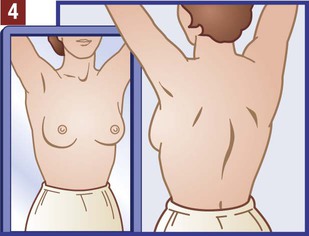
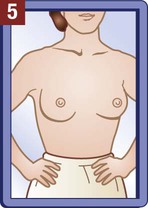
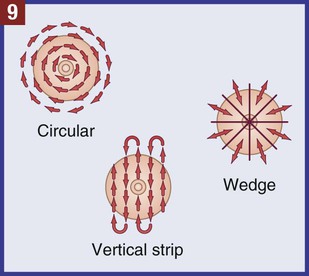
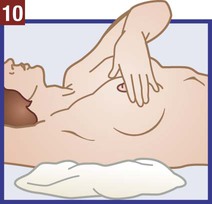
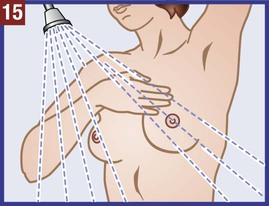
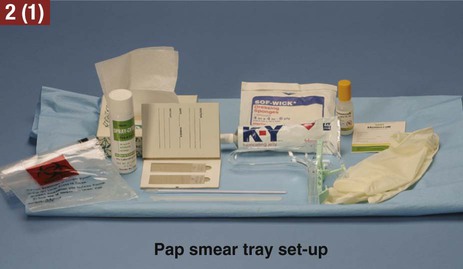
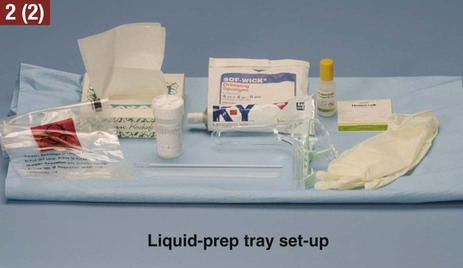
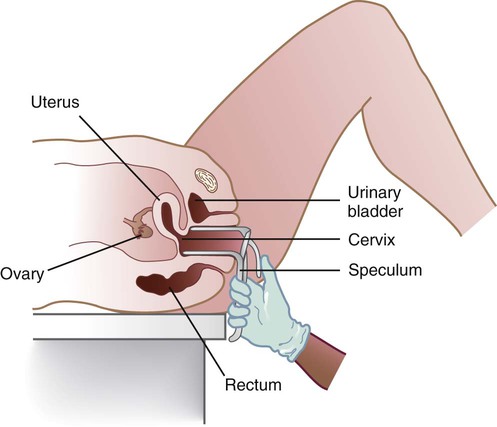
The medical assistant should have a thorough knowledge of the female reproductive system (refer to Chapter 16) and the following terms associated with the female reproductive system: Amenorrhea Absence or cessation of the menstrual period. Amenorrhea occurs normally before puberty, during pregnancy, and after menopause. Cervix The lower narrow end of the uterus that opens into the vagina. Colposcopy Examination of the cervix using a colposcope (a lighted instrument with a magnifying lens). Dysmenorrhea Pain associated with the menstrual period. Dyspareunia Pain in the vagina or pelvis experienced by a woman during sexual intercourse. Dysplasia The growth of abnormal cells. Dysplasia is a precancerous condition that may or may not develop into cancer. Menopause The permanent cessation of menstruation, which usually occurs between the ages of 45 and 55 with an average age of 51. Menorrhagia Excessive bleeding during a menstrual period, in the number of days, the amount of blood, or both. Also called dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB). Metrorrhagia Bleeding between menstrual periods. Perimenopause Before the onset of menopause, the phase during which a woman with regular periods changes to irregular cycles and increased periods of amenorrhea. Perineum The external region between the vaginal orifice and the anus in a female and between the scrotum and the anus in a male. Risk factor Anything that increases an individual’s chance of developing a disease. Some risk factors (e.g., smoking) can be avoided, but others cannot (e.g., age and family history). The patient should know how to examine her breasts at home for the presence of lumps and other changes with a breast self-examination (BSE). Most breast cancers are first discovered by women themselves. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that women 20 years of age and older examine their breasts once every month. The medical assistant may be responsible for instructing the patient in this procedure at the medical office (Procedure 23-1). If a lump or other change is discovered, the woman should schedule an appointment with her physician as soon as possible. Most breast lumps are not cancerous, but the physician must make that diagnosis. • Inspection of the external genitalia, vagina, and cervix • Collection of a specimen for a Pap test The medical assistant can help the patient relax during the examination by telling her to breathe deeply, slowly, and evenly through the mouth. If the patient is relaxed, it is easier for the physician to insert the vaginal speculum and to perform the bimanual pelvic examination; it also is more comfortable for the patient. It is recommended that the medical assistant remain in the room during the pelvic examination to provide legal protection for the physician, to reassure the patient, and to assist the physician. Procedure 23-2 outlines the medical assistant’s role in assisting the physician with a gynecologic examination. Next, the physician inserts a vaginal speculum into the vagina. Specula are available in two forms—metal and plastic. Metal specula are reusable and must be sanitized and sterilized after each use. Plastic specula are disposable and are designed to be used only once. Vaginal specula come in three sizes—small, medium, and large. The physician determines the size required based on the physical and sexual maturity of the patient. The function of the speculum is to hold the walls of the vagina apart to allow visual inspection of the vagina and cervix (Figure 23-1).
The Gynecologic Examination and Prenatal Care
Learning Objectives
Procedures
Gynecologic Examination
Breast Examination
Instruct patient in the procedure for a breast self-examination.
Pelvic Examination
Prepare patient for a gynecologic examination.
Assist the physician with a gynecologic examination.
Complete a cytology requisition form.
Vaginal Infections
Assist in the collection of a vaginal microbiologic specimen.
Prenatal Visits
Calculate the expected date of delivery (EDD).
Complete a prenatal health history.
Assist with an initial prenatal examination.
Assist with a return prenatal examination.
Gynecologic Examination
Gynecology
Terms Related to Gynecology
Breast Examination
Pelvic Examination
Inspection of External Genitalia, Vagina, and Cervix
The Gynecologic Examination and Prenatal Care
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access