Miscellaneous Agents
Objectives
1 Summarize the primary actions and potential uses of the miscellaneous agents cited.
2 Describe patient education needed when miscellaneous agents are used.
![]() http://evolve.elsevier.com/Clayton
http://evolve.elsevier.com/Clayton
Miscellaneous Agents
Actions
The exact mechanism of action is not known, but colchicine interrupts the cycle of urate crystal deposition in the tissues that results in an acute attack of gout. It does not affect the amount of uric acid in the blood or urine; therefore, it is not a uricosuric agent.
Uses
Colchicine is an alkaloid that has been used for hundreds of years to prevent or relieve acute attacks of gout. Joint pain and swelling begin to subside within 12 hours and are usually gone within 48 to 72 hours after initiating therapy.
Therapeutic Outcome
The primary therapeutic outcome expected from colchicine therapy is elimination of joint pain secondary to acute gout attack.
 Nursing Implications for Colchicine
Nursing Implications for Colchicine
Premedication Assessment
Availability
PO: 0.6-mg tablets.
Dosage and Administration
Adult: PO: Acute gout: Initially 0.5 to 1.3 mg, followed by 0.6 mg every 1 to 2 hours until pain subsides or nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea develop. A total dose of 4 to 10 mg may be required. After the acute attack, 0.5 to 0.6 mg should be administered every 6 hours for a few days to prevent relapse. Do not repeat high-dose therapy for at least 3 days. Prophylaxis for recurrent gout: 0.5 to 0.6 mg every 1 to 3 days, depending on the frequency of gout attacks.
Fluid Intake.
Monitor intake and output during therapy. Maintain fluid intake at eight to twelve 8-ounce glasses daily.
Monitoring
Common Adverse Effects
Gastrointestinal
Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea.
These are common adverse effects of colchicine therapy. Discontinue therapy when gastrointestinal symptoms develop. Always report bright red blood in vomitus, coffee-ground vomitus, or dark tarry stools.
Serious Adverse Effects
Hematologic
Blood Dyscrasias.
Serious, potentially fatal blood dyscrasias, including anemia, agranulocytosis, and thrombocytopenia, have been associated with colchicine therapy. Although the development of blood dyscrasias is rare, periodic differential blood counts are recommended if the patient requires prolonged treatment. Routine laboratory studies (e.g., red blood cell [RBC], white blood cell [WBC], differential counts) should be scheduled. Stress to the patient the importance of returning for this laboratory work. Monitor for the development of sore throat, fever, purpura, jaundice, or excessive and progressive weakness, and report any such development immediately to the health care provider.
Drug Interactions
No clinically significant drug interactions have been reported.
Actions
Donepezil is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that allows acetylcholine to accumulate at cholinergic synapses, causing a prolonged and exaggerated cholinergic effect.
Uses
Although the causes are unknown, Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by a loss of cholinergic neurons in the central nervous system (CNS), resulting in memory loss and cognitive deficits (dementia). Donepezil is used in patients with mild to moderate dementia to enhance cholinergic function. Its function diminishes with ongoing loss of cholinergic neurons. Donepezil does not prevent or slow the neurodegeneration caused by Alzheimer’s disease.
Therapeutic Outcome
The primary therapeutic outcome expected from donepezil therapy is improved cognitive skills (e.g., word recall, object naming, language, word finding, task performance).
 Nursing Implications for Donepezil
Nursing Implications for Donepezil
Premedication Assessment
Availability
PO: 5-, 10-, and 23-mg tablets; 5- and 10-mg orally disintegrating tablets.
Dosage and Administration
Adult: PO: Initial dosage: 5 mg daily at bedtime. After 4 to 6 weeks of therapy, dosage may be increased to 10 mg daily to assess therapeutic benefit. Donepezil may be taken with or without food. The orally disintegrating tablets may be helpful for patients who have difficulty swallowing. Allow tablets to dissolve on the tongue and follow with a glass of water.
Monitoring
Common Adverse Effects
Gastrointestinal
Nausea, Vomiting, Dyspepsia, Diarrhea.
These are natural extensions of the pharmacologic effects of cholinergic agents. Dosage may need to be reduced if the patient has difficulty with these adverse effects. Symptoms are less common with lower doses and tend to subside after 2 to 3 weeks of therapy. Gradually increasing the dose may help avoid these complications.
Serious Adverse Effects
Cardiovascular
Bradycardia.
Cholinergic agents cause a slowing of the heart. Notify the health care provider if the heart rate is regularly less than 60 beats/min.
Drug Interactions
Drugs That Enhance Therapeutic and Toxic Effects.
Ketoconazole and quinidine may inhibit the metabolism of donepezil. Monitor closely for enhancement of adverse effects.
Drugs That Reduce Therapeutic Effects.
Carbamazepine, dexamethasone, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and rifampin increase the metabolism of donepezil, reducing its therapeutic effects. The dose of donepezil may need to be increased or the patient switched to another medicine to treat Alzheimer’s disease.
Anticholinergic Agents.
As a cholinergic agent, donepezil has the potential to reduce the activity of anticholinergic agents (e.g., benztropine, diphenhydramine, orphenadrine, procyclidine, trihexyphenidyl).
Succinylcholine-Type Muscle Relaxants, Cholinergic Agents.
As a cholinesterase inhibitor, donepezil is likely to exaggerate the actions of the depolarizing muscle relaxant (succinylcholine) during anesthesia and enhance the pharmacologic activity of cholinergic agents such as bethanechol.
Actions
Memantine is an N-methyl-d-aspartate (NDMA) receptor inhibitor. It is a synthetic compound structurally related to gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
Uses
Although the causes are unknown, one of the neurochemical characteristics of Alzheimer’s disease is persistent activation of NDMA receptors in the CNS. Memantine blocks these receptors and is used alone or in combination with an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for the treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer’s dementia. Patients taking memantine show improvement in cognitive function and behavioral symptoms and a slower decline in activities of daily living, but memantine does not prevent or slow the neurodegeneration of Alzheimer’s disease.
Therapeutic Outcome
The primary therapeutic outcome expected from memantine therapy is improved cognitive skills (e.g., word recall, object naming, language, word finding, task performance).
 Nursing Implications for Memantine
Nursing Implications for Memantine
Premedication Assessment
Availability
Dosage and Administration
Adult: PO: 5 mg once daily. The dose should be increased in 5-mg increments to 10, 15, and 20 mg daily. The minimal interval between dose increases is 1 week. Memantine can be taken with or without food.
Conversion: Patients taking 10-mg immediate-release tablets twice daily may switch to a 28-mg extended-release capsule once daily the day following the last dose of a 10-mg immediate-release tablet.
Monitoring
Common and Serious Adverse Effects
Neurologic
Headache, Dizziness, Akathisia, Insomnia, Restlessness, Increased Motor Activity, Excitement, Agitation.
Many of these symptoms decline with continued therapy and can be reduced with a longer dosage titration. Dosage may need to be reduced if the patient has difficulty with these adverse effects.
Drug Interactions
Acetazolamide, Sodium Bicarbonate.
Medicines that alkalinize the pH of the urine will reduce excretion of memantine. Severe medical conditions such as renal tubular acidosis and severe urinary tract infections also may cause alkalization of the urine, with potential toxicity of memantine.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


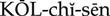 )
)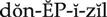 )
) )
)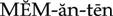 )
)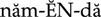 )
)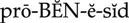 )
)