Assisting With the Nursing Process
Objectives
• Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter.
• Explain the purpose of the nursing process.
• Describe the 5 steps of the nursing process.
• Explain your role in each step of the nursing process.
• Explain the difference between objective data and subjective data.
• Identify the observations that you need to report to the nurse.
• Explain the purpose of care conferences.
• Explain how to use assignment sheets.
• Explain how to promote PRIDE in the person, the family, and yourself.
Key Terms
Nurses communicate with each other about the person’s strengths, problems, needs, and care. This information is shared through the nursing process. The nursing process is the method nurses use to plan and deliver nursing care. It has 5 steps.
The nursing process focuses on the person’s nursing needs. The person and nursing team need good communication.
Each step is important. With good communication, nursing care is organized and has purpose. All nursing team members do the same things for the person. They have the same goals. The person feels safe and secure with consistent care.
The nursing process is used in all health care settings and for all age-groups. It is on-going. New information is gathered and the person’s needs may change. However, the steps are the same. You will see how the nursing process is continuous as each step is explained (Fig. 8-1, p. 84).
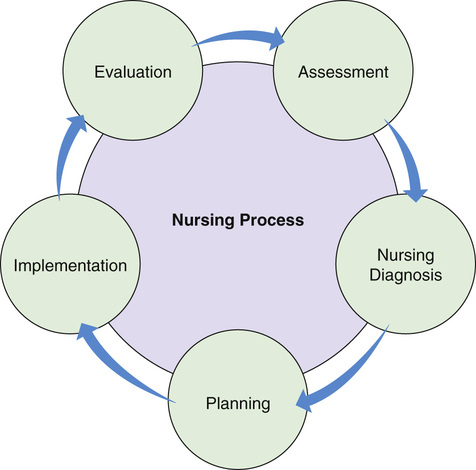
Assessment
Assessment involves collecting information about the person. The nurse takes a health history about current and past health problems. The family’s health history is important. Many diseases are genetic. That is, the risk for certain diseases is inherited from parents. For example, a mother had breast cancer. Her daughters are at risk. The nurse reviews information from the doctor, test results, and past medical records.
An RN (registered nurse) assesses the person’s body systems and mental status. You play a key role in assessment. You make many observations as you give care and talk to the person.
Observation is using the senses of sight, hearing, touch, and smell to collect information.
Objective data (signs) are seen, heard, felt, or smelled by an observer. You can feel a pulse. You can see urine color. Subjective data (symptoms) are things a person tells you about that you cannot observe through your senses. You cannot feel or see the person’s pain, fear, or nausea.
Box 8-1 lists the observations to report at once. Box 8-2 lists the basic observations you need to make and report to the nurse. Make notes of your observations. Use them to report and record observations. Carry a note pad and pen in your pocket. Note your observations as you make them. The agency may provide electronic devices for recording (Fig. 8-2).



