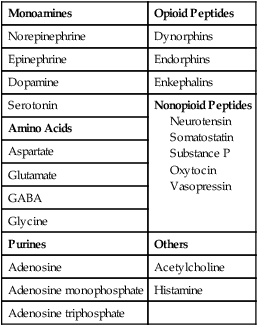
CHAPTER 20 In contrast to the peripheral nervous system, in which only three compounds—acetylcholine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine—serve as neurotransmitters, the CNS contains at least 21 compounds that serve as neurotransmitters (Table 20–1). Furthermore, since there are numerous sites within the CNS for which no transmitter has been identified, it is clear that additional compounds, yet to be discovered, also mediate central neurotransmission. TABLE 20–1
Introduction to central nervous system pharmacology
Transmitters of the CNS

Monoamines
Opioid Peptides
Norepinephrine
Dynorphins
Epinephrine
Endorphins
Dopamine
Enkephalins
Serotonin
Nonopioid Peptides
Neurotensin
Somatostatin
Substance P
Oxytocin
Vasopressin
Amino Acids
Aspartate
Glutamate
GABA
Glycine
Purines
Others
Adenosine
Acetylcholine
Adenosine monophosphate
Histamine
Adenosine triphosphate
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


