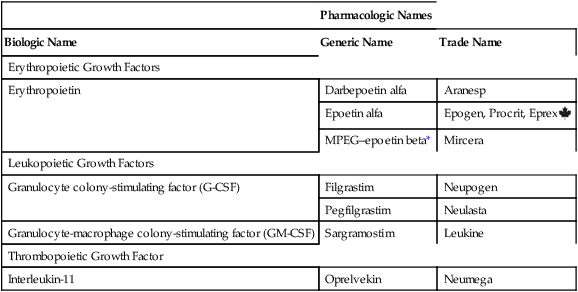
CHAPTER 56 The names used for the hematopoietic growth factors are a potential source of confusion. Why? Because each product has a biologic name, a generic name, and one or more proprietary (trade) names. The biologic, generic, and proprietary names for available products are listed in Table 56–1. TABLE 56–1 Nomenclature for Hematopoietic Growth Factors *MPEG–epoetin beta = methoxy polyethylene glycol–epoetin beta. The ESA APPRISE Oncology Program* sets additional requirements for using ESAs in cancer patients. Prescribers must enroll in ESA APPRISE, complete a brief training module, discuss the risks and benefits of ESAs with the patient, and sign a form acknowledging that the discussion took place. Hospitals that dispense ESAs must be enrolled in ESA APPRISE, and must ensure that all ESA prescribers are enrolled as well. Prescribers who use ESAs for patients who do not have cancer are not required to enroll in ESA APPRISE.
Hematopoietic agents
Hematopoietic growth factors

Pharmacologic Names
Biologic Name
Generic Name
Trade Name
Erythropoietic Growth Factors
Erythropoietin
Darbepoetin alfa
Aranesp
Epoetin alfa
Epogen, Procrit, Eprex ![]()
MPEG–epoetin beta*
Mircera
Leukopoietic Growth Factors
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)
Filgrastim
Neupogen
Pegfilgrastim
Neulasta
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)
Sargramostim
Leukine
Thrombopoietic Growth Factor
Interleukin-11
Oprelvekin
Neumega
Erythropoietic growth factors
Epoetin alfa (erythropoietin)
Risk evaluation and mitigation strategy
Cancer patients.
Darbepoetin alfa (erythropoietin, long acting)

Hematopoietic agents
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access


