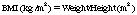74 Providing nutritional support
Assessment
Dietary history
Physical assessment
Estimating nutritional requirements
Carbohydrate (CHO) requirements:
Excess amounts of CHO are not utilized or tolerated. Overfeeding of CHO may lead to hyperglycemia, increased CO2 production, hypophosphatemia, and fluid overload in short-term use or fatty liver syndrome in long-term use. Patients with diabetes will need to be counseled regarding how to count carbohydrates for appropriate glycemic control (see “Diabetes Mellitus,” p. 348).
Fat requirements:
Saturated fat intake should be limited, especially in patients with coronary artery disease (see p. 150).
Fluid requirements:
Nutritional support modalities
Specialized nutritional support refers to provision of an artificial formulation of nutrients via oral, enteral, or parenteral route for the treatment or prevention of malnutrition. Oral supplements are the preferred route because they are less invasive, more natural, and less costly, whereas enteral nutrition is preferred over parenteral.