Drugs Used to Treat the Musculoskeletal System
Objectives
1 Describe the nursing assessment data needed to evaluate a patient with a skeletal muscle disorder.
Key Terms
cerebral palsy ( ) (p. 718)
) (p. 718)
multiple sclerosis ( ) (p. 718)
) (p. 718)
hypercapnia (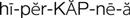 ) (p. 719)
) (p. 719)
spasticity ( ) (p. 721)
) (p. 721)
muscle spasms (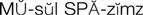 ) (p. 721)
) (p. 721)
stroke syndrome (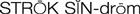 ) (p. 723)
) (p. 723)
neuromuscular blocking agents (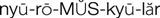
 ) (p. 724)
) (p. 724)
![]() http://evolve.elsevier.com/Clayton
http://evolve.elsevier.com/Clayton
The muscular system involves all of the voluntary muscles that line the skeleton of the body and allow for movement. The most common musculoskeletal disorders are cerebral palsy and multiple sclerosis. Cerebral palsy is a condition in which movement of the extremities is marked with any combination of the following: exaggerated reflexes, abnormal posture, involuntary movements, and walking difficulties. Cerebral palsy can be caused by an injury or a birth defect.
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms may be mild, such as numbness in the limbs, or severe, such as paralysis or loss of vision. The progression, severity and specific symptoms of multiple sclerosis are unpredictable and highly variable between persons.
Muscle Relaxants and Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
 Nursing Implications for Skeletal Muscle Relaxants and Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
Nursing Implications for Skeletal Muscle Relaxants and Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
Assessment
Assessment for Skeletal Muscle Disorders.
Musculoskeletal disorders may produce varying degrees of pain and immobility, impairing the individual’s ability to perform the activities of daily living. The nursing assessments performed are individualized to the muscles affected and the underlying disease.
Current History
History
Medication History
Activity and Exercise
Sleep and Rest
Elimination
Nutrition
Physical Examination
• During examination, note differences in circumference, symmetry, or length of limbs.
• Record any abnormalities present (e.g., scoliosis, contractures, atrophy).
• Record range of motion present in joints, gait, and degree of mobility.
• Evaluate capillary refill, and check for presence of paresthesia (numbness and tingling).
Laboratory and Diagnostic Studies
Assessment for Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
• Monitor the patient closely for clinical signs of hypoxia and hypercapnia (tachycardia, hypotension, and cyanosis). Arterial blood gas levels (see Table 31-1) may be determined to confirm the clinical observations.
Detection of Respiratory Depression
Pain Assessment.
Assess the degree of pain present because neuromuscular blocking agents paralyze the muscles but do NOT relieve pain.
Implementation
Nursing Interventions With Musculoskeletal Disorders
Nursing Interventions With Neuromuscular Blockers
 Patient Education and Health Promotion
Patient Education and Health Promotion
Pain Relief
Activities and Exercise.
The patient must resume activities of daily living within the boundaries set by her or his health care provider. Activities such as regular moderate exercise, meal preparation, resumption of usual sexual activities, and social interaction must be encouraged once specific orders have been obtained.
Psychosocial.
For chronic disorders, encourage the patient to express feelings regarding chronic illness. The adjustment to this situation involves working through great personal fears, frustrations, hostilities, and resentments associated with the loss of personal control in one’s life.
Medications.
Many of the medications used in the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders produce sedation. Teach the patient about safety precautions such as avoiding using power equipment or driving while taking these medications.
Fostering Health Maintenance
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


