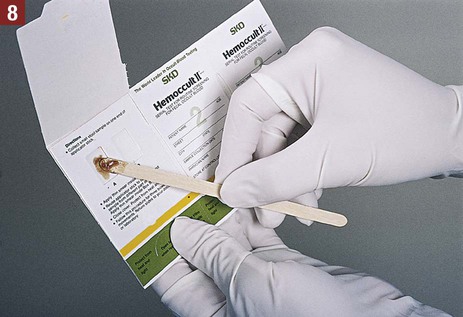
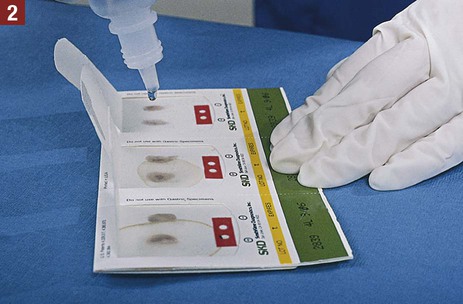
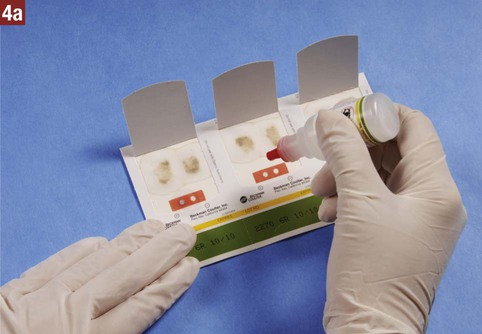
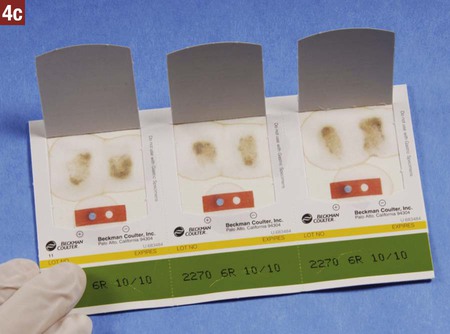
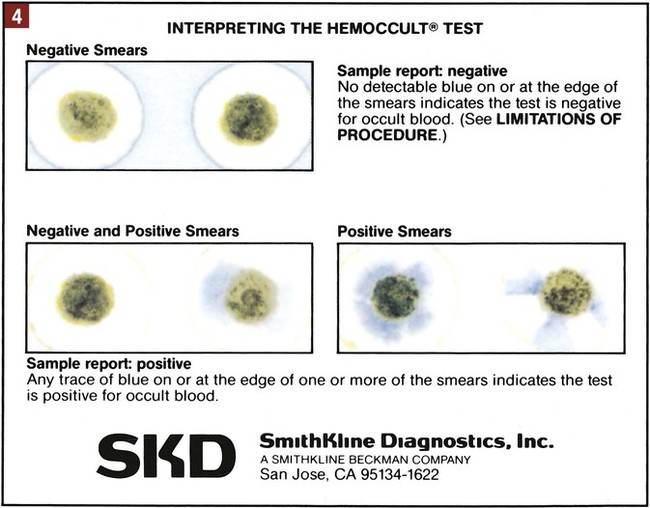
21. Explain how nuclear medicine is used to produce an image of a body part or organ. Routine screening of stool specimens for occult blood is frequently performed in the medical office. The guaiac slide test is a chemical test used to screen for fecal occult blood and is discussed in detail in this chapter. This test is commercially available with the brand names of Hemoccult, ColoScreen (Figure 28-1), and Seracult. Certain medications irritate the gastrointestinal tract, which may result in a small amount of bleeding, and thus could result in a false-positive result on the guaiac slide test. Medications that should be avoided include ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil), naproxen (Aleve), and more than one adult aspirin per day. In addition, an iron supplement may cause a false-positive result, and a vitamin C supplement (greater than 250 mg per day) can cause a false-negative result. All of these substances should be discontinued before testing. Table 28-1 lists the specific patient preparation requirements for fecal occult blood testing using the guaiac slide test. Table 28-1 Patient Preparation for the Fecal Occult Guaiac Slide Test The medical assistant should apply 1 drop of the developing solution between the positive and negative performance monitor areas on each of the three slides. The results must be read within 10 seconds after application of the developer. If the slides and developer are functioning properly, the positive area turns blue, whereas the negative area shows no color change. Failure of the expected control results to occur indicates an error, and the test results are not considered valid; possible causes include the use of outdated slides or developing solution; an error in technique; and subjection of the slides to heat, sunlight, strong fluorescent light, or volatile chemicals. Procedure 28-1 outlines the medical assistant’s responsibilities related to fecal occult blood testing using the Hemoccult guaiac slide test. Procedure 28-2 describes the development of a Hemoccult slide test.
Specialty Examinations and Procedures
Colon Procedures, Male Reproductive Health, and Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
PROCEDURES
Fecal Occult Blood Testing
1. Explain the purpose of a fecal occult blood test.
Instruct a patient in the preparation and procedure for a fecal occult blood test (guaiac slide test).
2. Describe the patient preparation for fecal occult blood testing (guaiac slide method).
Develop a fecal occult blood test.
3. Explain the purpose of each type of preparation for fecal occult blood testing (guaiac slide method).
Sigmoidoscopy
4. Explain the purpose of a digital rectal examination before a sigmoidoscopic examination.
Instruct a patient in the preparation required for a sigmoidoscopy.
5. Explain the purpose of a sigmoidoscopy.
Assist the physician with sigmoidoscopy.
6. Describe the patient preparation for a sigmoidoscopy.
Colonoscopy
7. Explain the purpose of a colonoscopy.
Instruct a patient in the preparation required for a colonoscopy.
8. List the conditions that can be detected and assessed during a colonoscopy.
9. Describe the patient preparation for a colonoscopy.
Male Reproductive Health
10. List the symptoms of prostate cancer.
Assist the physician with a digital rectal examination.
11. Explain the purpose of the digital rectal examination (DRE).
Instruct a patient in the preparation for a PSA test.
12. Explain the purpose of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test.
13. State the risk factors for testicular cancer.
Teach a patient how to perform a testicular self-examination (TSE).
14. Describe the TSE schedule.
Radiology
15. State the function of radiographs in medicine.
16. Explain the importance of proper patient preparation for a radiographic examination.
17. Explain the function of a contrast medium.
18. Describe the purpose of a fluoroscope.
19. Explain the purpose of each of the following types of radiographic examinations:
Instruct a patient in the proper preparation necessary for each of the following types of radiographic examinations:
Diagnostic Imaging
20. Explain the purpose of each of the following diagnostic imaging procedures:
22. State the guidelines that may be required for nuclear medicine.
Instruct a patient on the purpose and advance preparation for each of the following diagnostic imaging procedures:
Digital Radiology
23. Explain the advantages of digital radiology.
Colon Procedures
Introduction to Colon Procedures
Fecal Occult Blood Test
Guaiac Slide Test
Patient Preparation
Dietary and Medication Guidelines
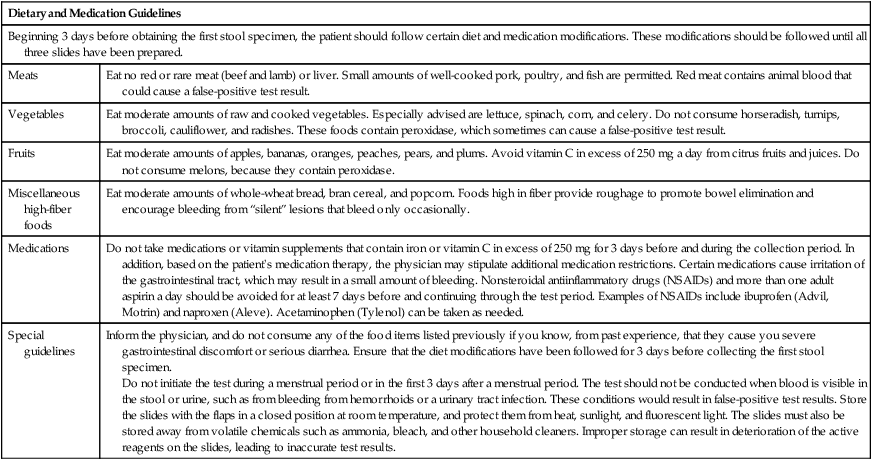
Beginning 3 days before obtaining the first stool specimen, the patient should follow certain diet and medication modifications. These modifications should be followed until all three slides have been prepared.
Meats
Eat no red or rare meat (beef and lamb) or liver. Small amounts of well-cooked pork, poultry, and fish are permitted. Red meat contains animal blood that could cause a false-positive test result.
Vegetables
Eat moderate amounts of raw and cooked vegetables. Especially advised are lettuce, spinach, corn, and celery. Do not consume horseradish, turnips, broccoli, cauliflower, and radishes. These foods contain peroxidase, which sometimes can cause a false-positive test result.
Fruits
Eat moderate amounts of apples, bananas, oranges, peaches, pears, and plums. Avoid vitamin C in excess of 250 mg a day from citrus fruits and juices. Do not consume melons, because they contain peroxidase.
Miscellaneous high-fiber foods
Eat moderate amounts of whole-wheat bread, bran cereal, and popcorn. Foods high in fiber provide roughage to promote bowel elimination and encourage bleeding from “silent” lesions that bleed only occasionally.
Medications
Do not take medications or vitamin supplements that contain iron or vitamin C in excess of 250 mg for 3 days before and during the collection period. In addition, based on the patient’s medication therapy, the physician may stipulate additional medication restrictions. Certain medications cause irritation of the gastrointestinal tract, which may result in a small amount of bleeding. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and more than one adult aspirin a day should be avoided for at least 7 days before and continuing through the test period. Examples of NSAIDs include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve). Acetaminophen (Tylenol) can be taken as needed.
Special guidelines
Inform the physician, and do not consume any of the food items listed previously if you know, from past experience, that they cause you severe gastrointestinal discomfort or serious diarrhea. Ensure that the diet modifications have been followed for 3 days before collecting the first stool specimen.
Do not initiate the test during a menstrual period or in the first 3 days after a menstrual period. The test should not be conducted when blood is visible in the stool or urine, such as from bleeding from hemorrhoids or a urinary tract infection. These conditions would result in false-positive test results. Store the slides with the flaps in a closed position at room temperature, and protect them from heat, sunlight, and fluorescent light. The slides must also be stored away from volatile chemicals such as ammonia, bleach, and other household cleaners. Improper storage can result in deterioration of the active reagents on the slides, leading to inaccurate test results.
Quality Control