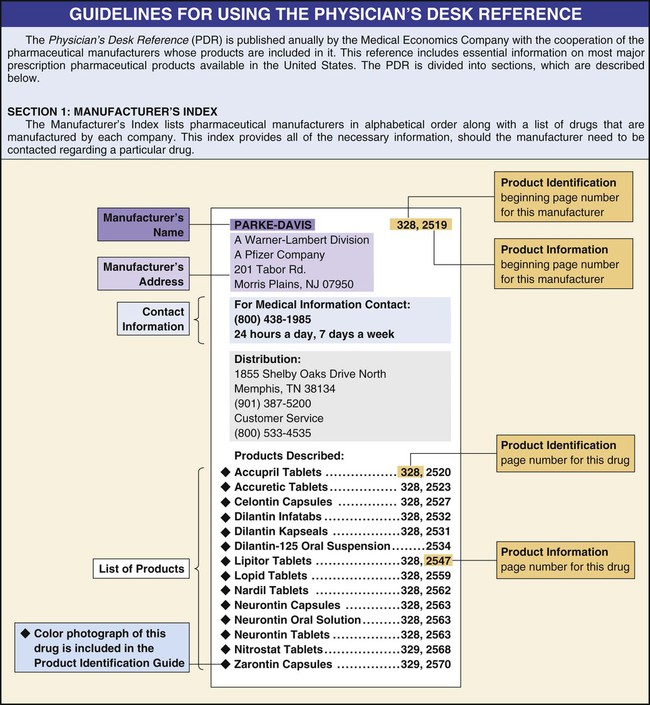
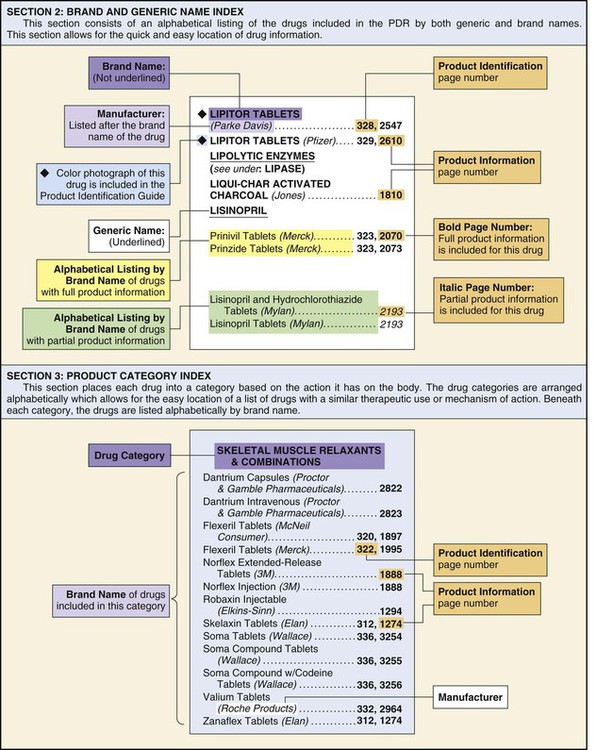
The medical assistant is obligated to become familiar with the drugs that are most frequently used in his or her office. It is essential to know their indications, adverse reactions, routes of administration, dosage, and storage. With each drug (including drug samples and injectable medications), the manufacturer includes a package insert (PI), which contains valuable information regarding the drug. In addition, many drug references are available. The Physician’s Desk Reference (PDR) is frequently used in the medical office. The PDR contains information on most major prescription pharmaceutical products available in the United States. The drug information in the PDR consists of the actual drug package insert. Figure 26-1 provides guidelines for using the PDR. These guidelines not only assist in learning how to use the PDR, but they also provide the necessary information for understanding how to interpret drug package inserts. Drug information is also available on the Internet on certain recognized websites; many of these sites are listed at the end of the chapter under the section entitled On the Web: For Information on Pharmacology. Each drug has four names: chemical, generic, official, and brand (also known as trade) names. 1. Chemical name. The chemical name provides a precise description of the drug’s chemical composition; pharmaceutical manufacturers and pharmacists are most concerned with the chemical makeup of a drug. 2. Generic name. The generic name is assigned by the pharmaceutical manufacturer who develops the drug, before it receives official approval by the FDA. The generic name is often a shortened derivative of the chemical name. 3. Official name. The official name is the name under which the drug is listed in official publications, such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and the National Formulary (NF). Official publications set specific standards to regulate the strength, purity, packaging, safety, labeling, and dosage form of each drug. The generic name is frequently used for the official name. 4. Brand name. The brand name is the name under which a pharmaceutical manufacturer markets a drug. Because a drug may be manufactured by more than one pharmaceutical company, it may have several brand names. The generic name of a common analgesic is acetaminophen; brand names for this drug include Tylenol, Tempra, Datril, Exdol, Panadol, and Liquiprin. Elixir A drug that is dissolved in a solution of alcohol and water. Elixirs are sweetened and flavored and are taken orally. Example: Dimetapp elixir. Emulsion A mixture of fats or oils in water. Example: Durezol ophthalmic emulsion. Liniment A drug combined with oil, soap, alcohol, or water. Liniments are applied externally, using friction, to produce a feeling of heat or warmth. Example: Heet liniment. Lotion An aqueous preparation that contains suspended ingredients. Lotions are used to treat external skin conditions. They work to soothe, protect, and moisten the skin and to destroy harmful bacteria. Example: Caladryl lotion. Solution A liquid preparation that contains one or more completely dissolved substances. The dissolved substance is known as the solute, and the liquid in which it is dissolved is known as the solvent. Most drugs administered parenterally (by injection) consist of solutions. Example: Depo-Provera injectable solution. Spirit A drug combined with an alcoholic solution that is volatile (a substance that is volatile evaporates readily). Example: Aromatic spirit of ammonia. Spray A fine stream of medicated vapor, usually used to treat nose and throat conditions. Example: Dristan nasal spray. Suspension A drug that contains solid insoluble drug particles in a liquid; the preparation must be shaken before administration. Example: Amoxicillin oral suspension. Suspension aerosol A pressurized form in which solid aerosol or liquid drug particles are suspended in a gas to be dispensed in a cloud or mist. Example: Proventil inhalation aerosol. Syrup A drug dissolved in a solution of sugar, water, and sometimes a flavoring to disguise an unpleasant taste. Example: Robitussin cough syrup. Tincture A drug dissolved in a solution of alcohol or alcohol and water. Example: Tincture of iodine. Tablet A powdered drug that has been pressed into a disc. Some tablets are scored, that is, they are marked with an indentation so that they can be broken into halves or quarters for proper dosage. Example: Tylenol tablets. Chewable tablet A powdered drug that has been flavored and pressed into a disc. Chewable tablets are often used for antacids, antiflatulents, and children’s medications. Example: Pepto-Bismol chewable tablets. Sublingual tablet A powdered drug that has been pressed into a disc and is designed to dissolve under the tongue, which permits its rapid absorption into the bloodstream. Example: Nitroglycerin sublingual tablets (Nitrostat). Enteric-coated tablet A tablet coated with a substance that prevents it from dissolving until it reaches the intestines. The coating protects the drug from being destroyed by gastric juices and prevents it from irritating the stomach lining. To prevent the active ingredients from being released prematurely in the stomach, enteric-coated tablets must not be crushed or chewed. Example: Ecotrin enteric-coated aspirin. Capsule A drug contained in a gelatin capsule that is water-soluble and functions to prevent the patient from tasting the drug. Example: Benadryl capsules. Sustained-release capsule A capsule that contains granules that dissolve at different rates to provide a gradual and continuous release of medication. This reduces the number of doses that must be administered. (Sustained-release medication also comes in other preparations, such as tablets and caplets.) Example: Sudafed 12-hour sustained-release capsules. Caplet A drug contained in an oblong tablet with a smooth coating to make swallowing easier. Example: Advil caplets. Lozenge A drug contained in a candy-like base. Lozenges are circular and are designed to dissolve on the tongue. Example: Chloraseptic throat lozenges. Cream A drug combined in a base that is generally nongreasy, resulting in a semisolid preparation. Creams are applied externally to the skin. Example: Hydrocortisone topical cream. Ointment A drug with an oil base, resulting in a semisolid preparation. Ointments are applied externally to the skin and are usually greasy. Example: Cortisporin topical ointment. Suppository A drug mixed with a firm base, such as cocoa butter, that is designed to melt at body temperature. A suppository is shaped into a cylinder or a cone for easy insertion into a body cavity, such as the rectum or vagina. Example: Preparation H suppositories. Transdermal patch A patch with an adhesive backing, which contains a drug, that is applied to the skin. The drug enters the circulation after being absorbed through the skin. Example: Nitroglycerin patches (Nitro-Dur). Drugs also can be classified according to the action they have on the body. The medical assistant should know in which category a particular drug belongs and its primary uses and major therapeutic effects. Table 26-1 contains classifications based on action and examples of drugs that are commonly administered and prescribed in the medical office. Table 26-1 Classification of Drugs Based on Action
Administration of Medication and Intravenous Therapy
Introduction to the Administration of Medication
Drug References
Drug Nomenclature
Classification of Drugs Based on Preparation
Liquid Preparations
Solid Preparations
Classification of Drugs Based on Action
COMMONLY PRESCRIBED DRUGS
Drug Category
Primary Use and Major Therapeutic Effects
Generic
Brand
Analgesics (Opioid)
Used to manage moderate to severe pain
Work by altering perception of and response to painful stimuli
codeine/APAP
 Tylenol w/Codeine (III)
Tylenol w/Codeine (III)
fentanyl
hydrocodone/APAP
hydrocodone/ASA
hydrocodone/ibuprofen
meperidine
oxycodone
oxycodone/APAP
oxycodone/ASA
propoxyphene
propoxyphene N/APAP
tramadol
Actiq  Vicodin (III)
Vicodin (III)
Lortab/ASA (III) Vicoprofen (III)
Vicoprofen (III)
Demerol (II) OxyContin (II)
OxyContin (II) Percocet (II)
Percocet (II)
Percodan (II)
Darvon (IV) Darvocet-N (IV)
Darvocet-N (IV) Ultram
Ultram
Analgesics (Barbiturate)
Used to manage moderate to severe pain of tension headaches
Work by relieving pain and relaxing muscle contractions
butalbital/APAP/caffeine
butalbital/ASA/caffeine
 Fioricet (III)
Fioricet (III)
Fiorinal (III)
Analgesics/Antipyretics
Used to manage mild to moderate pain and to reduce fever
Work by relieving pain and reducing fever
acetaminophen
aspirin
Tylenol*
Bayer*
Ecotrin*
Analgesics/Antipyretics
NSAIDs
diclofenac
Voltaren
ibuprofen
Advil*  Motrin*
Motrin*
Aleve*
naproxen
 Anaprox
Anaprox Naprosyn
Naprosyn
Anesthetics (Local)
Used to produce local anesthesia through loss of feeling to a body part
Work by preventing initiation and conduction of normal nerve impulses in body part
lidocaine
dibucaine
Xylocaine
Nupercainal ointment*
Antacids
Used to treat heartburn, hyperacidity, indigestion, and gastroesophageal reflux disease, and to promote healing of ulcers
Work by neutralizing gastric acid to relieve gastric pain and irritation
aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide
Maalox*
Mylanta*
calcium carbonate
Tums*
sodium bicarbonate/ASA
Alka-Seltzer*
Anti-Alzheimer Agents
Used to treat mild to moderate dementia associated with Alzheimer disease
Work by elevating acetylcholine concentration in the cerebral cortex
donepezil
memantine
rivastigmine
 Aricept
Aricept Namenda
Namenda
Exelon
Antianemics
Iron Supplements
Used to prevent or cure iron-deficiency anemia
Work by increasing amount of iron in body
ferrous sulfate
Feosol*
iron dextran
DexFerrum
InFed
Vitamin B12 Injections
Used to treat pernicious anemia
Work by increasing amount of vitamin B12 in body
cyanocobalamin
Cobex
Cyanoject
Folic Acid Supplements
Used to promote normal fetal development
Work by stimulating production of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
folic acid
 Folvite
Folvite
Antianginals
Used to relieve or prevent angina attacks
Work by increasing blood supply to myocardial tissue
Nitrates
isosorbide dinitrate
Sorbitrate
isosorbide mononitrate
nitroglycerin
 Imdur
Imdur
Nitro-Bid
Nitro-Dur
Nitrostat
Beta-Blockers
atenolol
Tenormin
propranolol
Inderal
metoprolol
 Toprol-XL
Toprol-XL
Calcium Channel Blockers
amlodipine
 Norvasc
Norvasc
bepridil
Vascor
diltiazem
Cardizem
Dilacor XR
nifedipine
Adalat
Procardia XL
verapamil
 Calan
Calan
Isoptin
Verelan
Antianxiety Agents
Used to treat anxiety
Work at many levels in central nervous system to produce anxiolytic (anxiety-relieving) effect
alprazolam
 Xanax (IV)
Xanax (IV)
buspirone
BuSpar
chlordiazepoxide
Librium (IV)
diazepam
 Valium (IV)
Valium (IV)
lorazepam
 Ativan (IV)
Ativan (IV)
Anticholinergics
Used to decrease preoperatively oral and respiratory secretions
Work by blocking effects of acetylcholine in autonomic nervous system
atropine
Atro-Pen
Anticoagulants
Used to prevent and treat venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and myocardial infarction by preventing clot extension and formation
Work by delaying or preventing blood coagulation
heparin
enoxaparin
 Lovenox
Lovenox
warfarin
 Coumadin
Coumadin
Anticonvulsants
Used to prevent or relieve seizures
Work by decreasing incidence and severity of seizures
carbamazepine
Tegretol
clonazepam
 Klonopin (IV)
Klonopin (IV)
divalproex
 Depakote
Depakote
gabapentin
 Neurontin
Neurontin
lamotrigine
 Lamictal
Lamictal
phenytoin
 Dilantin
Dilantin
pregabalin
 Lyrica
Lyrica
topiramate
 Topamax
Topamax
Antidepressants
Used to prevent, cure, or alleviate depression, and to treat anxiety disorders (panic attacks) and obsessive-convulsive disorder
Work by inhibiting reuptake of neurotransmitters in the central nervous system
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
citalopram
 Celexa
Celexa
escitalopram
 Lexapro
Lexapro
fluoxetine
 Prozac
Prozac
fluvoxamine
Luvox
paroxetine
 Paxil
Paxil
sertraline
 Zoloft
Zoloft
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
desvenlafaxine
Pristiq
duloxetine
 Cymbalta
Cymbalta
venlafaxine
 Effexor XR
Effexor XR
Miscellaneous
amitriptyline
 Elavil
Elavil
bupropion
 Wellbutrin SR
Wellbutrin SR
mirtazapine
 Remeron
Remeron
nefazodone
Serzone
trazodone
 Desyrel
Desyrel
Antidiabetics
Oral Hypoglycemics
Used to manage non–insulin-dependent type 2 diabetes mellitus
Work by stimulating release of insulin from pancreas and increasing sensitivity to insulin
glimepiride
 Amaryl
Amaryl
glipizide
 Glucotrol XL
Glucotrol XL
glyburide
 Micronase
Micronase
metformin
 Glucophage
Glucophage
pioglitazone
 Actos
Actos
rosiglitazone
 Avandia
Avandia
Antidiabetics
Insulins
Used to manage diabetes mellitus
Work by reducing blood glucose levels
regular insulin
Humulin R*
Novolin R*
NPH insulin
Humulin N*
Novolin N*
NPH/regular insulin
Humulin 70/30*
Novolin 70/30*
insulin glargine
 Lantus
Lantus
insulin lispro
Humalog
Antidiarrheals
Used to control and relieve diarrhea
Work by inhibiting peristalsis, reducing fecal volume, and preventing loss of fluids and electrolytes
bismuth subsalicylate
Pepto-Bismol*
diphenoxylate/atropine
Lomotil (V)
kaolin/pectin
Kaopectate*
loperamide
Imodium*
Antidysrhythmics
Used to control or prevent cardiac dysrhythmias
Work by decreasing myocardial excitability and slowing conduction velocity
metoprolol
 Lopressor
Lopressor Toprol-XL
Toprol-XL
procainamide
Pronestyl
propranolol
Inderal
Antiemetics
Used to prevent or relieve nausea and vomiting
Work by depressing chemoreceptor trigger zone in central nervous system to inhibit nausea and vomiting
dronabinol
Marinol (III)
ondansetron
Zofran
prochlorperazine
Compazine
promethazine
 Phenergan
Phenergan
meclizine
Bonine*
Antiflatulents
Used to relieve discomfort of excess gas and bloating in gastrointestinal tract
Work by causing coalescence of gas bubbles in intestinal tract
simethicone
Gas-X*
Mylanta Gas*
Antifungals
Used to treat fungal infections
Work by killing or inhibiting growth of susceptible fungi
amphotericin B
Fungizone
clotrimazole
Gyne-Lotrimin*
fluconazole
 Diflucan
Diflucan
itraconazole
Sporanox
ketoconazole
Nizoral
miconazole
Monistat*
nystatin
Mycostatin*
terbinafine
 Lamisil
Lamisil
Antigout Agents
Used to prevent attacks of gout
Work by inhibiting production of uric acid
allopurinol
colchicine
 Zyloprim
Zyloprim
Colchicine tablets
Anthelmintics
Used to treat worm infections (pinworms, roundworms, hookworms)
Work by destroying worms
mebendazole
Vermox
Antihistamines
Used to relieve symptoms associated with allergies (increased sneezing; rhinorrhea; itchy eyes, nose, and throat)
Work by blocking effects of histamine at histamine receptor sites
brompheniramine
Dimetane*
cetirizine
 Zyrtec*
Zyrtec*
chlorpheniramine
Chlor-Trimetron*
Teldrin*
desloratadine
 Clarinex
Clarinex
diphenhydramine
Benadryl*
fexofenadine/pseudoephedrine
 Allegra
Allegra
levocetirizine
Xyzal
loratadine
 Claritin*
Claritin*
promethazine
 Phenergan
Phenergan
Antihypertensives
Used to manage hypertension
Work by causing systemic vasodilation to reduce blood pressure
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors
benazepril
Lotensin
captopril
Capoten
enalapril
 Vasotec
Vasotec
lisinopril
 Prinivil
Prinivil
quinapril
 Accupril
Accupril
ramipril
 Altace
Altace
Peripherally Acting Adrenergic Blockers
clonidine
 Catapres
Catapres
doxazosin
Cardura
prazosin
Minipress
Antihypertensives, cont’d
Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists
candesartan
Atacand
irbesartan
 Avapro
Avapro
losartan
 Cozaar
Cozaar
olmesartan
 Benicar
Benicar
telmisartan
Micardis
valsartan
 Diovan
Diovan
Beta-Blockers
atenolol
 Tenormin
Tenormin
carvedilol
 Coreg
Coreg
metoprolol
 Lopressor
Lopressor Toprol-XL
Toprol-XL
propranolol
Inderal
sotalol
Betaspace
Calcium Channel Blockers
amlodipine
 Norvasc
Norvasc
diltiazem
 Cardizem
Cardizem
felodipine
Plendil
Vasodilators
hydralazine
Apresoline
Miscellaneous
amlodipine/atorvastatin
Caduet
amlodipine/benazepril
 Lotrel
Lotrel
bisoprolol/hydrochlorothiazide
Ziac
irbesartan/hydrochlorothiazide
 Avalide
Avalide
losartan/hydrochlorothiazide
 Hyzaar
Hyzaar
olmesartan/hydrochlorothiazide
 Benicar HCT
Benicar HCT
triamterene/hydrochlorothiazide
 Maxzide
Maxzide
valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide
Diovan HCT
Antiimpotence Agents
Used to treat erectile dysfunction
Work by promoting increased blood flow to penis
sildenafil
 Viagra
Viagra
tadalafil
 Cialis
Cialis
vardenafil
Levitra
Antiinfectives
Used to treat infections
Work by killing or inhibiting growth of bacteria
Penicillins
amoxicillin
 Amoxil
Amoxil Trimox
Trimox
amoxicillin/clavulanate
 Augmentin
Augmentin
ampicillin
Omnipen
benzathine penicillin
Bicillin
penicillin V
 Veetids
Veetids
procaine penicillin
Wycillin
Macrolides
azithromycin
 Zithromax
Zithromax
clarithromycin
Biaxin
erythromycin
Ery-Tab
Cephalosporins
cefaclor
Ceclor
cefdinir
 Omnicef
Omnicef
cefprozil
 Cefzil
Cefzil
ceftriaxone
Rocephin
cefuroxime
Ceftin
cephalexin
 Keflex
Keflex
Antiinfectives, cont’d
Fluoroquinolones
ciprofloxacin
 Cipro
Cipro
levofloxacin
 Levaquin
Levaquin
moxifloxacin
Avelox
ofloxacin
Floxin
Tetracyclines
doxycycline
Doryx  Vibramycin
Vibramycin
minocycline
Arestin
tetracycline
Achromycin
Sumycin
Aminoglycosides
gentamicin
Garamycin
kanamycin
Kantrex
neomycin
Neobiotic
tobramycin
Nebcin
Sulfonamides
sulfamethoxazole
Gantanol
trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
 Bactrim
Bactrim
Miscellaneous
clindamycin
Cleocin
chloramphenicol
Chloromycetin
nitrofurantoin
 Macrobid
Macrobid
Macrodantin
vancomycin
Vancocin
Antiinflammatory Agents
Used to relieve signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis in adults
Work by decreasing pain and inflammation
aspirin
Bayer*
Ecotrin*
celecoxib
 Celebrex
Celebrex
etodolac
Lodine
ibuprofen
Advil*
Motrin*
indomethacin
Indocin
meloxicam
 Mobic
Mobic
nabumetone
 Relafen
Relafen
naproxen
Aleve*
Anaprox
Naprosyn
piroxicam
Feldene
valdecoxib
Bextra
Antimanics
Used to treat bipolar affective disorders
Work by altering cation transport in nerves and muscles
lithium
Eskalith
Eskalith CR
Antimigraines
Used in acute treatment of migraine attacks
Work by causing vasoconstriction in large intracranial arteries
sumatriptan
 Imitrex
Imitrex
Antineoplastics
Used to treat tumors
Work by preventing development, growth, or proliferation of malignant cells
cyclophosphamide
Cytoxan
methotrexate
Mexate
Folex
Anti-Parkinson Agents
Used to treat symptoms of Parkinson disease
Work by restoring balance between acetylcholine and dopamine in central nervous system
carbidopa/levodopa
Sinemet
ropinirole
Requip
Antiprotozoals
Used to treat protozoal infections
Work by destroying protozoa
metronidazole
Flagyl
Antipsychotics
Used to treat psychotic disorders
Work by blocking dopamine and serotonin receptors in central nervous system
haloperidol
Haldol
aripiprazole
 Abilify
Abilify
olanzapine
 Zyprexa
Zyprexa
risperidone
 Risperdal
Risperdal
quetiapine
 Seroquel
Seroquel
Antiretrovirals
Used to manage human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections and to reduce maternal-fetal transmission of HIV
Work by inhibiting replication of retroviruses
efavirenz
Sustiva
emtricitabine
Emtriva
lamivudine
Epivir
ritonavir
Norvir
tenofovir
Viread
zidovudine
Retrovir
Antispasmodics
Used to control hypermotility in irritable bowel syndrome, spastic colitis, spastic bladder, and pylorospasm
Work by preventing or relieving spasms of gastrointestinal or genitourinary tract
dicyclomine
Bentyl
hyoscyamine
Levsin
Antituberculars
Used to treat tuberculosis
Work by killing or inhibiting growth of mycobacteria
isoniazid
INH
rifampin
Rifadin
Antitussives
Used in prevention or relief of coughs caused by minor viral upper respiratory infections or inhaled irritants
Work by suppressing cough reflex by direct effect on cough center in central nervous system
benzonatate
Tessalon
chlorpheniramine/hydrocodone
Tussionex (III)
dextromethorphan
Robitussin DM*
guaifenesin/codeine
Robitussin A-C (V)
Antiulcers
Used to manage ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease, heartburn, indigestion, and gastric hyperacidity
Work by preventing accumulation of acid in stomach
Proton Pump Inhibitors
esomeprazole
 Nexium
Nexium
lansoprazole
 Prevacid
Prevacid
omeprazole
 Prilosec*
Prilosec*
pantoprazole
 Protonix
Protonix
rabeprazole
 AcipHex
AcipHex
H2-Receptor Antagonists
cimetidine
Tagamet*
famotidine
 Pepcid AC*
Pepcid AC*
ranitidine
 Zantac*
Zantac*
Antivirals
Used to manage herpes infections
Work by inhibiting viral replication
acyclovir
 Zovirax
Zovirax
famciclovir
Famvir
valacyclovir
 Valtrex
Valtrex
Bone Resorption Inhibitors
Used to treat and prevent osteoporosis
Work by inhibiting resorption of bone
alendronate
 Fosamax
Fosamax
ibandronate
Boniva
raloxifene
 Evista
Evista
risedronate
 Actonel
Actonel
Bronchodilators
Used to manage reversible airway obstruction caused by asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Work by relaxing smooth muscle of respiratory tract resulting in bronchodilation
albuterol
 Proventil
Proventil
fluticasone/salmeterol
 Advair Diskus
Advair Diskus
formoterol
Foradil
ipratropium/albuterol
 Combivent
Combivent
levalbuterol
Xopenex
montelukast
 Singulair
Singulair
salmeterol
Serevent
theophylline
Bronkodyl
tiotropium
 Spiriva
Spiriva
Cardiac Glycosides
Used to treat congestive heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias
Work by increasing strength and force of myocardial contractions and slowing heart rate
digitoxin
Crystodigin  Digitek
Digitek
digoxin
Lanoxicaps  Lanoxin
Lanoxin
Central Nervous System Stimulants
Used to treat narcolepsy and manage attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
Work by increasing level of catecholamines in central nervous system
atomoxetine
 Strattera
Strattera
dextroamphetamine
Dexedrine (II)
dextroamphetamine saccharate and sulfate
 Adderall (II)
Adderall (II)
lisdexamfetamine
Vyvanse (II)
methylphenidate
 Ritalin (II)
Ritalin (II) Concerta (II)
Concerta (II)
Contraceptives (Hormonal)
Used to prevent pregnancy and to regulate menstrual cycle
Work by inhibiting ovulation
Oral Contraceptives
ethinyl estradiol/drospirenone
 Yasmin
Yasmin
Yaz
ethinyl estradiol/levonorgestrel
Alesse
Levien
ethinyl estradiol/norethindrone
Kariva  Ortho-Novum
Ortho-Novum Loestrin Fe
Loestrin Fe
ethinyl estradiol/norgestimate
 Ortho Tri-Cyclen
Ortho Tri-Cyclen
Tri-Sprintec
Injectable Contraceptives
medroxyprogesterone
 Depo-Provera
Depo-Provera
Transdermal Contraceptives
ethinyl estradiol/norelgestromin
 Ortho Evra
Ortho Evra
Vaginal Ring Contraceptives
ethinyl estradiol/etonogestrel
NuvaRing
Corticosteroids
Systemic Corticosteroids
Used to treat inflammation, allergies, asthma, and autoimmune disorders and as replacement therapy in adrenal insufficiency
Work by suppressing inflammation and modifying normal immune response
cortisone
Cortone
fluticasone
 Flovent
Flovent
hydrocortisone
Cortef
methylprednisolone
Medrol
Depo-Medrol
triamcinolone
Aristocort
Nasal Corticosteroids
Used to treat chronic nasal inflammatory conditions (e.g., allergic rhinitis)
Work by suppressing inflammation and reducing hypersecretions of respiratory tract
fluticasone
 Flonase
Flonase
mometasone
 Nasonex
Nasonex
prednisone
 Deltasone
Deltasone
triamcinolone
 Nasacort
Nasacort
Decongestants
Used to decrease nasal congestion
Work by producing vasoconstriction in respiratory tract mucosa
oxymetazoline
Afrin*
Dristan*
phenylephrine
Neo-Synephrine*
pseudoephedrine
Sudafed*
Diuretics
Used to manage hypertension, edema in congestive heart failure, and renal disease
Work by removing excess fluid from the body by increasing urine output
Loop Diuretics
bumetanide
Bumex
furosemide
 Lasix
Lasix
Thiazide Diuretics
chlorthalidone
Hygroton
hydrochlorothiazide
 Microzide
Microzide
Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
spironolactone
Aldactone
triamterene
Dyrenium
Electrolyte Replacements
Used to treat or prevent electrolyte depletion
Work by replacing electrolytes in body
Potassium Supplements
potassium chloride
 K-Dur
K-Dur Klor-Con
Klor-Con
Emetics
Used to treat poisoning
Work by inducing vomiting
syrup of ipecac
Expectorants
Used to manage coughs by expelling mucus
Work by decreasing viscosity of bronchial secretions to promote clearance of mucus from respiratory tract
guaifenesin
Robitussin*
Mucinex*
Naldecon*
Hormone Replacements
Used to treat moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms of menopause
Work by restoring hormonal balance
conjugated estrogens
 Premarin
Premarin
conjugated estrogen/progesterone
 Prempro
Prempro
estradiol/norethindrone
Activella
Immunizations
Used to prevent (vaccine-preventable) diseases
Work by stimulating body to produce antibodies
diphtheria, tetanus toxoids, and acellular pertussis vaccine
Acel-Imune
Certiva
Daptacel
Infanrix
Tripedia
Haemophilus b conjugate vaccine
ActHIB
HibTITER
hepatitis A vaccine
Havrix
Vaqta
hepatitis B vaccine
Engerix-B
Recombivax HB
human papillomavirus vaccine
Gardasil
inactivated polio vaccine
IPOL
influenza virus vaccine types A and B
Afluria
FluShield
Fluzone
FluMist
measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine
M-M-R II
meningococcal conjugate vaccine
Menactra
pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
Prevnar
Pneumovax II
rotavirus
Rotarix
RotaShield
rubella vaccine
Meruvax II
varicella vaccine
Varivax
Immunosuppressants
Used to treat severe rheumatoid arthritis and to prevent and treat rejection of transplanted organs
Work by inhibiting body’s normal immune response
cyclosporine
Sandimmune
Neoral
methotrexate
Rheumatrex
Laxatives
Used to relieve constipation
Work by promoting defecation of normal, soft stool
bisacodyl
Dulcolax*
docusate
Colace*
phenolphthalein
Phenolax*
psyllium
Metamucil*
Lipid-Lowering Agents
Used to lower cholesterol to reduce risk of myocardial infarction and stroke
Work by inhibiting enzyme needed to synthesize cholesterol in body
atorvastatin
 Lipitor
Lipitor
ezetimibe
 Zetia
Zetia
ezetimibe/simvastatin
 Vytorin
Vytorin
fenofibrate
 Tricor
Tricor
fluvastatin
Lescol
gemfibrozil
Lopid
lovastatin
 Mevacor
Mevacor
pravastatin
 Pravachol
Pravachol
rosuvastatin
 Crestor
Crestor
simvastatin
 Zocor
Zocor
Muscle Relaxants (Skeletal)
Used to treat acute painful musculoskeletal conditions
Work by relaxing skeletal muscles
baclofen
 Lioresal
Lioresal
carisoprodol
 Soma
Soma
cyclobenzaprine
 Flexeril
Flexeril
metaxalone
Skelaxin
methocarbamol
Robaxin
tizanidine
 Zanaflex
Zanaflex
Ophthalmic Antiinfectives
Used to treat eye infections
Work by destroying bacteria
dexamethasone/tobramycin
TobraDex
moxifloxacin
Vigamox
polymyxin/bacitracin
Polysporin
polymyxin/neomycin
Neosporin
polymyxin/trimethoprim
Polytrim
tobramycin
Tobrex
Otic Preparations
Used to treat ear conditions
Analgesics
Work by relieving ear pain
benzocaine
Auralgan
Antiinfectives
Work by treating otitis externa
neomycin/polymyxin/hydrocortisone
Cortisporin Otic
ofloxacin
Floxin Otic
Cerumenolytics
Work by softening cerumen
carbamide peroxide
Debrox*
Platelet Inhibitors
Used to reduce incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke
Work by interfering with ability of platelets to adhere to each other
clopidogrel
 Plavix
Plavix
salicylates
Aspirin*
Sedatives and Hypnotics
Used for short-term treatment of insomnia
Work by promoting sleep by central nervous system depression
eszopiclone
 Lunesta (IV)
Lunesta (IV)
flurazepam
Dalmane (IV)
hydroxyzine
Atarax
Vistaril
phenobarbital
Luminal (IV)
temazepam
 Restoril (IV)
Restoril (IV)
zolpidem
 Ambien (IV)
Ambien (IV)
Smoking Deterrents
Used to manage nicotine withdrawal to cease cigarette smoking
Work by providing nicotine during controlled withdrawal from cigarette smoking
bupropion
Zyban
nicotine
Nicorette Gum*
Nicotrol Inhaler
Nicoderm Patch*
Commit Lozenges*
varenicline
Chantix
Thrombolytic Agents
Used for acute management of coronary thrombosis (myocardial infarction)
Work by dissolving existing clots
alteplase
Activase
anistreplase
Eminase
reteplase
Retavase
streptokinase
Streptase
Thyroid Preparations
Thyroid Hormones
Used as replacement or substitute therapy for diminished or absent thyroid functioning of many causes
Work by increasing basal metabolic rate
levothyroxine
 Levoxyl
Levoxyl Synthroid
Synthroid
Antithyroid Agents
Used to treat hyperthyroidism
Work by inhibiting thyroid hormone synthesis, reducing basal metabolic rate
methimazole
Tapazole
Urinary Tract–Antispasmodics
Used to treat overactive bladder function
Work by inhibiting bladder contractions
oxybutynin
Ditropan
tolterodine
 Detrol
Detrol
Vasopressors
Used to treat severe allergic reactions and cardiac arrest
Work by increasing blood pressure and cardiac output and by dilating bronchi
epinephrine
Adrenalin
EpiPen
Weight Control Agents
Used to manage obesity
Appetite Suppressants
Work by suppressing appetite center in central nervous system
diethylpropion
Tenuate (IV)
phentermine
Fastin (IV)
sibutramine
Meridia (IV)
orlistat
Xenical
Lipase Inhibitors
Work by inhibiting action of lipase to decrease absorption of dietary fats
Alli* ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Administration of Medication and Intravenous Therapy
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access