CHAPTER 46 Research and Evidence-Based Practice
Nursing Education and Research Functions
Application to Clinical Practice
II. NURSING EDUCATION AND RESEARCH FUNCTIONS
A. Educational Institutions Incorporate Various Research Activities into Their Programs to Familiarize Nurses with the Research Process and Related Responsibilities
B. The American Nurses Association (1994) Delineated the Following Educational Preparation for Nurses Involved in Research:
1. Associate degree in nursing
2. Baccalaureate degree in nursing
III. RESEARCH PROJECTS
B. Research Study
1. Uses formal plan to study problem
2. Looks for several solutions simultaneously
3. Is based on theory or generates a theory
4. Uses statistical analysis for quantitative research and uses words or themes as basis for analysis with qualitative research
5. Is concerned with issues of reliability and validity in quantitative research and auditability, credibility, and fittingness in qualitative research
6. May suggest solutions with wide applications for quantitative research or describe and give meaning to life experiences for qualitative research
IV. RESEARCH METHODOLOGIES
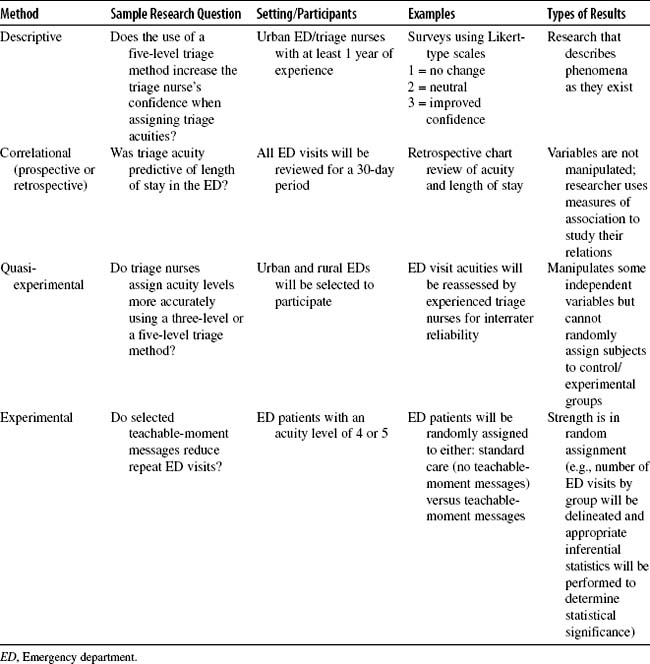
A. Quantitative (Table 46-1)
1. Described as a formal, objective, and systemic process: deductive process
2. Uses numeric data to quantify findings
3. Used to describe variables, examine relationships among variables, and determine cause-and-effect interactions between variables
4. Is most frequently used method of research studies
5. Identification of dependent and independent variables
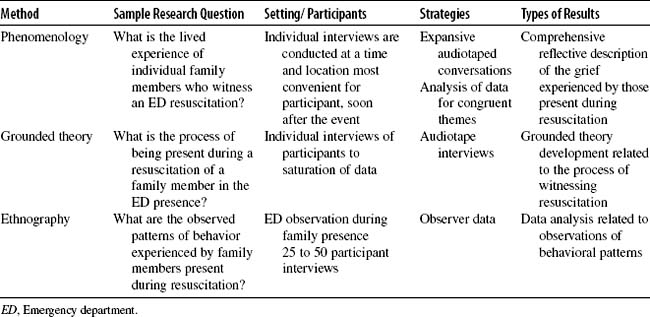
B. Qualitative (Table 46-2)
1. Described as a systematic, interactive, and subjective approach
2. Uses words, not numbers, to give meaning to data
3. Used to describe life experiences and give them meaning
4. Is used less frequently than quantitative research, often generates rich, meaningful data
C. Triangulation (Blended Methods)
1. Can be employed in both quantitative and qualitative studies; may combine two types of the same methodology or may be a blending of both methodologies
2. Allows limitations of two methodologies to be overcome by comparing findings from different perspectives
3. May be used to overcome weaknesses in a specific method of data collection by using many strategies to avoid potential deficiencies of a single methodology or theory
V. RESEARCH PROCESS STEPS
B. Problem Statement
2. Elements of problem statement
3. Theoretical or conceptual framework
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree