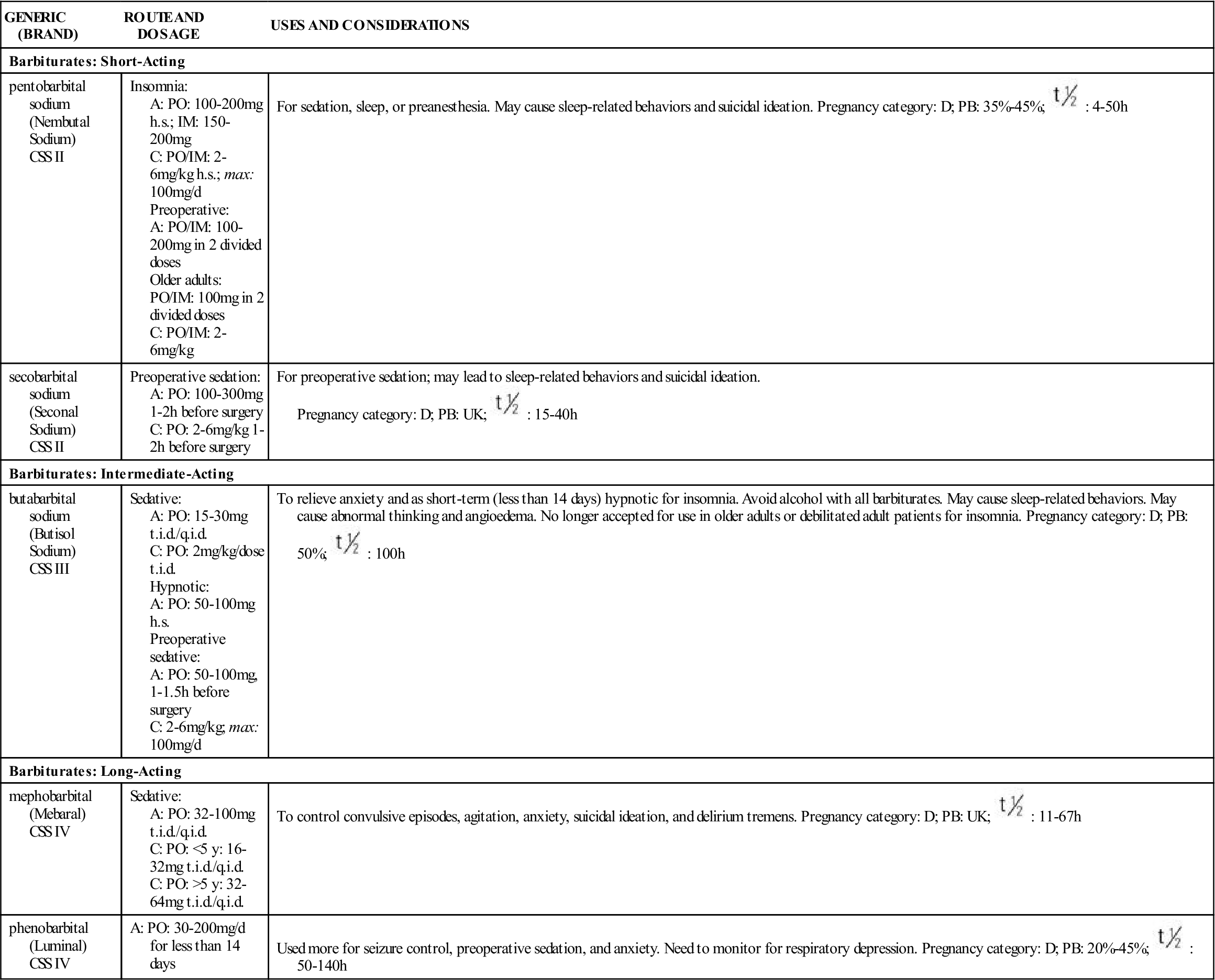
TABLE 21-2
SEDATIVE-HYPNOTICS: BARBITURATES AND OTHERS
| GENERIC (BRAND) | ROUTE AND DOSAGE | USES AND CONSIDERATIONS |
| Barbiturates: Short-Acting | ||
| pentobarbital sodium (Nembutal Sodium) CSS II | Insomnia: A: PO: 100-200 mg h.s.; IM: 150-200 mg C: PO/IM: 2-6 mg/kg h.s.; max: 100 mg/d Preoperative: A: PO/IM: 100-200 mg in 2 divided doses Older adults: PO/IM: 100 mg in 2 divided doses C: PO/IM: 2-6 mg/kg | For sedation, sleep, or preanesthesia. May cause sleep-related behaviors and suicidal ideation. Pregnancy category: D; PB: 35%-45%; 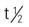 : 4-50 h : 4-50 h |
| secobarbital sodium (Seconal Sodium) CSS II | Preoperative sedation: A: PO: 100-300 mg 1-2 h before surgery C: PO: 2-6 mg/kg 1-2 h before surgery | For preoperative sedation; may lead to sleep-related behaviors and suicidal ideation. Pregnancy category: D; PB: UK; 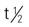 : 15-40 h : 15-40 h |
| Barbiturates: Intermediate-Acting | ||
| butabarbital sodium (Butisol Sodium) CSS III | Sedative: A: PO: 15-30 mg t.i.d./q.i.d. C: PO: 2 mg/kg/dose t.i.d. Hypnotic: A: PO: 50-100 mg h.s. Preoperative sedative: A: PO: 50-100 mg, 1-1.5 h before surgery C: 2-6 mg/kg; max: 100 mg/d | To relieve anxiety and as short-term (less than 14 days) hypnotic for insomnia. Avoid alcohol with all barbiturates. May cause sleep-related behaviors. May cause abnormal thinking and angioedema. No longer accepted for use in older adults or debilitated adult patients for insomnia. Pregnancy category: D; PB: 50%; 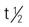 : 100 h : 100 h |
| Barbiturates: Long-Acting | ||
| mephobarbital (Mebaral) CSS IV | Sedative: A: PO: 32-100 mg t.i.d./q.i.d. C: PO: <5 y: 16-32 mg t.i.d./q.i.d. C: PO: >5 y: 32-64 mg t.i.d./q.i.d. | To control convulsive episodes, agitation, anxiety, suicidal ideation, and delirium tremens. Pregnancy category: D; PB: UK; 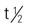 : 11-67 h : 11-67 h |
| phenobarbital (Luminal) CSS IV | A: PO: 30-200 mg/d for less than 14 days | Used more for seizure control, preoperative sedation, and anxiety. Need to monitor for respiratory depression. Pregnancy category: D; PB: 20%-45%; 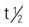 : 50-140 h : 50-140 h |
Pharmacokinetics
Pentobarbital (Nembutal) has been available for nearly half a century and was the hypnotic of choice until the introduction of benzodiazepines in the 1960s. It has a slow absorption rate and is moderately protein-bound. The long half-life is mainly because of the formation of active metabolites resulting from liver metabolism.
Pharmacodynamics
Pentobarbital and secobarbital are used primarily for short-term treatment of insomnia. Other uses include control of seizures, preoperative anxiety, and sedation induction. They have a rapid onset with a short duration of action and are considered short-acting barbiturates. The onset of action of pentobarbital is slower when administered intramuscularly (IM) than when administered orally (PO).
Many drug interactions are associated with barbiturates. Alcohol, narcotics, and other sedative-hypnotics used in combination with barbiturates may further depress the CNS. Pentobarbital increases hepatic enzyme action, causing an increased metabolism and decreased effect of drugs such as oral anticoagulants, glucocorticoids, tricyclic antidepressants, and quinidine. Pentobarbital may cause hepatotoxicity if taken with large doses of acetaminophen.
Benzodiazepines
Selected benzodiazepines (minor tranquilizer or anxiolytic) were introduced with chlordiazepoxide (Librium) in the 1960s as antianxiety agents. This drug group is ordered as sedative-hypnotics for inducing sleep. Several benzodiazepines marketed as hypnotics include flurazepam (Dalmane), alprazolam (Xanax) (Prototype Drug Chart 21-1), temazepam (Restoril), triazolam (Halcion), estazolam (ProSom), and quazepam (Doral) (Table 21-3). Increased anxiety might be the cause of insomnia for some patients, so lorazepam (Ativan) and diazepam (Valium) can be used to alleviate the anxiety. These drugs are classified as schedule IV according to the Controlled Substances Act. The benzodiazepines increase the action of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) to the GABA receptors. Neuron excitability is reduced.

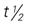 , half-life; t.i.d., three times a day; UK, unknown; wk, week; <, less than; >, greater than.
, half-life; t.i.d., three times a day; UK, unknown; wk, week; <, less than; >, greater than.



















