Chapter 10 Oncology
Basic concepts—cell biology of cancer
4 What are the phases of the cell cycle? Where is the restriction point?
Most cells in the human body are quiescent (i.e., not actively dividing). Exceptions include cells of the hematopoietic system, the integument, and the intestinal mucosa. However, those cells that divide follow a well-defined cyclic pattern. Major challenges in cell replication include high-fidelity DNA duplication (in the S phase) and segregation of chromosomes into daughter cells (during mitosis or the M phase). Different phases and checkpoints help address these issues (Fig. 10-1):
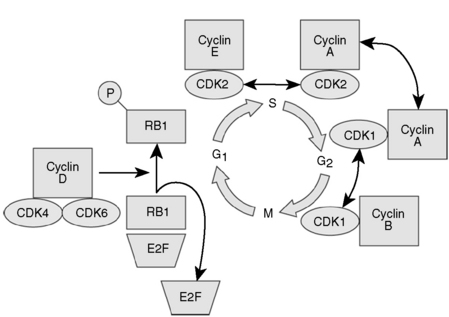
Figure 10-1 Regulation of the cell cycle.
(From Hoffman R, Benz EJ Jr, Shattil SJ, et al: Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice, 4th ed. Philadelphia, Churchill Livingstone, 2005.)
5 What is the function of checkpoints and cell cycle arrests?
Cyclins are proteins that regulate progression from one phase of the cell cycle to the next. Cyclins phosphorylate cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) to form cyclin-CDK complexes that must be in either an activated or inactivated state for various cell cycle stages to commence or terminate. CDKs are regulated by CDK inhibitors such as p16, p21, and p27. If these CDK inhibitors are mutated, the cell cycle becomes deregulated and cancer can result. Table 10-1 lists the regulators of the cell cycle that you should know for boards.
Table 10-1 Regulators of the Cell Cycle
| Stage | Promoter(s) | Inhibitor |
|---|---|---|
| G1 to S | Cyclin D/CDK4 and CDK6 Cyclin E-CDK2 | p53 Rb |
| S to G2 | Cyclin A-CDK2 | — |
| G2 to M | Cyclin B-CDK1 CDc25 | — |
Basic concepts—cancer epidemiology
12 Aside from skin cancer, which cancers have the highest incidence in men and in women? Which cancers are the leading cause of death in men and in women?
Cancers with the highest incidence in men:
Cancers with the highest incidence in women:
Leading causes of cancer deaths in men:
Leading causes of cancer deaths in women:
Basic concepts—cancer classification
13 What is the difference between “grade” and “stage” of a neoplasm?
 T: Tumor size. T refers to local growth measured by the size of the primary tumor.
T: Tumor size. T refers to local growth measured by the size of the primary tumor.
 N: Nodes. N refers to the involvement of regional lymph nodes and is an indication of the extent of tumor spread.
N: Nodes. N refers to the involvement of regional lymph nodes and is an indication of the extent of tumor spread.
 M: Metastases. M refers to the presence or absence of distant metastases. Presence of metastases typically confers a high stage.
M: Metastases. M refers to the presence or absence of distant metastases. Presence of metastases typically confers a high stage.
Staging is most helpful in determining prognosis. Higher stages indicate a poorer prognosis.
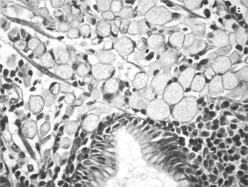
8 In gastric adenocarcinoma, what are the two histologic patterns in which neoplastic cells can distribute?
Diffuse type: In this pattern, there is no cellular cohesion. Neoplastic cells invade the wall of the stomach diffusely without producing a distinct lesion. This type tends to occur in younger patients and has a poor prognosis. Note: Diffuse gastric adenocarcinomas present with signet ring cells (Fig. 10-2).
Intestinal type: In this pattern, cells do cohere and form glandular structures that often have an ulcerative appearance. Lesions are most often found in the antrum and lesser curvature of the stomach. This type tends to occur in older patients and has a better prognosis than the diffuse type.
10 If the patient were to be examined again at a much later stage of disease, what specific signs might be found on physical examination that might indicate metastasis?
11 In retrospect, what aspects of this patient’s presentation are most suspicious for gastric cancer?
 Onset of dyspepsia after age 40
Onset of dyspepsia after age 40
 Unintentional weight loss of 10 lb in 3 months
Unintentional weight loss of 10 lb in 3 months
 No response to proton pump inhibitor therapy
No response to proton pump inhibitor therapy
Summary Box: Gastric Adenocarcinoma
 The presentation of gastric adenocarcinoma is very similar to that of peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
The presentation of gastric adenocarcinoma is very similar to that of peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
 From 60% to 90% of cases of distal gastric adenocarcinoma are attributed to chronic Helicobacter pylori infection.
From 60% to 90% of cases of distal gastric adenocarcinoma are attributed to chronic Helicobacter pylori infection.
 An ulcerated gastric lesion should always be biopsied because as many as 5% may harbor gastric cancer cells.
An ulcerated gastric lesion should always be biopsied because as many as 5% may harbor gastric cancer cells.
 Adenocarcinoma comprises almost all gastric cancers and can be classified by gross or microscopic pathologic appearance.
Adenocarcinoma comprises almost all gastric cancers and can be classified by gross or microscopic pathologic appearance.
 Adenocarcinoma may produce distinct lesions or may infiltrate the stomach diffusely.
Adenocarcinoma may produce distinct lesions or may infiltrate the stomach diffusely.
3 What do the following physical examination findings indicate?
Dermatitis or Paget carcinoma is possible. Although nipple erosions most frequently represent a dermatitis or bacterial infection, this sign may also indicate an underlying ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). As pictured in Figure 10-3, the neoplastic cells propagate toward the surface of the breast without violating the basement membrane. The presence of neoplastic cells does violate the epithelial barrier, allowing extrusion of extracellular fluid onto the nipple surface.
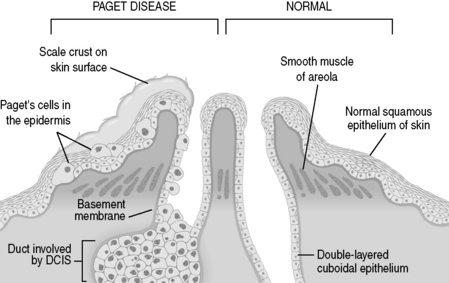
Figure 10-3 Paget disease of the nipple. DCIS, ductal carcinoma in situ.
(From Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N: Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 7th ed. Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 2005.)
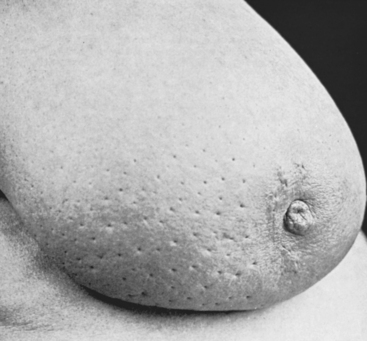
Inflammatory carcinoma is possible. Invasion of the subdermal lymphatics by carcinoma can cause spreading erythema that can often be mistaken for infection. Resultant edema produces typical peau d’orange appearance (Fig. 10-4).
4 What is the most common cause of a dominant breast mass for a woman in her 20s?
6 What disease is she at risk for with the finding of bilateral breast masses and a family history of two first-degree relatives?
7 What specific genetic mutations confer a lifetime risk of 50% to 85% for developing breast cancer?
8 If her tumor is found to be positive for BRCA1, for what other malignancy would this patient be at risk?
She would be at risk for ovarian cancer.
9 What are the common histologic types of breast cancer?
Carcinomas are divided into two broad categories: in situ and invasive carcinomas.
Breast cancers are also classified as ductal or lobular based on where they arise: Ductal origin refers to cancers arising from the epithelial lining of the large or intermediate-sized ducts, and lobular origin refers to cancers arising from the epithelium of the terminal ducts of the lobules (Fig. 10-5).
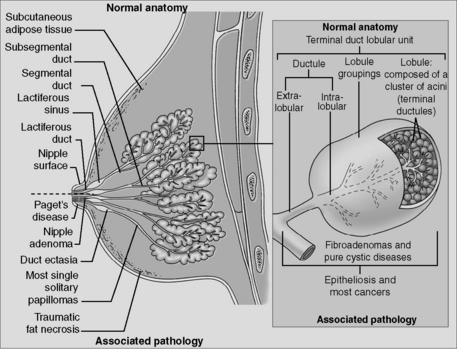
Figure 10-5 Anatomy of the breast.
(From Hayes D: Breast cancer. In Skarin AT [ed]: Atlas of Diagnostic Oncology. Philadelphia, Lippincott, 1991.)
 In situ carcinoma describes a neoplastic population of cells that has not penetrated the basement membrane of the affected duct or lobule.
In situ carcinoma describes a neoplastic population of cells that has not penetrated the basement membrane of the affected duct or lobule.
 DCIS makes up 80% of in situ carcinomas. Approximately half of mammographically detected cancers are DCIS because they tend to present with calcifications. DCIS is thought to progress to invasive ductal carcinoma in most women.
DCIS makes up 80% of in situ carcinomas. Approximately half of mammographically detected cancers are DCIS because they tend to present with calcifications. DCIS is thought to progress to invasive ductal carcinoma in most women.
 Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) never forms a density or calcifications and is therefore always an incidental finding on breast biopsy. It is found to be bilateral in 20% to 40% of women and turns into invasive cancer at a rate of approximately 1% per year; therefore, LCIS can be thought of as a risk factor for the development of invasive carcinoma.
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) never forms a density or calcifications and is therefore always an incidental finding on breast biopsy. It is found to be bilateral in 20% to 40% of women and turns into invasive cancer at a rate of approximately 1% per year; therefore, LCIS can be thought of as a risk factor for the development of invasive carcinoma.
 Ductal carcinoma accounts for up to 80% of invasive carcinomas. Most histologic types of invasive cancer (colloid, medullary, etc.) are subtypes of invasive ductal carcinoma.
Ductal carcinoma accounts for up to 80% of invasive carcinomas. Most histologic types of invasive cancer (colloid, medullary, etc.) are subtypes of invasive ductal carcinoma.
 Lobular carcinoma shows the classic histologic description of linear arrangements of cells (sometimes only one cell wide) invading surrounding tissue.
Lobular carcinoma shows the classic histologic description of linear arrangements of cells (sometimes only one cell wide) invading surrounding tissue.
 Medullary carcinoma is found in women with the BRCA1 gene; up to 13% of cancers are of this type.
Medullary carcinoma is found in women with the BRCA1 gene; up to 13% of cancers are of this type.
10 What are two important biomarkers of a breast cancer that help guide treatment?
 Estrogen receptor (ER)/progesterone receptor (PR): If these receptors are present in the cytoplasm of cancer cells, then there is a better prognosis. After resection, patients are typically treated with tamoxifen (a selective estrogen receptor modulator [SERM]), which inhibits endogenous hormone stimulation of tumor cells. As a result, breast cancer is less likely to recur and mortality rate may be decreased by as much as 25% among women with receptor-positive tumors. Anastrazole (an aromatase inhibitor) is used when the patient has contraindications to tamoxifen use.
Estrogen receptor (ER)/progesterone receptor (PR): If these receptors are present in the cytoplasm of cancer cells, then there is a better prognosis. After resection, patients are typically treated with tamoxifen (a selective estrogen receptor modulator [SERM]), which inhibits endogenous hormone stimulation of tumor cells. As a result, breast cancer is less likely to recur and mortality rate may be decreased by as much as 25% among women with receptor-positive tumors. Anastrazole (an aromatase inhibitor) is used when the patient has contraindications to tamoxifen use.
 HER2/neu (also known as ERBB2): If a patient has a metastatic breast carcinoma that overexpresses this gene, trastuzumab (Herceptin) may be used. Trastuzumab is a monoclonal antibody directed against the HER-2 protein. When used with first-line chemotherapy following surgery, trastuzumab increases the time to disease progression.
HER2/neu (also known as ERBB2): If a patient has a metastatic breast carcinoma that overexpresses this gene, trastuzumab (Herceptin) may be used. Trastuzumab is a monoclonal antibody directed against the HER-2 protein. When used with first-line chemotherapy following surgery, trastuzumab increases the time to disease progression.
 Nontender, firm breast masses with poorly delineated margins are concerning for invasive breast cancer.
Nontender, firm breast masses with poorly delineated margins are concerning for invasive breast cancer.
 Other findings concerning for breast cancer include nipple discharge, nipple scaling, breast asymmetry, nipple inversion, peau d’orange, erythema, and warmth.
Other findings concerning for breast cancer include nipple discharge, nipple scaling, breast asymmetry, nipple inversion, peau d’orange, erythema, and warmth.
 The most common cause of breast masses in young women is fibroadenoma.
The most common cause of breast masses in young women is fibroadenoma.
 BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations predispose to the development of breast cancer and account for approximately 25% of familial breast cancer syndromes.
BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations predispose to the development of breast cancer and account for approximately 25% of familial breast cancer syndromes.
 BRCA1 mutations additionally confer increased risk for development of ovarian cancer.
BRCA1 mutations additionally confer increased risk for development of ovarian cancer.
 Most breast cancers arise from the intermediate ducts and are invasive (invasive ductal carcinoma).
Most breast cancers arise from the intermediate ducts and are invasive (invasive ductal carcinoma).
 Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is thought to progress to invasive ductal carcinoma in most women.
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is thought to progress to invasive ductal carcinoma in most women.
 Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) progresses to invasive lobular carcinoma in some women but not at the same rate of DCIS progression.
Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) progresses to invasive lobular carcinoma in some women but not at the same rate of DCIS progression.
 Estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor (ER/PR) and HER2/neu (ERBB2) are important biomarkers and may guide adjuvant therapy for breast cancer following resection.
Estrogen receptor/progesterone receptor (ER/PR) and HER2/neu (ERBB2) are important biomarkers and may guide adjuvant therapy for breast cancer following resection.