CHAPTER 109 Drugs that alter the pH of urine can accelerate the excretion of organic acids and bases. Agents that elevate urinary pH (ie, make the urine more alkaline) will promote the excretion of acids. Drugs that lower urinary pH will promote the excretion of bases. The mechanism underlying these effects is called ion trapping (see Chapter 4). The drugs given to treat heavy metal poisoning are called chelating agents or chelators. These agents interact with metals to form chelates—ring structures in which the metal and the chelating agent form two or more points of attachment. The chelate formed by mercury and dimercaprol illustrates this concept (Fig. 109–1).
Management of poisoning
Drugs and procedures used for poison removal
Drugs that enhance renal excretion
Specific antidotes
Heavy metal antagonists
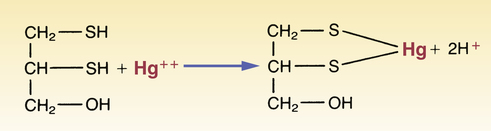
 Chelation of mercury by dimercaprol.
Chelation of mercury by dimercaprol.![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Management of poisoning
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
