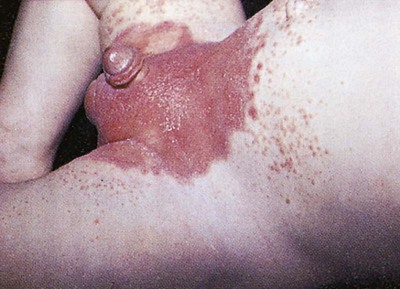
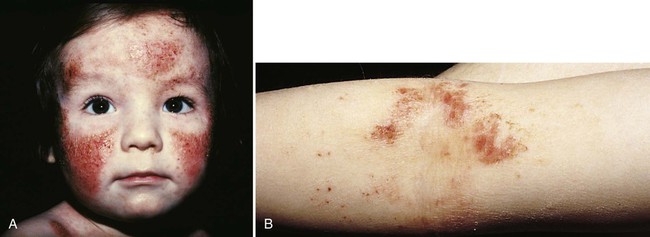
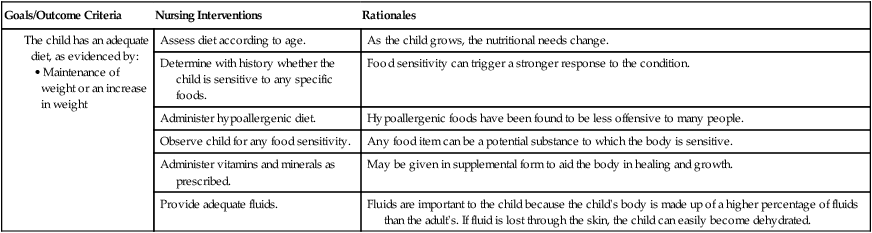
1. Define the vocabulary terms listed 2. Differentiate diaper dermatitis from candidiasis 3. Summarize the nursing care for an infant who has atopic dermatitis, and give the rationale for each nursing measure 4. Discuss care of the child with impetigo 5. Identify complications associated with Staphylococcus 6. Discuss care of the child with cellulitis 7. Define two sources of pediculosis transmission 8. Identify two methods of evaluating burn injury 9. Discuss wound management precautions associated with burn injury White patches that resemble milk curds are visible on the tongue, inner lips, gums, and oral mucosa. Initially, these are painless but do not wipe away. The patches may bleed if attempts are made to scrape them away. Because of the discomfort, anorexia may be present. The systemic symptoms are mild if the infection remains in the mouth; however, it can pass along the mucous membranes into the gastrointestinal tract, causing inflammation of the esophagus and stomach. The infant may develop a beefy red, weeping diaper rash in the genitalia area (see Diaper Dermatitis). Development of symptoms indicates that the infant is oversensitive to certain substances called allergens, which enter the body via the digestive tract (food), inhalation (dust, pollen), direct contact (wool, soap, strong sunlight), or injections (insect bites, vaccines). Of children who have atopic dermatitis, 50% to 60% present with symptoms in the first year of life and 80% to 85% present by 5 years of age. Overall, 10% to 20% of children are affected by the disease (Cardona et al., 2006). Many children (80%) develop the triad of atopic dermatitis, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. The nurse should establish a good working relationship with the parents. Families report high stress and feelings of helplessness in caring for children with atopic dermatitis. Parents express issues with the child’s sleeplessness due to itching and the child’s decreased self-esteem due to his or her physical appearance. The nurse should listen to ensure that parents understand the physician’s instructions and should clarify matters as needed (Nursing Care Plan 16-1).
Integumentary Disorders
![]() http://evolve.elsevier.com/Price/pediatric/
http://evolve.elsevier.com/Price/pediatric/
Integumentary System
Thrush (Oral Candidiasis)
Signs and Symptoms
Atopic Dermatitis (Infantile Eczema)
Nursing Care

Integumentary Disorders
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access