Chapter 9 Male and Female Reproductive Systems
Basic concepts
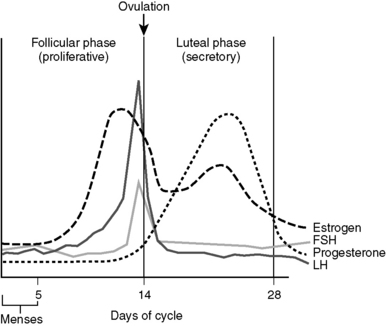
1 What is the normal duration of the menstrual cycle? What are the two ovarian phases, and which occurs first?
Normal cycle time is approximately 28 days, and the ovarian phases consist of the follicular and luteal phases, with the follicular phase occurring first. The first day of the menstrual cycle (and follicular phase) is defined as the day on which menstruation begins (Fig. 9-1).
6 What happens in the ovary and endometrium during the luteal phase?
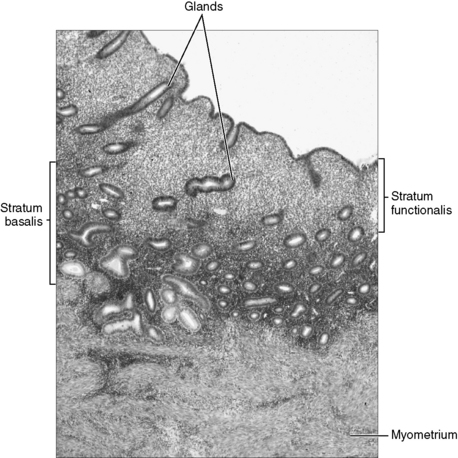
You are expected to be able to differentiate between the histologic appearances of the endometrial lining during the follicular and luteal phases (Fig. 9-2). Notice the glandular hypertrophy, irregular shape of glands, and well-developed spiral arteries in the luteal (secretory) phase. In contrast, the glands in the follicular phase are smaller and straighter, and there is less vascularity in the stroma.
7 In women with amenorrhea (absence of menses), why does bleeding after the cessation of a brief course of progesterone indicate that the cause of amenorrhea is due to the lack of ovulation?
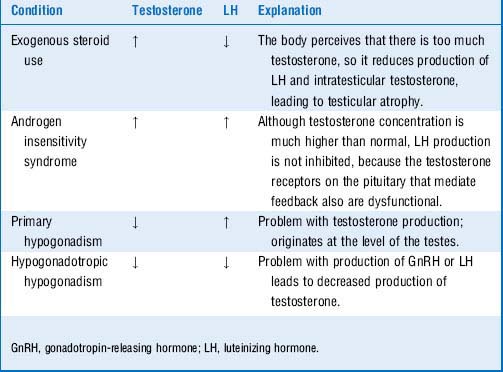
13 What is 5α-reductase deficiency?
The enzyme 5α-reductase is responsible for converting testosterone into DHT. Because DHT stimulates the production of male external genitalia and the prostate, lack of DHT at birth leads to ambiguous external genitalia in these males. Internal genitalia are unaffected, because testicular development is governed exclusively by the presence of the Y chromosome. At puberty, increased concentrations of testosterone are adequate to stimulate development of the male external genitalia (Table 9-1). Patients with this autosomal recessive condition are thus said to develop a “penis at 12.”
Disorders that influence the development of male and female genitalia are high-yield for Step 1. Do not be surprised if you receive a question on your test that asks you to identify whether various hormone levels are increased/decreased/normal in a patient with a genital development disorder. Use Table 9-1 as a guide.
4 What do oral contraceptives typically consist of and what is their mechanism of action?
Other methods of hormonal contraception:
 Transdermal patch and the vaginal ring are other forms of the estrogen and progesterone therapy.
Transdermal patch and the vaginal ring are other forms of the estrogen and progesterone therapy.
 Injectable progesterone is an intramuscular form of progesterone injected every 3 months.
Injectable progesterone is an intramuscular form of progesterone injected every 3 months.
6 Your patient asks if taking hormonal contraceptives will increase her risk for endometrial cancer. How does taking oral contraceptives affect the risk of endometrial, ovarian, and breast cancer? What is supposed to explain this effect?
8 Why may the drugs phenytoin, phenobarbital, and rifampin make oral contraceptives less effective at preventing pregnancy?
Summary Box: Oral Contraceptives
 Hormonal contraceptives increase the risk for thromboembolic events. They are contraindicated for smokers over age 35.
Hormonal contraceptives increase the risk for thromboembolic events. They are contraindicated for smokers over age 35.
 Hormonal contraceptives can be progesterone-only or a combination of estrogen and progesterone.
Hormonal contraceptives can be progesterone-only or a combination of estrogen and progesterone.
 It is principally the withdrawal of progesterone (not estrogen) that causes normal menses.
It is principally the withdrawal of progesterone (not estrogen) that causes normal menses.
 Hormonal contraceptives decrease risk of ovarian and endometrial cancer. How they affect the risk of breast cancer is unclear.
Hormonal contraceptives decrease risk of ovarian and endometrial cancer. How they affect the risk of breast cancer is unclear.
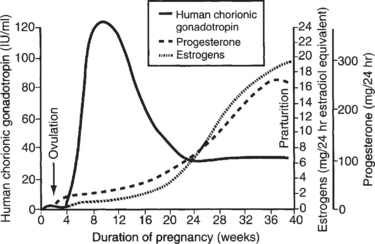
4 What is β-human chorionic gonadotropin and what is its normal function, aside from serving as a marker for pregnancy?
The hormone β-hCG is similar in structure and activity to LH. It is secreted early in pregnancy by the placenta (specifically, the syncytiotrophoblast cells) and functions to maintain the corpus luteum, which is the principal site of ovarian steroidogenesis during the luteal phase. Production begins approximately 1 week after conception and doubles in quantity every 2 days. The hormone is detectable in the blood by 8 days after conception and in the urine approximately 14 days after conception (around the time a woman would expect her next period). Plasma levels of β-hCG peak in the first trimester (by 10 weeks of gestation). Then, as the placenta begins to take over as the main site of maternal estrogen and progesterone secretion, β-hCG levels taper off (Fig. 9-3).
5 Relative to a normal pregnancy, how would the β-human chorionic gonadotropin level differ for an ectopic pregnancy?
6 Assuming the positive β-human chorionic gonadotropin test confirms a pregnancy in this woman, what was the approximate date of conception?
7 What is the difference between the gestational age and the time since conception (developmental age)?
9 What is fetal alcohol syndrome?
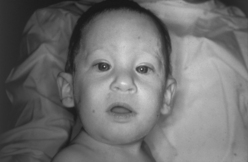
Fetal alcohol syndrome is the leading cause of congenital malformations in the United States and results from excessive alcohol intake during pregnancy. It is associated with a wide range of congenital defects including mental retardation, microcephaly, seizures, and motor disorders, all of which result from a disruption of neuroblast migration. Other defects include limb dislocation, heart abnormalities, and facial abnormalities (flat nasal bridge, upturned nose, “railroad track” ears, epicanthal folds, smooth philtrum, and small palpebral fissures) (Fig. 9-4).
10 The risk of which fetal developmental abnormalities can be reduced by taking supplemental folic acid early during pregnancy?
12 Why should ergot alkaloids (e.g., ergonovine), triptans (e.g., sumatriptan), and synthetic prostaglandins (e.g., misoprostol) all be stringently avoided during pregnancy?
Summary Box: Secondary Amenorrhea
 Most common cause: Pregnancy. Always check serum β-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)levels.
Most common cause: Pregnancy. Always check serum β-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)levels.
 β-hCG levels peak at 10 weeks gestation (approximately 100,000 mIU/mL).
β-hCG levels peak at 10 weeks gestation (approximately 100,000 mIU/mL).
 Ectopic pregnancies are associated with low β-hCG levels, and β-hCG levels do not double every 48 hours as they do in normal pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancies are associated with low β-hCG levels, and β-hCG levels do not double every 48 hours as they do in normal pregnancy.
 Gestational age is determined from the first day of the last menstrual period and is therefore 2 weeks earlier than the date of conception.
Gestational age is determined from the first day of the last menstrual period and is therefore 2 weeks earlier than the date of conception.
1 What is the differential diagnosis for first-trimester bleeding (<12-14 weeks)?
Case 9-3 continued:
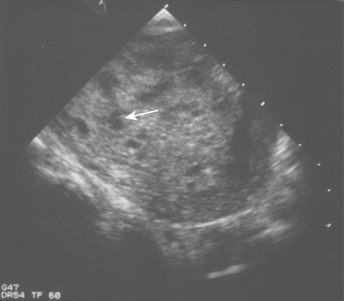
She has not been seen in clinic, but she knows she is pregnant by a positive urine pregnancy test. She has had severe nausea and vomiting but thinks that is normal “morning sickness.” You are concerned about a spontaneous abortion and ectopic pregnancy. A pelvic ultrasound (Fig. 9-5) reveals a “snowstorm” pattern and no discernible fetus. Serum β-hCG levels are elevated far and above what would be expected during pregnancy.
3 How can β-human chorionic gonadotropin levels differentiate between a normal pregnancy and a molar pregnancy (complete or incomplete mole)?
4 What is the difference between an invasive mole and choriocarcinoma and from what does each generally arise?
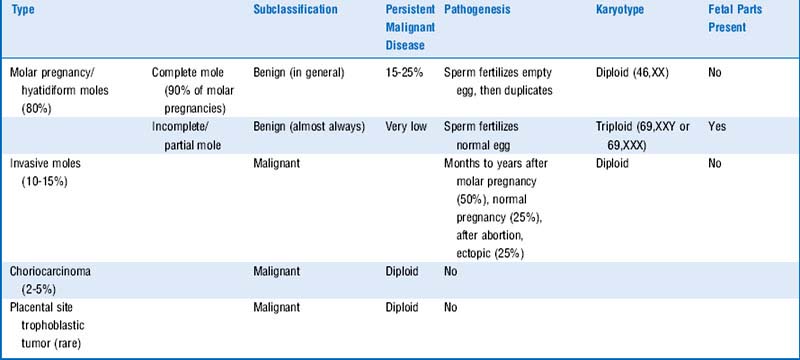
5 Cover the columns on the right side of Table 9-2 and try to identify the characteristics of the different gestational trophoblastic diseases
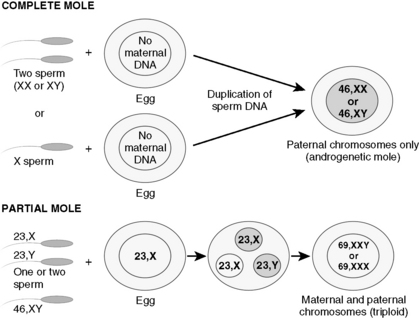
See Table 9-2 and Figure 9-6.
Summary Box: First-Trimester Bleeding and Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
 Molar pregnancy is characterized by heavy vaginal bleeding in the first trimester, passage of “grape like vesicles,” snowstorm appearance on ultrasound, and increase in normal β-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level.
Molar pregnancy is characterized by heavy vaginal bleeding in the first trimester, passage of “grape like vesicles,” snowstorm appearance on ultrasound, and increase in normal β-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level.
 Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) refers to abnormal proliferation of placental tissue: mostly benign; molar pregnancies; and the malignant GTD: invasive moles, choriocarcinoma, and placental site trophoblastic tumor (PSTT).
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) refers to abnormal proliferation of placental tissue: mostly benign; molar pregnancies; and the malignant GTD: invasive moles, choriocarcinoma, and placental site trophoblastic tumor (PSTT).
 Complete moles are the most common molar pregnancy and have a higher percentage of persistent malignant disease.
Complete moles are the most common molar pregnancy and have a higher percentage of persistent malignant disease.
2 What would you like to do for further workup?
A thyroid panel to rule out hyperthyroidism would be helpful.
5 How are maternal levels of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone likely to be affected in this woman, given that she is pregnant?
6 Why is the decline in estrogen and progesterone after delivery beneficial for the beginning of lactation?
7 How does breastfeeding act as a natural contraceptive?
Summary Box: Endocrinology of Pregnancy
 In pregnancy the total thyroxine (T4) is usually elevated because estrogen increases the synthesis of thyroxine-binding globulin by the liver.
In pregnancy the total thyroxine (T4) is usually elevated because estrogen increases the synthesis of thyroxine-binding globulin by the liver.
 Increases in free T4 and triiodothyronine (T3) levels results in hyperthyroidism.
Increases in free T4 and triiodothyronine (T3) levels results in hyperthyroidism.
 High levels of prolactin in a nursing mother inhibit hypothalamic secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), resulting in reduced gonadotropin secretion and suppression of ovulation.
High levels of prolactin in a nursing mother inhibit hypothalamic secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), resulting in reduced gonadotropin secretion and suppression of ovulation.