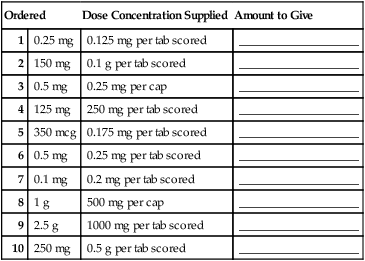
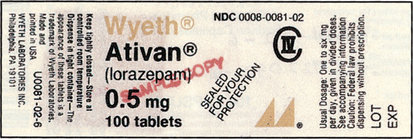
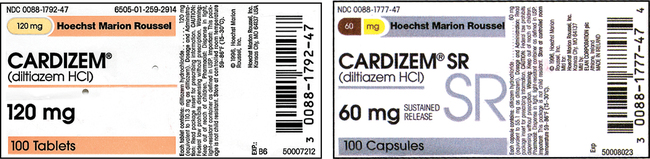
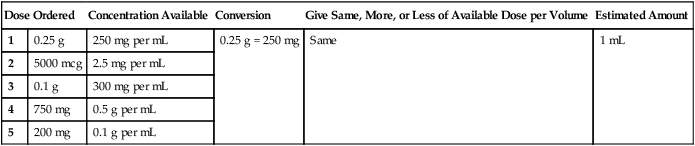
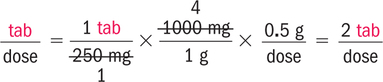• Estimate, calculate, and evaluate a variety of solid and liquid medication doses. • Calculate dosages for liquid medications to the nearest tenth of a milliliter. • Measure oral liquids in a calibrated measuring cup. • Measure syringe volumes in 3- and 5-mL syringes. • Calculate and evaluate safe dose ranges (SDRs) for medication doses.
Solid and Liquid Oral Dose Calculations
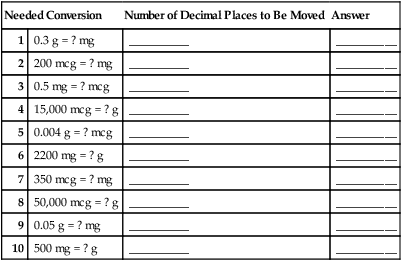
Converting Grams to Micrograms and Micrograms to Grams by Moving Decimal Places
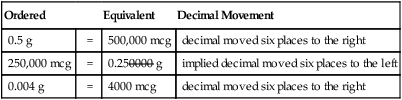
![]() Converting micrograms to grams and grams to micrograms involves two steps—1000 mcg = 1 mg, and 1000 mg = 1 g—for a total of 6 decimal place movements. It is expedient to study the relationships among the mcg/mg/g conversions at one time.
Converting micrograms to grams and grams to micrograms involves two steps—1000 mcg = 1 mg, and 1000 mg = 1 g—for a total of 6 decimal place movements. It is expedient to study the relationships among the mcg/mg/g conversions at one time.
Solid and Liquid Oral Dose Calculations
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access