Less than 500 neutrophils/mm3 lasting more than 5 days
OR
OR
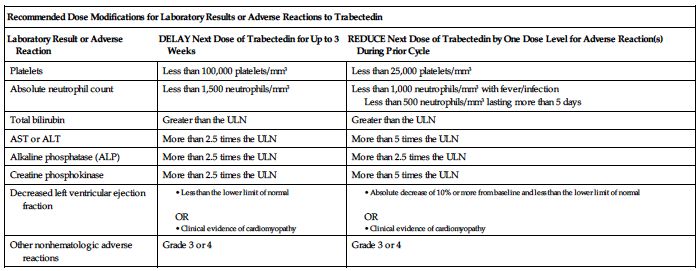
Permanently discontinue trabectedin for (1) persistent adverse reactions requiring a delay in dosing of more than 3 weeks, (2) adverse reactions requiring a dose reduction after trabectedin administration at 1 mg/M2, (3) severe liver dysfunction (all of the following: bilirubin 2 times the ULN, AST or ALT 3 times the ULN, and alkaline phosphatase less than 2 times the ULN in the previous treatment cycle), (4) rhabdomyolysis, or (5) symptomatic cardiomyopathy or persistent left ventricular dysfunction that does not recover to the lower limit of normal within 3 weeks.
Dilution
Specific techniques required; see Precautions. Available as a lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial containing 1 mg of trabectedin. Using aseptic technique, inject 20 mL of SWFI into the vial. Shake the vial until complete dissolution. The reconstituted solution is clear, colorless to pale brownish-yellow, and contains 0.05 mg/mL of trabectedin. Inspect for particulate matter and discoloration before further dilution. Discard vial if particles or discoloration are observed. Immediately following reconstitution, withdraw the calculated volume of trabectedin and further dilute in 500 mL of NS or D5W.
Filters:
Use of a 0.2-micron polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filter is recommended to reduce the risk of exposure to adventitious pathogens that may be introduced during solution preparation.
Storage:
Before use, store vials in a refrigerator at 2° to 8° C (36° to 46° F). Discard any unused portion of the reconstituted solution, and discard any remaining diluted solution within 30 hours of reconstituting the lyophilized powder.
Compatibility
Manufacturer states, “Do not mix trabectedin with other drugs.” Trabectedin diluted solution is compatible with Type I colorless glass vials; polyvinylchloride (PVC) and polyethylene (PE) bags and tubing; PE and polypropylene (PP) mixture bags; polyethersulfone (PES) in-line filters; titanium, platinum, or plastic ports; silicone and polyurethane catheters; and pumps having contact surfaces made of PVC, PE, or PE/PP.
Rate of administration
Infuse the reconstituted, diluted solution over 24 hours through a central venous line using an infusion set with a 0.2-micron PES in-line filter. Complete infusion within 30 hours of initial reconstitution.
Actions
Trabectedin is an alkylating drug that binds guanine residues in the minor groove of DNA, forming adducts and resulting in a bending of the DNA helix toward the major groove. Adduct formation triggers a cascade of events that can affect the subsequent activity of DNA binding proteins, resulting in perturbation of the cell cycle and eventual cell death. Highly protein bound (97%). Terminal elimination half-life is approximately 175 hours. No accumulation in plasma is observed with repeated administrations every 3 weeks. Extensively metabolized with negligible unchanged drug in urine and feces following administration.
Indications and uses
Treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma who received a prior anthracycline-containing regimen.
Contraindications
Known severe hypersensitivity, including anaphylaxis, to trabectedin.
Precautions
Follow guidelines for handling cytotoxic agents. See Appendix A, p. 1331. ■ Administered under the direction of a physician knowledgeable in its use in a facility with adequate diagnostic and treatment facilities to monitor the patient and respond to any medical emergency. ■ Neutropenic sepsis, including fatal cases, can occur. Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, and sepsis have been reported. ■ Rhabdomyolysis and musculoskeletal toxicity have occurred. Has led to renal failure and death in some cases. ■ Hepatotoxicity, including hepatic failure, has occurred. Patients with serum bilirubin levels above the ULN or AST or ALT levels greater than 2.5 times the ULN were excluded from clinical trials. ■ Cardiomyopathy, including cardiac failure, congestive heart failure, decreased ejection fraction, diastolic dysfunction, or right ventricular dysfunction, has been reported. Patients with a history of New York Heart Association Class II to IV heart failure or abnormal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) at baseline were excluded from clinical trials. ■ Extravasation resulting in tissue necrosis and requiring debridement can occur. Evidence of tissue necrosis can occur more than 1 week after the extravasation. Use of a central venous line required. ■ Based on its mechanism of action, trabectedin can cause fetal harm; see Patient Education and Maternal/Child.
Monitor:
Premedication required; see Usual Dose. ■ Obtain baseline CBC with differential and platelets, SCr, and liver function tests (LFTs). ■ Obtain CBC, including differential and platelet count, before each dose of trabectedin and periodically throughout the treatment cycle. Withhold trabectedin for neutrophil counts of less than 1,500 cells/mm3 on the day of dosing. Permanently reduce the dose of trabectedin for life-threatening or prolonged, severe neutropenia in the preceding cycle; see Dose Adjustments. ■ Obtain creatine phosphokinase (CPK) levels before each dose of trabectedin. Withhold trabectedin for serum CPK levels more than 2.5 times the ULN. Permanently discontinue trabectedin if rhabdomyolysis occurs; see Dose Adjustments. ■ Assess LFTs before each dose of trabectedin. Monitor for S/S of hepatotoxicity (e.g., abdominal pain [upper right], jaundice, lethargy, nausea, vomiting). Manage elevated LFTs with treatment interruption, dose reduction, or permanent discontinuation based on severity and duration of LFT abnormality; see Dose Adjustments. ■ Assess left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) by echocardiogram or multigated acquisition (MUGA) scan before initiation of trabectedin and at 2- to 3-month intervals thereafter until trabectedin is discontinued. Monitor for S/S of cardiomyopathy (e.g., chest pain; dyspnea; edema of the legs, ankles, or feet; heart palpitations). Withhold trabectedin for LVEF below the lower limit of normal; see Dose Adjustments. Permanently discontinue trabectedin for symptomatic cardiomyopathy or persistent left ventricular dysfunction that does not recover to the lower limit of normal within 3 weeks. ■ Monitor for S/S of hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, hypotension, pruritus, rash, urticaria, or wheezing). ■ Monitor IV site for any sign of extravasation. ■ Effects of any degree of hepatic impairment, severe renal impairment, or ESRD on trabectedin exposure is unknown.
Patient education:
Review manufacturer’s medication guide. ■ Females of reproductive potential must use effective contraception during therapy and for at least 2 months after the last dose of trabectedin. Notify your health care provider if you become pregnant or suspect a pregnancy. ■ Males with female partners of reproductive potential must use effective contraception during therapy and for at least 5 months after the last dose of trabectedin. ■ Immediately report S/S of a hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, chest tightness, wheezing, severe dizziness or light-headedness, swelling of the lips, or skin rash). ■ Promptly report discomfort, itchiness, leaking, redness, or swelling at the injection site. ■ Promptly report fever, unusual bruising, bleeding, severe muscle pain or weakness, tiredness, or paleness. ■ Promptly report S/S of hepatotoxicity (e.g., yellowing of the skin and eyes [jaundice], pain in the upper right quadrant, severe nausea or vomiting, difficulty concentrating, disorientation, or confusion). ■ Promptly report new-onset chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, lower extremity edema, or heart palpitations. ■ See Appendix D, p. 1333.
Maternal/child:
Based on its mechanism of action, trabectedin can cause fetal harm; effective contraception is required for females and males; see Patient Education. May damage spermatozoa, resulting in possible genetic and fetal abnormalities, and may result in decreased fertility in males and females. ■ Discontinue breast-feeding. ■ Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients not established.
Elderly:
Numbers insufficient to determine differences in response in elderly patients compared with younger adults.
Drug/lab interactions
Coadministration of trabectedin with strong CYP3A inhibitors increases the systemic exposure of trabectedin. Avoid the use of strong CYP3A inhibitors (e.g., atazanavir [Reyataz], boceprevir [Victrelis], clarithromycin [Biaxin], conivaptan [Vaprisol], indinavir (Crixivan), itraconazole [Sporanox], ketoconazole [Nizoral], lopinavir/ritonavir [Kaletra], nefazodone, nelfinavir (Viracept), posaconazole [Noxafil], ritonavir [Norvir], saquinavir [Invirase], telaprevir [Incivek], telithromycin [Ketek], and voriconazole [VFEND]). If a strong CYP3A inhibitor must be used for a short time (fewer than 14 days), wait to administer until 1 week after the trabectedin infusion, and discontinue the day before the next scheduled infusion. ■ Avoid grapefruit and/or grapefruit juice during therapy. ■ Coadministration with strong CYP3A inducers decreases the systemic exposure of trabectedin. Avoid the use of strong CYP3A inducers (e.g., phenobarbital [Luminal], rifampin [Rifadin], St. John’s wort).
Side effects
The most common adverse reactions are constipation, decreased appetite, diarrhea, dyspnea, fatigue, headache, nausea, peripheral edema, and vomiting. Other clinically important adverse reactions include hypoesthesia, paresthesia, peripheral neuropathy, and pulmonary embolism. The most common Grades 3 to 4 laboratory abnormalities are anemia; hypoalbuminemia; increased AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase, CPK, and creatinine; neutropenia; and thrombocytopenia.
Antidote
Keep physician informed of all side effects. May constitute a medical emergency or will be treated symptomatically as indicated. Withhold trabectedin as indicated in Dose Adjustments (e.g., neutrophil counts less than 1,500 cells/mm3; total bilirubin greater than the ULN; AST, ALT, ALP, and CPK more than 2.5 times the ULN; LVEF less than the lower limit of normal; cardiomyopathy; or other Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions) on the day of dosing. Permanently reduce the dose of trabectedin for life-threatening or prolonged severe neutropenia in the preceding cycle. Discontinue administration at the first sign of a serious hypersensitivity reaction and treat as indicated (e.g., oxygen, diphenhydramine, epinephrine, corticosteroids, vasopressors, and/or fluids). Discontinue permanently for (1) persistent adverse reactions requiring a delay in dosing of more than 3 weeks, (2) adverse reactions requiring a dose reduction after trabectedin administration at 1 mg/M2, (3) severe liver dysfunction (all of the following: bilirubin 2 times the ULN, AST or ALT 3 times the ULN, and alkaline phosphatase less than 2 times the ULN in the previous treatment cycle), (4) rhabdomyolysis, or (5) symptomatic cardiomyopathy or persistent left ventricular dysfunction that does not recover to the lower limit of normal within 3 weeks. See Precautions and Monitor. Administration of whole blood products (e.g., packed RBCs, platelets, leukocytes) and/or blood modifiers (e.g., darbepoetin alfa [Aranesp], epoetin alfa [Epogen], filgrastim [Neupogen, Zarxio], pegfilgrastim [Neulasta], sargramostim [Leukine]) may be indicated to treat bone marrow toxicity. There is no specific antidote for trabectedin. Hemodialysis is not expected to enhance the elimination of trabectedin because trabectedin is highly bound to plasma proteins and not significantly renally excreted. Resuscitate as indicated.
Tranexamic acid
(TRAN-eks-am-ik AS-id)
Cyklokapron
Antifibrinolytic
Antihemorrhagic
pH 6.5 to 8
Usual dose
Dental extraction in adults and pediatric patients with hemophilia:
Preoperative: Normal renal function required. 10 mg/kg IV immediately before surgery. Postoperative: 10 mg/kg IV every 6 to 8 hours for 2 to 8 days.
Trauma-associated hemorrhage (unlabeled):
A loading dose of 1,000 mg IV over 10 minutes followed by an infusion of 1,000 mg over 8 hours. Treatment should begin within 8 hours of injury.
Total knee replacement surgery, blood loss reduction (unlabeled):
Several regimens have been studied and include:
10 mg/kg IV over 30 minutes before inflation of the tourniquet followed by 10 mg/kg IV 3 hours after the first dose
OR
10 mg/kg IV administered 30 minutes before deflation of the tourniquet followed by an infusion of 1 mg/kg/hr. Infusion begins at the end of surgery and continues for 6 hours postoperatively.
Dose adjustments
Lower-end initial and/or reduced doses may be indicated in the elderly based on the potential for decreased organ function and concomitant disease or drug therapy. ■ Reduce dose in impaired renal function according to the following chart.
| Tranexamic Dose Guidelines in Impaired Renal Function | |
| Serum Creatinine (mg/dL) | Dose |
| 1.36-2.83 mg/dL | 10 mg/kg two times per day |
| 2.83-5.66 mg/dL | 10 mg/kg once per day |
| >5.66 mg/dL | 10 mg/kg every 48 hours or 5 mg/kg every 24 hours |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


