Cancer, Immune System, and Skin Disorders
Objectives
• Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter.
• Explain the differences between benign tumors and cancer.
• Identify cancer risk factors, signs, and symptoms.
• Explain the common cancer treatments.
• Describe the needs of persons with cancer.
• Describe the common immune system disorders.
• Describe the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
• Explain how to assist in the care of persons with AIDS.
• Describe the cause, signs and symptoms, and treatment of shingles.
• Explain how to promote PRIDE in the person, the family, and yourself.
Key Terms
Understanding cancer, immune system, and skin disorders gives meaning to the required care. Refer to Chapter 10 while you study this chapter.
Cancer
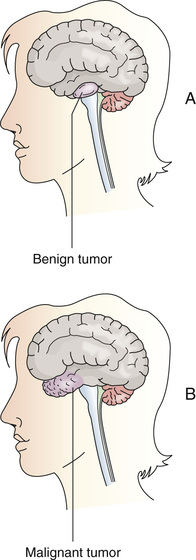
Cells reproduce for tissue growth and repair. Cells divide in an orderly way. Sometimes cell division and growth are out of control. A mass or clump of cells develops. This new growth of abnormal cells is called a tumor. Tumors are benign or malignant (Fig. 43-1, p. 694).
• Benign tumors do not spread to other body parts. They can grow to a large size but rarely threaten life. They usually do not grow back when removed.
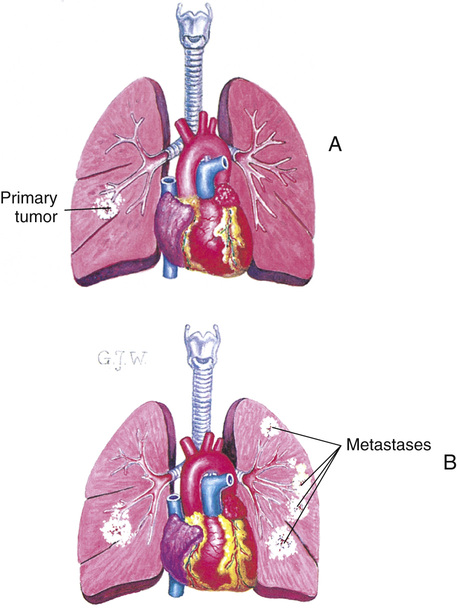
• Malignant tumors (cancer) invade and destroy nearby tissues. They can spread to other body parts (Fig. 43-2, p. 694). They may be life-threatening. Sometimes they grow back after removal.
Metastasis is the spread of cancer to other body parts (Fig. 43-3, p. 694). Cancer cells break off the tumor and travel to other body parts. New tumors grow at those sites. This occurs if cancer is not treated and controlled.
Cancer can occur almost anywhere. If detected early, cancer can be treated and controlled (Box 43-1, p. 695).
See Focus on Children and Older Persons: Cancer, p. 696.
Risk Factors
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the United States. The National Cancer Institute describes these risk factors.
• Age. Advancing age is the most important risk factor. However, cancer can occur at any age.
• Radiation. Sources are sun light, x-rays, and radon gas that forms in the soil and some rocks.
• Infections. Certain viruses and bacteria increase the risk of cancers—cervix, penis, vagina, anus, mouth, liver, lymphoma, leukemia, Kaposi’s sarcoma (associated with AIDS, p. 700), stomach.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree