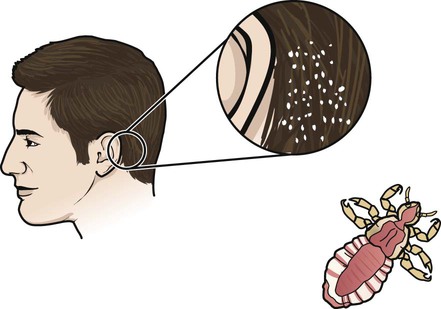
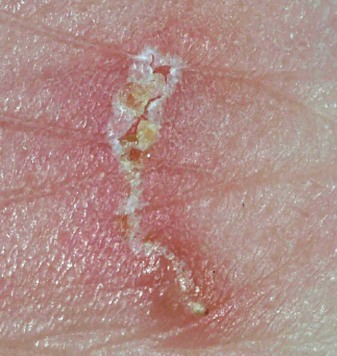
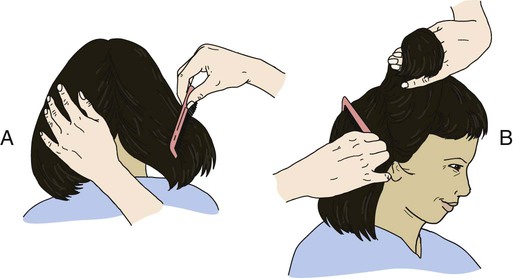
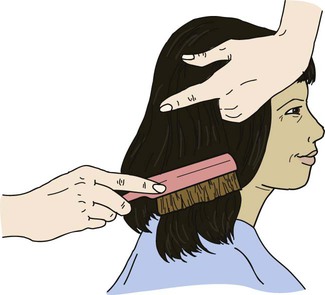
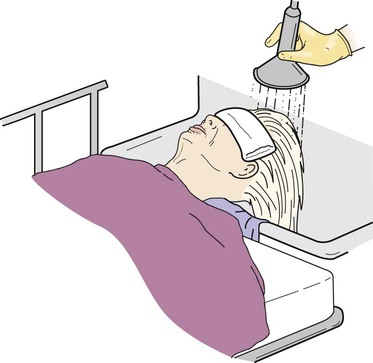
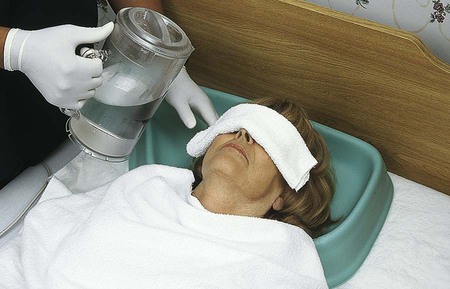
• Define the key terms and key abbreviations listed in this chapter. • Explain why grooming is important. • Describe how to safely provide grooming measures—hair care, shaving, nail and foot care, and changing clothing and gowns. • Perform the procedures described in this chapter. • Explain how to promote PRIDE in the person, the family, and yourself. As with hygiene, the person should perform grooming measures to the extent possible. This promotes independence and quality of life. The person may use adaptive devices for grooming (Chapter 27). See Focus on Surveys: Assisting With Grooming. Skin and scalp conditions include: • Alopecia means hair loss. Hair loss may be complete or partial. Male pattern baldness occurs with aging. It results from heredity. Hair also thins in some women with aging. Cancer treatments (radiation therapy to the head and chemotherapy) often cause alopecia in persons of all ages. • Hirsutism is excessive body hair. It can occur in men, women, and children. It results from heredity and abnormal amounts of male hormones. • Dandruff is the excessive amount of dry, white flakes from the scalp. Itching is common. Sometimes eyebrows and ear canals are involved. • Pediculosis (lice) is the infestation with wingless insects. See Figure 17-1. Infestation means being in or on a host. Lice attach their eggs (nits) to hair shafts. Nits are oval and yellow to white in color. After hatching, they bite the scalp or skin to feed on blood. Adult lice are tan to grayish white in color and about the size of a sesame seed. Lice bites cause severe itching in the affected area. Lice easily spread to others through clothing, head coverings, furniture, beds, towels, bed linen, sexual contact, and by sharing combs and brushes. Lice are treated with medicated shampoos, lotions, and creams specific for lice. Thorough bathing is needed. So is washing clothing and linens in hot water. • Pediculosis capitis (“head lice”) is the infestation of the scalp (capitis) with lice. • Pediculosis pubis (“crabs”) is the infestation of the pubic (pubis) hair with lice. • Pediculosis corporis is the infestation of the body (corporis) with lice. • Scabies is a skin disorder caused by the female mite—a very small spider-like organism (Fig. 17-2). The female mite burrows into the skin and lays eggs. When the eggs hatch, the females produce more eggs. The person becomes infested with mites. The person has a rash and intense itching. Common sites are between the fingers, around the wrists, in the underarm areas, on the thighs, and in the genital area. Other sites include the breasts, waist, and buttocks. Highly contagious, scabies is transmitted to others by close contact. Special creams are used to kill the mites. The person’s room is cleaned. Clothing and linens are washed in hot water. See Focus on Communication: Skin and Scalp Conditions. • Shampoo during the shower or tub bath. The person shampoos in the shower. You use a hand-held nozzle for those using shower chairs or taking tub baths. You direct a spray of water at the hair. • Shampoo at the sink. The person sits or lies facing away from the sink. A folded towel is placed over the sink edge to protect the neck. The person’s head is tilted back over the edge of the sink (Fig. 17-5). You use a water pitcher or hand-held nozzle to wet and rinse the hair. • Shampoo in bed. The person’s head and shoulders are moved to the edge of the bed if possible. A shampoo tray placed under the head drains water into a basin placed on a chair by the bed (Fig. 17-6). You use a water pitcher to wet and rinse the hair. See Focus on Older Persons: Shampooing. See Delegation Guidelines: Shampooing. See Promoting Safety and Comfort: Shampooing. See procedure: Shampooing the Person’s Hair, p. 256. Many men shave for comfort and well-being. Many women shave their legs and underarms. Some women shave facial hair. Or they may use other hair removal methods—waxing, hair removal products, plucking, threading. See Box 17-1 for shaving rules. Safety razors or electric shavers are used (Fig. 17-7). Patients and residents may have their own electric shavers. If the agency’s shaver is used, clean it before and after use. To brush out whiskers, follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Also follow agency policy for cleaning electric shavers. See Focus on Older Persons: Shaving. See Delegation Guidelines: Shaving. See Promoting Safety and Comfort: Shaving, p. 258. See procedure: Shaving the Person’s Face With a Safety Razor, p. 258.
Assisting With Grooming
Hair Care
Skin and Scalp Conditions
![]() Shampooing
Shampooing
![]() Shaving
Shaving
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Nurse Key
Fastest Nurse Insight Engine
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access