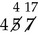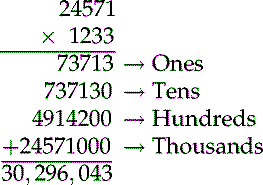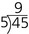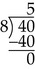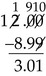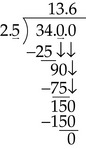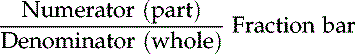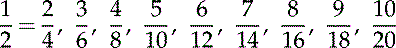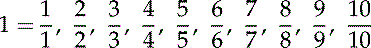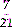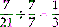1 Mathematics
Basic Addition and Subtraction
Vocabulary
Digit: Any number 1 through 9 and 0 (e.g., the number 7 is a digit).

(From Ogden SJ, Fluharty LK: Calculation of drug dosages: A work text, ed 9, St. Louis, 2012, Elsevier/Mosby.)
Basic Multiplication (Whole Numbers)
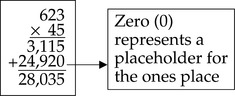
The process of multiplication is essentially repeated addition.
Vocabulary
Product: The answer to a multiplication problem.
Basic Division (Whole Numbers)
Vocabulary
Dividend: The number being divided.
Divisor: The number by which the dividend is divided.
Quotient: The answer to a division problem.
Remainder: The portion of the dividend that is not evenly divisible by the divisor.
Example 2
| 672 ÷ 6 | 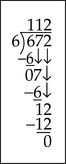 |
Example 3
| 174 ÷ 5 | 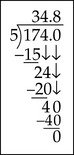 |
Decimals
A decimal pertains to tenths or to the number 10.
Addition and Subtraction of Decimals
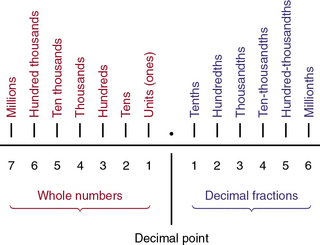
(From Ogden SJ, Fluharty LK: Calculation of drug dosages: A work text, ed 9, St. Louis, 2012, Elsevier/Mosby.)
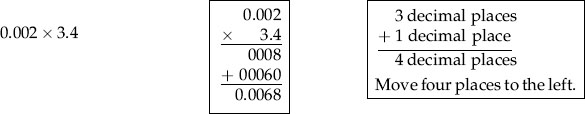
Multiplication of Decimals
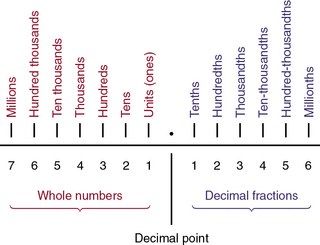
(From Ogden SJ, Fluharty LK: Calculation of drug dosages: A work text, ed 9, St. Louis, 2012, Elsevier/Mosby.)
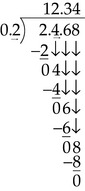
Division of Decimals
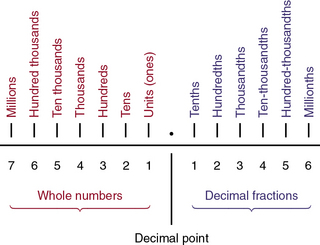
(From Ogden SJ, Fluharty LK: Calculation of drug dosages: A work text, ed 9, St. Louis, 2012, Elsevier/Mosby.)
Fractions
In mathematics, a fraction is a way to express a part in relation to the total.
Vocabulary
Numerator: The top number in a fraction.
Denominator: The bottom number in a fraction.
Factor: A number that divides evenly into another number.
Least Common Denominator: The smallest multiple that two numbers share.
Improper Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is larger than the denominator.
Proper Fraction: A fraction where the denominator is larger than the numerator.
Common Denominator: Two or more fractions having the same denominator.
Reciprocals: Pairs of numbers that equal 1 when multiplied together.
Terminating Decimal: A decimal that is not continuous.
Reducing Fractions Using the Greatest Common Factor
A factor is a number that divides evenly into another number.
Reducing fractions can also be called reducing a fraction to its lowest terms or simplest form.