• Differentiate oral and parenteral anticoagulant agents and related tests. • Calculate doses for oral and parenteral anticoagulant agents. • Evaluate and titrate anticoagulant doses based upon relevant laboratory tests. • Identify antidotes for anticoagulant therapy. • Identify critical patient safety issues related to anticoagulant therapy. Anticoagulants are now prescribed for many conditions, for example: • Pre-, intra, and postoperative lower extremity orthopedic surgery • Potential, intra, and post-cardiac events, such as arrhythmias, myocardial infarcts, and cardiac surgery • Intra- and post-pelvic surgery • History of thromboembolic conditions, such as deep vein thromboses, pulmonary emboli, and stroke 1. What is the difference between DVT and PE? _________________________________________________________________________ 1. What are some of the differences between heparin, warfarin, and LMWH products? _________________________________________________________________________ 1. What is the preferred test for patients receiving heparin products, as opposed to the test for those receiving warfarin products? ________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the main risk for patients who have thrombocytopenia? ________________________________________________________________ 1. If a control value for a coagulation test is 12 seconds and the therapeutic range is 1.5 to 2.5 times the control value, would the patient’s test result be within therapeutic range if it was 24 seconds? (Use simple arithmetic with or without a calculator.) ________________________________________________________________ 1. Anticoagulants are used for the following purposes: _________ 2. An oral anticoagulant that is ordered for outpatient use is _________ 3. The standardized relevant laboratory test for monitoring therapeutic levels of warfarin is called _________ 4. The most commonly used laboratory test to monitor therapeutic levels of heparin is _________ 5. The main danger of excessive anticoagulant therapy is _________
Anticoagulant Agents
Introduction
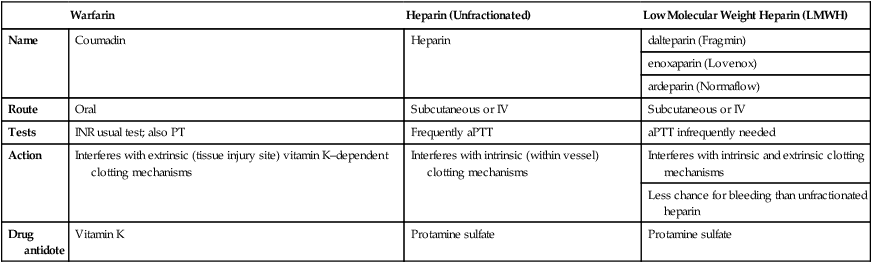
![]() Comparison of Anticoagulant Products
Comparison of Anticoagulant Products
Warfarin
Heparin (Unfractionated)
Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH)
Name
Coumadin
Heparin
dalteparin (Fragmin)
enoxaparin (Lovenox)
ardeparin (Normaflow)
Route
Oral
Subcutaneous or IV
Subcutaneous or IV
Tests
INR usual test; also PT
Frequently aPTT
aPTT infrequently needed
Action
Interferes with extrinsic (tissue injury site) vitamin K–dependent clotting mechanisms
Interferes with intrinsic (within vessel) clotting mechanisms
Interferes with intrinsic and extrinsic clotting mechanisms
Less chance for bleeding than unfractionated heparin
Drug antidote
Vitamin K
Protamine sulfate
Protamine sulfate
![]() Heparin and LMWH doses are not interchangeable.
Heparin and LMWH doses are not interchangeable.
![]() Plasma, plasma expanders, and blood also may be needed to counteract loss of blood from overdoses of anticoagulants.
Plasma, plasma expanders, and blood also may be needed to counteract loss of blood from overdoses of anticoagulants.
![]() Examine the drug labels as you work through the chapter.
Examine the drug labels as you work through the chapter.
Anticoagulant Agents
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access





