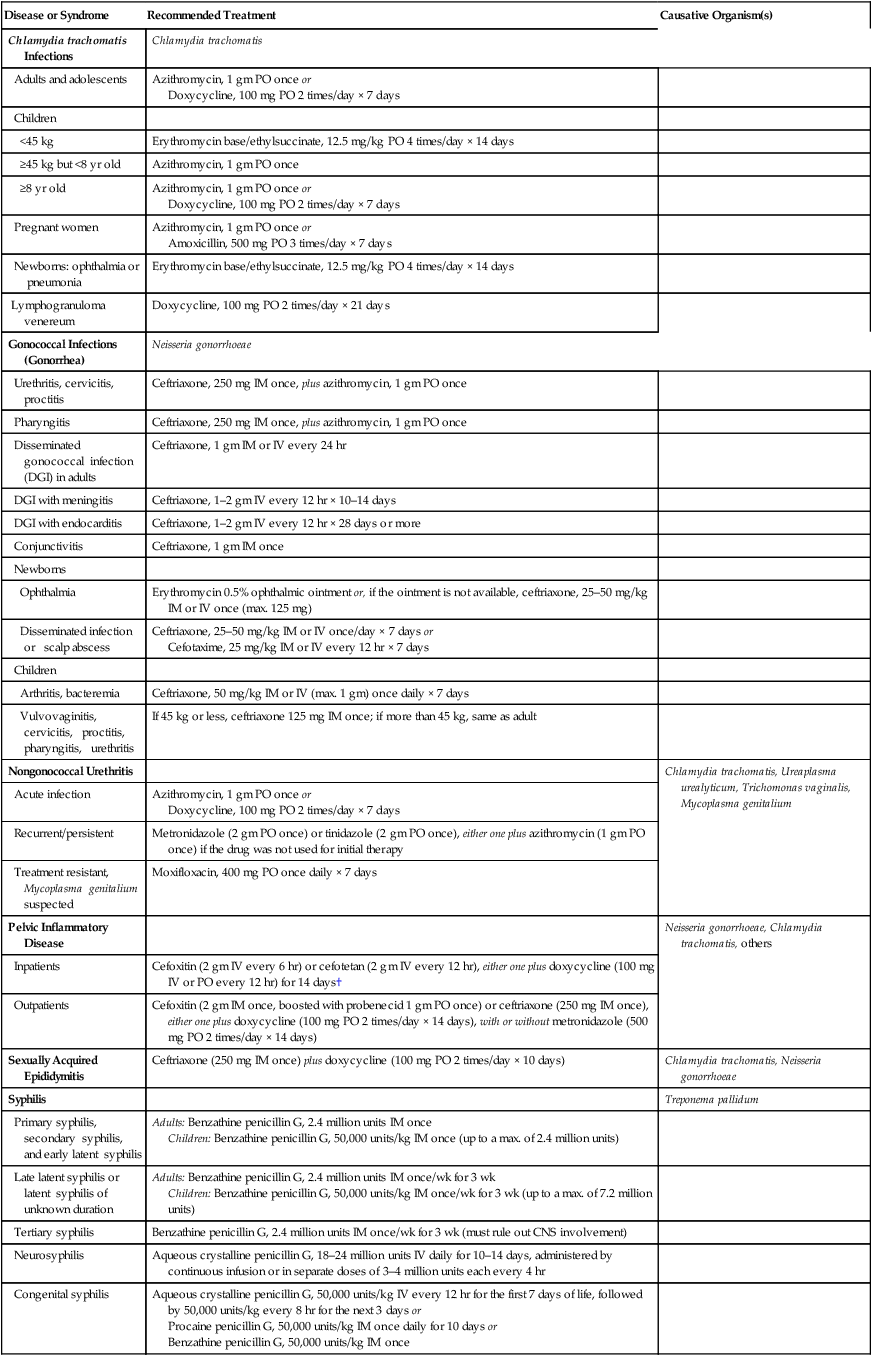
CHAPTER 95 Our objective in this chapter is to describe the principal STDs and provide an overview of their treatment. Table 95–1 presents a summary of the common STDs, causative organisms, and drugs of choice for treatment. The basic pharmacology of these drugs is discussed in other chapters. TABLE 95–1 Drug Therapy of Sexually Transmitted Diseases*
Drug therapy of sexually transmitted diseases

Disease or Syndrome
Recommended Treatment
Causative Organism(s)
Chlamydia trachomatis Infections
Chlamydia trachomatis
Adults and adolescents
Azithromycin, 1 gm PO once or
Doxycycline, 100 mg PO 2 times/day × 7 days
Children
<45 kg
Erythromycin base/ethylsuccinate, 12.5 mg/kg PO 4 times/day × 14 days
≥45 kg but <8 yr old
Azithromycin, 1 gm PO once
≥8 yr old
Azithromycin, 1 gm PO once or
Doxycycline, 100 mg PO 2 times/day × 7 days
Pregnant women
Azithromycin, 1 gm PO once or
Amoxicillin, 500 mg PO 3 times/day × 7 days
Newborns: ophthalmia or pneumonia
Erythromycin base/ethylsuccinate, 12.5 mg/kg PO 4 times/day × 14 days
Lymphogranuloma venereum
Doxycycline, 100 mg PO 2 times/day × 21 days
Gonococcal Infections (Gonorrhea)
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Urethritis, cervicitis, proctitis
Ceftriaxone, 250 mg IM once, plus azithromycin, 1 gm PO once
Pharyngitis
Ceftriaxone, 250 mg IM once, plus azithromycin, 1 gm PO once
Disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI) in adults
Ceftriaxone, 1 gm IM or IV every 24 hr
DGI with meningitis
Ceftriaxone, 1–2 gm IV every 12 hr × 10–14 days
DGI with endocarditis
Ceftriaxone, 1–2 gm IV every 12 hr × 28 days or more
Conjunctivitis
Ceftriaxone, 1 gm IM once
Newborns
Ophthalmia
Erythromycin 0.5% ophthalmic ointment or, if the ointment is not available, ceftriaxone, 25–50 mg/kg IM or IV once (max. 125 mg)
Disseminated infection or scalp abscess
Ceftriaxone, 25–50 mg/kg IM or IV once/day × 7 days or
Cefotaxime, 25 mg/kg IM or IV every 12 hr × 7 days
Children
Arthritis, bacteremia
Ceftriaxone, 50 mg/kg IM or IV (max. 1 gm) once daily × 7 days
Vulvovaginitis, cervicitis, proctitis, pharyngitis, urethritis
If 45 kg or less, ceftriaxone 125 mg IM once; if more than 45 kg, same as adult
Nongonococcal Urethritis
Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Trichomonas vaginalis, Mycoplasma genitalium
Acute infection
Azithromycin, 1 gm PO once or
Doxycycline, 100 mg PO 2 times/day × 7 days
Recurrent/persistent
Metronidazole (2 gm PO once) or tinidazole (2 gm PO once), either one plus azithromycin (1 gm PO once) if the drug was not used for initial therapy
Treatment resistant, Mycoplasma genitalium suspected
Moxifloxacin, 400 mg PO once daily × 7 days
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, others
Inpatients
Cefoxitin (2 gm IV every 6 hr) or cefotetan (2 gm IV every 12 hr), either one plus doxycycline (100 mg IV or PO every 12 hr) for 14 days†
Outpatients
Cefoxitin (2 gm IM once, boosted with probenecid 1 gm PO once) or ceftriaxone (250 mg IM once), either one plus doxycycline (100 mg PO 2 times/day × 14 days), with or without metronidazole (500 mg PO 2 times/day × 14 days)
Sexually Acquired Epididymitis
Ceftriaxone (250 mg IM once) plus doxycycline (100 mg PO 2 times/day × 10 days)
Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Syphilis
Treponema pallidum
Primary syphilis, secondary syphilis, and early latent syphilis
Adults: Benzathine penicillin G, 2.4 million units IM once
Children: Benzathine penicillin G, 50,000 units/kg IM once (up to a max. of 2.4 million units)
Late latent syphilis or latent syphilis of unknown duration
Adults: Benzathine penicillin G, 2.4 million units IM once/wk for 3 wk
Children: Benzathine penicillin G, 50,000 units/kg IM once/wk for 3 wk (up to a max. of 7.2 million units)
Tertiary syphilis
Benzathine penicillin G, 2.4 million units IM once/wk for 3 wk (must rule out CNS involvement)
Neurosyphilis
Aqueous crystalline penicillin G, 18–24 million units IV daily for 10–14 days, administered by continuous infusion or in separate doses of 3–4 million units each every 4 hr
Congenital syphilis
Aqueous crystalline penicillin G, 50,000 units/kg IV every 12 hr for the first 7 days of life, followed by 50,000 units/kg every 8 hr for the next 3 days or
Procaine penicillin G, 50,000 units/kg IM once daily for 10 days or
Benzathine penicillin G, 50,000 units/kg IM once
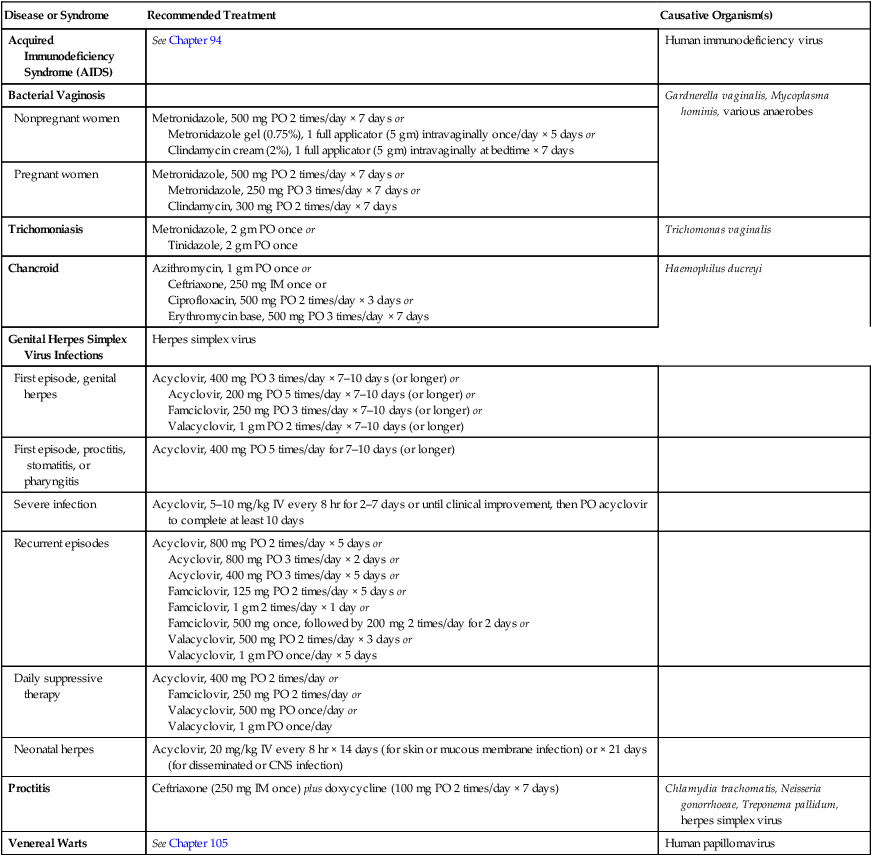
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
See Chapter 94
Human immunodeficiency virus
Bacterial Vaginosis
Gardnerella vaginalis, Mycoplasma hominis, various anaerobes
Nonpregnant women
Metronidazole, 500 mg PO 2 times/day × 7 days or
Metronidazole gel (0.75%), 1 full applicator (5 gm) intravaginally once/day × 5 days or
Clindamycin cream (2%), 1 full applicator (5 gm) intravaginally at bedtime × 7 days
Pregnant women
Metronidazole, 500 mg PO 2 times/day × 7 days or
Metronidazole, 250 mg PO 3 times/day × 7 days or
Clindamycin, 300 mg PO 2 times/day × 7 days
Trichomoniasis
Metronidazole, 2 gm PO once or
Tinidazole, 2 gm PO once
Trichomonas vaginalis
Chancroid
Azithromycin, 1 gm PO once or
Ceftriaxone, 250 mg IM once or
Ciprofloxacin, 500 mg PO 2 times/day × 3 days or
Erythromycin base, 500 mg PO 3 times/day × 7 days
Haemophilus ducreyi
Genital Herpes Simplex Virus Infections
Herpes simplex virus
First episode, genital herpes
Acyclovir, 400 mg PO 3 times/day × 7–10 days (or longer) or
Acyclovir, 200 mg PO 5 times/day × 7–10 days (or longer) or
Famciclovir, 250 mg PO 3 times/day × 7–10 days (or longer) or
Valacyclovir, 1 gm PO 2 times/day × 7–10 days (or longer)
First episode, proctitis, stomatitis, or pharyngitis
Acyclovir, 400 mg PO 5 times/day for 7–10 days (or longer)
Severe infection
Acyclovir, 5–10 mg/kg IV every 8 hr for 2–7 days or until clinical improvement, then PO acyclovir to complete at least 10 days
Recurrent episodes
Acyclovir, 800 mg PO 2 times/day × 5 days or
Acyclovir, 800 mg PO 3 times/day × 2 days or
Acyclovir, 400 mg PO 3 times/day × 5 days or
Famciclovir, 125 mg PO 2 times/day × 5 days or
Famciclovir, 1 gm 2 times/day × 1 day or
Famciclovir, 500 mg once, followed by 200 mg 2 times/day for 2 days or
Valacyclovir, 500 mg PO 2 times/day × 3 days or
Valacyclovir, 1 gm PO once/day × 5 days
Daily suppressive therapy
Acyclovir, 400 mg PO 2 times/day or
Famciclovir, 250 mg PO 2 times/day or
Valacyclovir, 500 mg PO once/day or
Valacyclovir, 1 gm PO once/day
Neonatal herpes
Acyclovir, 20 mg/kg IV every 8 hr × 14 days (for skin or mucous membrane infection) or × 21 days (for disseminated or CNS infection)
Proctitis
Ceftriaxone (250 mg IM once) plus doxycycline (100 mg PO 2 times/day × 7 days)
Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Treponema pallidum, herpes simplex virus
Venereal Warts
See Chapter 105
Human papillomavirus
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


