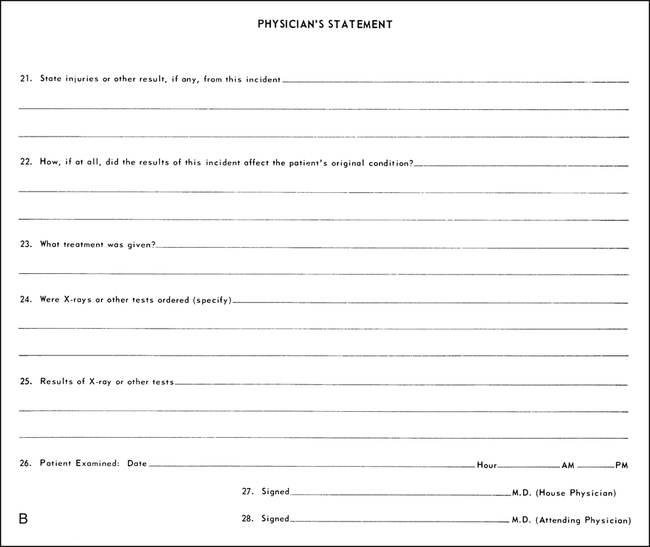
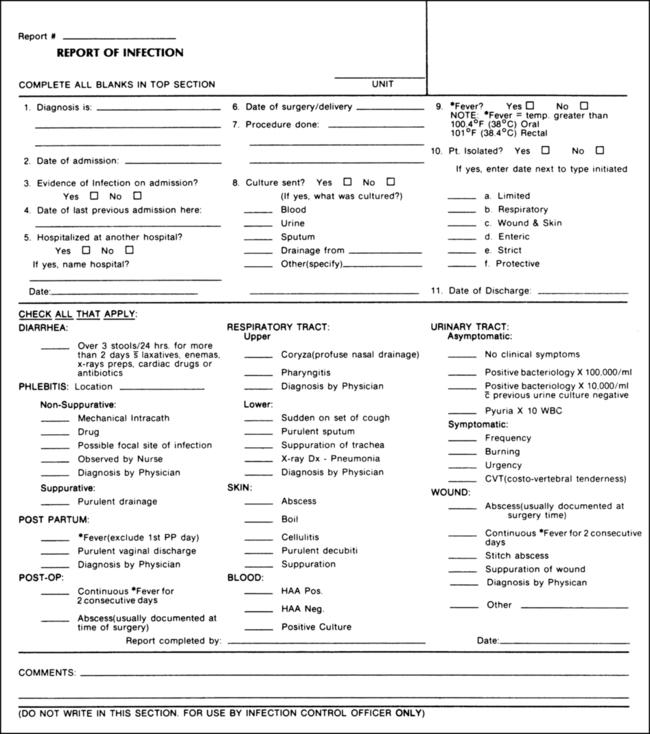
On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define the terms in the vocabulary list. 2. Write the meaning of the abbreviations in the abbreviations list. 3. Identify four categories of incidents that would initiate an incident report, and explain the purpose of completing an incident report. 4. Identify six components that constitute the chain of infection, and list four types of personal protective equipment used as barriers between the practitioner (health care worker) and the patient’s body fluids. 5. List four examples of diagnosed infections that would require a patient to be placed in airborne isolation. 6. Identify the most common way to confirm and identify microorganisms and to determine which antibiotic will destroy the identified microbes. 7. Identify three circumstances that would cause a patient to become immunocompromised and in need of being placed in reverse or protective isolation. 8. Discuss ways in which an individual working in the hospital environment can reduce his or her risk of infection. 9. Discuss four primary ways that the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) may be transmitted from one person to another, and identify two opportunistic diseases related to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). 10. Identify a highly contagious virus transmitted through blood and body fluids and an airborne pathogen that would require health care providers to take extra precautions such as blood and fluid precautions and to use special personal protective equipment (PPE). 11. Discuss the pathogenic microorganisms that are frequently responsible for nosocomial infections and the best way for health care providers to stop the spread of these hospital-acquired infections. 12. Discuss health unit coordinator (HUC) tasks related to prevention of infection in the hospital work environment. 13. Identify the meaning for each of the following color emergency call codes: red, blue, orange, pink, gray, and silver. 14. Identify the communication tool that provides details on chemical dangers and safety procedures. 15. Explain the RACE system, and describe what the responsibilities of the HUC would be during a fire code and a disaster procedure. 16. List six guidelines that should be followed for electrical safety. 17. Identify events that would activate the hospital disaster procedure. 18. List nine tasks that the HUC may perform in a medical emergency. 19. Describe how to handle flowers and mail delivered to the unit. Airborne Precautions (Isolation) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Diseases that may be transmitted from one person to another. An infectious blood-borne disease that is a major occupational hazard for health care workers. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) The virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) A basic hazard communication tool that gives details on chemical dangers and safety procedures. Emergencies that are life-threatening. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infections that are acquired from within the health care facility. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) A U.S. governmental regulatory agency that is concerned with the health and safety of workers. Disease-carrying organisms too small to be seen with the naked eye. Reverse or Protective Isolation A disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, an airborne pathogen. Incidents that require written reports include the following: • Thefts from persons on hospital property • Errors of omission of patient treatment or errors in administration of patient treatment, including medication • Exposure to blood and body fluids, as may be caused by a needle stick An incident report form (Fig. 21-1) should be completed for all incidents that occur to anyone, no matter how insignificant they may seem. Documentation of all incidents is important in identifying hazards and preventing continuing problems, and in the case of a lawsuit that may arise from them. The names and home addresses of witnesses are required in case the incident should result in a lawsuit and the witnesses are no longer employed at the hospital when the case is brought to court. The HUC is responsible for maintaining a supply of incident report forms for the nursing unit. For statistical purposes, records of infectious diseases must be maintained. A report should be submitted to the infectious disease department or to personnel in the hospital (Fig. 21-2). Most hospitals employ an epidemiologist or an infection control officer who maintains all infection records and investigates all hospital-acquired infections. Infection control is essential for providing a safe environment for patients and health care workers. Patients are at risk for acquiring infection because of lowered resistance to infectious microorganisms and increased exposure to numbers and types of disease-causing microorganisms, and because they must often undergo invasive procedures. The presence of a pathogen does not mean that an infection will begin. Development of an infection depends on six components called the chain of infection, as follows (Fig. 21-3):
Reports, Infection Control, Emergencies, and Special Services
Abbreviation
Meaning
AIDS
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
ARC
AIDS-related complex
CDC
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
HBV
hepatitis B virus
HCV
hepatitis C virus
HIV
human immunodeficiency virus
MRSA
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
OSHA
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
PPE
personal protective equipment
RACE
rescue individuals in danger.
alarm: Sound the alarm.
confine the fire by closing all doors and windows.
extinguish the fire with the nearest suitable fire extinguisher.
TB
tuberculosis
Incident Reports
Infection Control
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access