1. Define the key terms listed 2. Identify two major developmental tasks of adolescence 3. Discuss three ways in which youth can help prevent violence 4. Discuss anticipatory guidance for a 15-year-old girl just beginning to date 5. Describe three ways an adolescent can be given responsibility 6. Describe at least five ways a home health care worker can assist in caring for a disabled child 7. Explain three ways parents can be assisted in the skills of parenting adolescents 8. Discuss the strategies for decreasing adolescent pregnancy 9. Discuss how health care workers can assist adolescents in making informed decisions regarding body piercing and tattoos 10. Summarize the nutritional requirements of the adolescent, and cite two factors that may contribute to dietary deficiencies in this age group 11. Discuss the three leading causes of accidents in adolescence, and suggest methods of prevention for each The development of secondary sexual maturation can be assessed using Tanner staging. Stages are based on breast and pubic hair development for girls and genital and pubic hair development for boys (Table 10-1). Development (growth and sexual maturation) is predictable but variable. Tanner staging provides a more accurate assessment of a child’s development than chronologic age (James and Ashwill, 2007). In most girls, changes in the breast with the development of a small bud of breast tissue (thelarche) signals the earliest sign of puberty. The average age is 11 years. Menarche (onset of menstrual periods) occurs approximately 2 years afterward. Menarche can range from Table 10-1 Sexual Maturation Rating (SMR): Tanner Stages *Breast and pubic hair development may continue into late adolescence and increase with pregnancy. Modified from Tanner, J. M. (1962). Growth at adolescence (2nd ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications; Marshall, W. A., and Tanner, J. (1969). Variations in pattern of pubertal changes in girls. Arch Dis Child, 44(235), 291-303. Modified with permission from Blackwell Scientific Publications and The BMJ Publishing Group. Although breast cancer is rare in adolescents, this is a time when girls are aware of their bodies and breast self-examination should be introduced. Breast self-examination should be routinely performed beginning at 18 to 21 years of age (Fallat et al., 2008). The American Cancer Society provides various informational pamphlets describing the procedure. The first sign of puberty in boys is usually the enlargement of the testes, which begins between Adolescents are in a period of transition from childhood to adulthood (Table 10-2). Erik Erikson identified the major task of this group as identity formation versus role confusion. At this time, children must determine who they are, where they are going, and how they are getting there. This should not imply that adolescents wait until this stage to develop individuation. The child has been developing autonomy since toddlerhood. Table 10-2 Growth and Development During Adolescence Forms stable relationships and attachment to another Growing capacity for mutuality and reciprocity Intimacy involves commitment rather than exploration and romanticism
The Adolescent
General Characteristics and Development
![]() http://evolve.elsevier.com/Price/pediatric/
http://evolve.elsevier.com/Price/pediatric/
![]() Biological Development
Biological Development
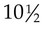 to 15 years and still be within normal guidelines. According to Hockenberry and Wilson (2007), girls’ peak height velocity occurs at about 12 years of age (6 to 12 months before menarche); girls gain 2 to 8 inches in height and 15 to 55 pounds during adolescence. In addition to secondary sex characteristics becoming more apparent before menarche, fat is deposited in the hips and thighs, causing them to enlarge. Hair grows in the pubic area and underarms. The body reaches its adult measurements about 3 years after the onset of puberty. At this time, the ends of the long bones knit securely to their shafts and further growth can no longer take place.
to 15 years and still be within normal guidelines. According to Hockenberry and Wilson (2007), girls’ peak height velocity occurs at about 12 years of age (6 to 12 months before menarche); girls gain 2 to 8 inches in height and 15 to 55 pounds during adolescence. In addition to secondary sex characteristics becoming more apparent before menarche, fat is deposited in the hips and thighs, causing them to enlarge. Hair grows in the pubic area and underarms. The body reaches its adult measurements about 3 years after the onset of puberty. At this time, the ends of the long bones knit securely to their shafts and further growth can no longer take place.
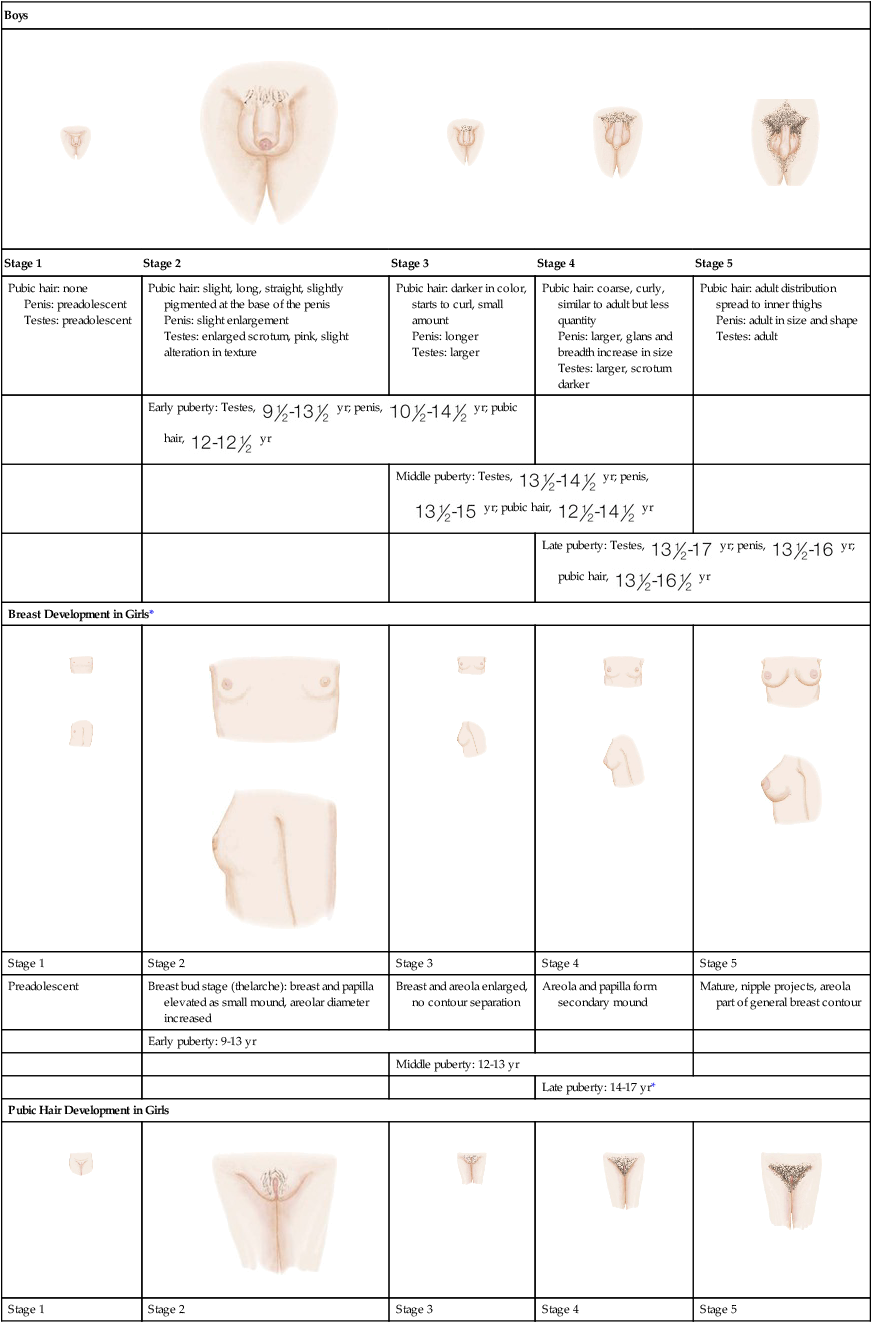
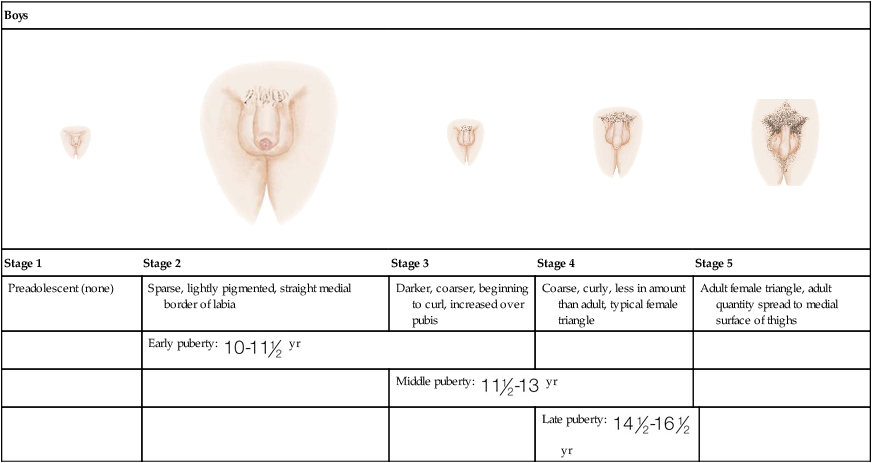
Boys
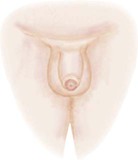
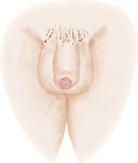
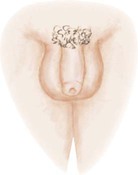
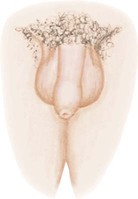
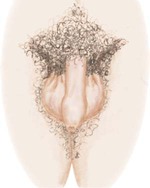
Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
Stage 4
Stage 5
Pubic hair: none
Penis: preadolescent
Testes: preadolescent
Pubic hair: slight, long, straight, slightly pigmented at the base of the penis
Penis: slight enlargement
Testes: enlarged scrotum, pink, slight alteration in texture
Pubic hair: darker in color, starts to curl, small amount
Penis: longer
Testes: larger
Pubic hair: coarse, curly, similar to adult but less quantity
Penis: larger, glans and breadth increase in size
Testes: larger, scrotum darker
Pubic hair: adult distribution spread to inner thighs
Penis: adult in size and shape
Testes: adult
Early puberty: Testes, 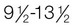 yr; penis,
yr; penis, 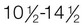 yr; pubic hair,
yr; pubic hair, 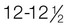 yr
yr
Middle puberty: Testes, 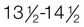 yr; penis,
yr; penis, 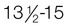 yr; pubic hair,
yr; pubic hair, 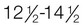 yr
yr
Late puberty: Testes, 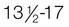 yr; penis,
yr; penis, 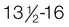 yr; pubic hair,
yr; pubic hair, 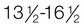 yr
yr
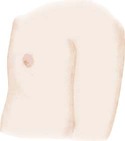
Breast Development in Girls*


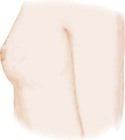

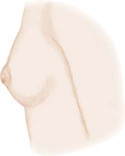

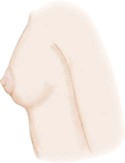
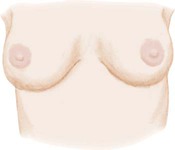
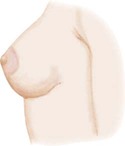
Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
Stage 4
Stage 5
Preadolescent
Breast bud stage (thelarche): breast and papilla elevated as small mound, areolar diameter increased
Breast and areola enlarged, no contour separation
Areola and papilla form secondary mound
Mature, nipple projects, areola part of general breast contour
Early puberty: 9-13 yr
Middle puberty: 12-13 yr
Late puberty: 14-17 yr*
Pubic Hair Development in Girls
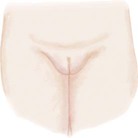
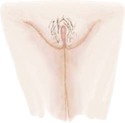
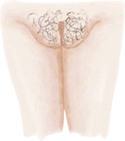
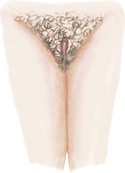

Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
Stage 4
Stage 5
Preadolescent (none)
Sparse, lightly pigmented, straight medial border of labia
Darker, coarser, beginning to curl, increased over pubis
Coarse, curly, less in amount than adult, typical female triangle
Adult female triangle, adult quantity spread to medial surface of thighs
Early puberty: 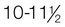 yr
yr
Middle puberty: 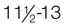 yr
yr
Late puberty: 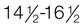 yr
yr
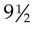 and 14 years of age. Ejaculation and the appearance of pubic hair occur approximately 1 year after this. The production of sperm begins between
and 14 years of age. Ejaculation and the appearance of pubic hair occur approximately 1 year after this. The production of sperm begins between 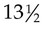 and
and 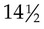 years of age. Complete fertility is not present at this time, but impregnation is possible. According to Hockenberry and Wilson (2007), boys’ peak height velocity occurs at around 14 years of age, followed by growth of the testes and penis. The penis elongates and widens, testes enlarge, and scrotum pigment becomes evident. Both axillary and facial hair increase, along with body odor. Voice changes are also noticeable. By late adolescence (17 to 21 years of age), adult genitalia is attained. The male voice deepens, and most linear growth is achieved. Overall, boys gain 4 to 12 inches in height; weight gain is between 15 and 65 pounds during adolescence.
years of age. Complete fertility is not present at this time, but impregnation is possible. According to Hockenberry and Wilson (2007), boys’ peak height velocity occurs at around 14 years of age, followed by growth of the testes and penis. The penis elongates and widens, testes enlarge, and scrotum pigment becomes evident. Both axillary and facial hair increase, along with body odor. Voice changes are also noticeable. By late adolescence (17 to 21 years of age), adult genitalia is attained. The male voice deepens, and most linear growth is achieved. Overall, boys gain 4 to 12 inches in height; weight gain is between 15 and 65 pounds during adolescence.
Developmental Theories
Early Adolescence (11-14 Yr)
Middle Adolescence (14-17 Yr)
Late Adolescence (17-20 Yr)
Growth
Cognition
Identity
Relationships with Parents
Relationships with Peers
Sexuality
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

The Adolescent
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access