On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define the terms in the vocabulary list. 2. Write the meaning of the abbreviations in the abbreviation list. 3. Explain how and why The Joint Commission’s “Do Not Use” list was developed and identify abbreviations that are on the “Do Not Use” list. 4. Identify patient activity and patient positioning orders. 5. List the four measurements included in a patient’s daily vital signs. 6. Describe five methods of taking a patient’s temperature. 7. Explain how orthostatic vital signs are measured. 8. Identify at least three tests that may be performed at the point of care or bedside (POCT). 9. Explain what type of patient would require blood glucose monitoring, and identify two types of blood glucose monitors that are commonly used. 10. Identify the hospital areas in which pulse oximetry would be used and the reason for it. 11. Identify the nursing unit that would employ a cardiac monitor technician. 12. Explain the function of nursing observation orders, and list at least four examples of nursing observation orders. 13. Explain the reason for a doctor ordering intake and output (I&O), and list the items that would be included in “intake” and “output.” A doctor’s order that defines the type and amount of activity a hospitalized patient may have. Heart rate obtained from the apex of the heart. The temperature reading obtained by placing the thermometer in the patient’s axilla (armpit). The measurement of the pressure of blood against the artery walls. A patient’s temperature, pulse, and respiration, taken at certain times each day. the patient sits and hangs their feet over the edge of the bed. Having an elevated body temperature (a fever). The measurement of the patient’s fluid intake and output. Neurologic Vital Signs (neuro checks) The temperature reading obtained by placing the thermometer in the patient’s mouth under the tongue. Orthostatic Vital Signs Measurement (Orthostatics) A noninvasive measurement of gas exchange and red blood cell oxygen-carrying capacity. The pulse rate obtained on the top of the foot. Medical testing at or near the site of patient care. Doctors’ orders that request that the patient be placed in a specified body position. The number of times per minute the heartbeat is felt through the walls of the artery. Pulse rate obtained on the wrist. The temperature reading obtained by placing the thermometer in the patient’s rectum. The number of times a patient breathes per minute. The quantity of body heat, measured in degrees—Fahrenheit or Celsius. The temperature reading obtained by placing an aural (ear) thermometer in the patient’s ear. Measurements of body functions, including temperature, pulse, respiration, and blood pressure. The Joint Commission (TJC), founded in 1951, has been acknowledged as the leader in developing the highest standards for quality and safety in the delivery of health care. Today more than 19,000 health care providers use TJC standards to guide how they administer care and continuously improve performance. In 2001 TJC issued a Sentinel Event Alert on the subject of medical abbreviations, and 1 year later a National Patient Safety Goal (NPSG) requiring accredited organizations to develop and implement a list of abbreviations not to use. In 2002 TJC established its NPSG program to help accredited organizations address specific areas of concern regarding patient safety. A panel called the Patient Safety Advisory Group composed of nurses, physicians, pharmacists, risk managers, clinical engineers, and other professionals works with and advises TJC staff to identify and address emerging patient safety issues. In 2004 TJC created its “do not use” list of abbreviations as part of the requirements for meeting that goal (Table 10-1). TABLE 10-1 The Joint Commission’s Official “Do Not Use” List∗
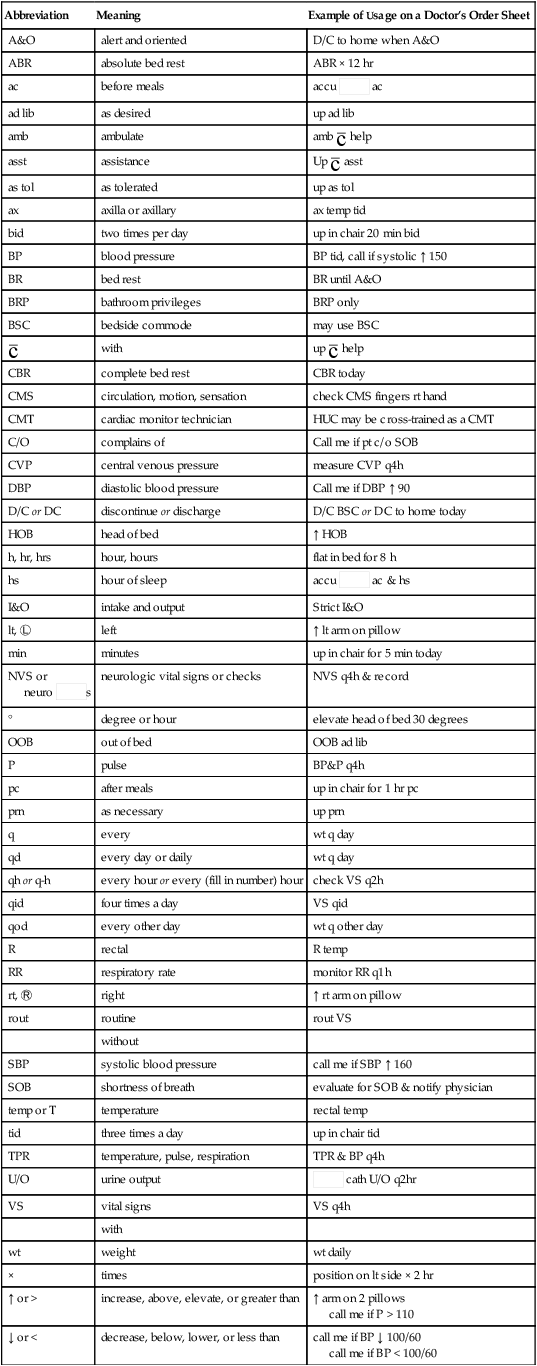
Patient Activity, Patient Positioning, and Nursing Observation Orders
Abbreviation
Meaning
Example of Usage on a Doctor’s Order Sheet
A&O
alert and oriented
D/C to home when A&O
ABR
absolute bed rest
ABR × 12 hr
ac
before meals
accu  ac
ac
ad lib
as desired
up ad lib
amb
ambulate
amb  help
help
asst
assistance
Up  asst
asst
as tol
as tolerated
up as tol
ax
axilla or axillary
ax temp tid
bid
two times per day
up in chair 20 min bid
BP
blood pressure
BP tid, call if systolic ↑ 150
BR
bed rest
BR until A&O
BRP
bathroom privileges
BRP only
BSC
bedside commode
may use BSC
with
up 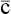 help
help
CBR
complete bed rest
CBR today
CMS
circulation, motion, sensation
check CMS fingers rt hand
CMT
cardiac monitor technician
HUC may be cross-trained as a CMT
C/O
complains of
Call me if pt c/o SOB
CVP
central venous pressure
measure CVP q4h
DBP
diastolic blood pressure
Call me if DBP ↑ 90
D/C or DC
discontinue or discharge
D/C BSC or DC to home today
HOB
head of bed
↑ HOB
h, hr, hrs
hour, hours
flat in bed for 8 h
hs
hour of sleep
accu 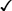 ac & hs
ac & hs
I&O
intake and output
Strict I&O
lt, Ⓛ
left
↑ lt arm on pillow
min
minutes
up in chair for 5 min today
NVS or
neuro 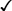 s
s
neurologic vital signs or checks
NVS q4h & record
°
degree or hour
elevate head of bed 30 degrees
OOB
out of bed
OOB ad lib
P
pulse
BP&P q4h
pc
after meals
up in chair for 1 hr pc
prn
as necessary
up prn
q
every
wt q day
qd
every day or daily
wt q day
qh or q-h
every hour or every (fill in number) hour
check VS q2h
qid
four times a day
VS qid
qod
every other day
wt q other day
R
rectal
R temp
RR
respiratory rate
monitor RR q1h
rt, Ⓡ
right
↑ rt arm on pillow
rout
routine
rout VS
without
SBP
systolic blood pressure
call me if SBP ↑ 160
SOB
shortness of breath
evaluate for SOB & notify physician
temp or T
temperature
rectal temp
tid
three times a day
up in chair tid
TPR
temperature, pulse, respiration
TPR & BP q4h
U/O
urine output
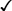 cath U/O q2hr
cath U/O q2hr
VS
vital signs
VS q4h
with
wt
weight
wt daily
×
times
position on lt side × 2 hr
↑ or >
increase, above, elevate, or greater than
↑ arm on 2 pillows
call me if P > 110
↓ or <
decrease, below, lower, or less than
call me if BP ↓ 100/60
call me if BP < 100/60

The Joint Commission
Do Not Use
Potential Problem
Use Instead
U, u (unit)
Mistaken for “0” (zero), the number “4” (four) or “cc”
Write “unit”
IU (International Unit)
Mistaken for IV (intravenous) or the number 10 (ten)
Write “International Unit”
Q.D., QD, q.d., qd (daily)
Q.O.D., QOD, q.o.d, qod
(every other day)
Mistaken for each other
Period after the Q mistaken for “I” and the “O” mistaken for “I”
Write “daily”
Write “every other day”
Trailing zero (X.0 mg)†
Lack of leading zero (.X mg)
Decimal point is missed
Write X mg
Write 0.X mg
MS
MSO4 and MgSO4
Can mean morphine sulfate or magnesium sulfate
Confused for each other
Write “morphine sulfate”
Write “morphine sulfate” or “magnesium sulfate”
Additional Abbreviations, Acronyms, and Symbols for Possible Future Inclusion in the Official “Do Not Use” List
> (greater than)
< (less than)
Misinterpreted as the number “7” (seven) or the letter “L”
Confused for each other
Write “greater than”
Write “less than”
Abbreviations for drug names
Misinterpreted due to similar abbreviations for
multiple drugs
Write drug names in full
Apothecary units
Unfamiliar to many practitioners
Confused with metric units
Use metric units
@
Mistaken for the number “2” (two)
Write “at”
cc
Mistaken for U (units) when poorly written
Write “mL”
or “ml” or “milliliters”
(“mL” is preferred)
μg
Mistaken for mg (milligrams), resulting in one thousand–fold overdose
Write “mcg” or “micrograms” ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Patient Activity, Patient Positioning, and Nursing Observation Orders
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
