(70 kg × 40% increase × 1 IU/kg = 2,800 IU). To maintain levels above 25%, calculate each dose to raise level to 40% to 60% of normal.
Minor hemorrhage:
A single injection calculated to increase plasma level to 20% to 30%. May be repeated in 24 hours if indicated.
Major trauma or surgery:
Increase plasma level to 25% to 50% and maintain at that level for a minimum of 1 week or as indicated. May require daily injections (every 18 to 30 hours).
Dental extraction:
Increase plasma level to 50% before procedure; repeat if indicated.
Prophylaxis:
10 to 20 IU/kg once or twice a week or increase plasma level to 20% to 30%.
Factor IX complex
Reversal of coumarin effect:
15 IU/kg.
Dilution
Diluent usually provided. Some preparations also supply double-ended needles for dilution and filter needle for aspiration into a syringe. Sterile technique imperative. Confirm expiration date. Use plastic syringes to prevent binding to glass surfaces. Factor IX and diluent should be at room temperature. Direct diluent from above to side of vial to gently moisten all contents. Swirl gently to dissolve; avoid foaming. Do not shake. May take 1 to 5 minutes. Should be clear and colorless. Must be used within 3 hours to avoid bacterial contamination. The addition of 2 to 3 units of heparin/mL factor IX complex may reduce the incidence of thrombosis. May be given through an IV administration set (often provided) if multiple vials are required. Discard any unused contents. Discard all administration equipment after single use; do not attempt to resterilize.
Alphanine SD:
Follow general directions above. After diluent is drawn through double-ended needle, remove diluent bottle first; then remove double-ended needle. Do not invert concentrate vial until ready to withdraw contents! Air from syringe into vial required to withdraw contents. Withdraw through filter.
Mononine:
Follow general directions listed previously. After diluent is drawn through double-ended needle, remove diluent bottle first; then remove double-ended needle. Use only the provided self-venting filter spike to transfer Mononine to a syringe! Do not inject any air into Mononine vial; could cause product loss. Discard filter and use only provided wing needle and micropore tubing to administer.
Filters:
Usually supplied by manufacturer. If more than one vial is required for a dose, multiple vials may be drawn into the same syringe; however, a new filter needle must be used to withdraw the contents of each vial of factor IX and/or factor IX complex (Human). Manufacturers of AlphaNine SD and Mononine provide a filter needle, which is to be used to withdraw reconstituted solution into a syringe. Discard filter needle after aspiration into the syringe. No further filtering is required for administration.
Storage:
Store lyophilized powder at 2° to 8° C (36° to 46° F); do not freeze. Do not refrigerate after dilution. Mononine may be stored at room temperature before dilution for up to 30 days.
Compatibility
Specific information not available. Consider specific use; consult pharmacist.
Rate of administration
Average rate is 2 to 3 mL or 100 units/min. Completely individualized according to patient’s condition. Decrease rate of administration for side effects such as burning or pain at injection site, chills, fever, flushing, headache, tingling, or changes in BP or pulse. Never exceed 10 mL/min.
Actions
A lyophilized concentrate of human coagulation factors: IX (plasma thromboplastin and antihemophilic factor B), II (prothrombin), VII (proconvertin), and X (Stuart-Prower factor). In contrast to other products, AlphaNine SD and Mononine are highly purified factor IX and contain only minimal amounts of the other factors. All products are obtained from fresh human plasma and prepared, irradiated, and dried by specific processes. Additional processes are used to prepare AlphaNine SD and Mononine that markedly reduce the possibility of viral contamination. Concentration of 25 units/mL is 25 times greater than normal plasma. Preparations contain varying amounts of total protein in each vial. Half-life is approximately 24 hours (range 18 to 36 hours).
Indications and uses
All factor IX products:
Prevention/control of bleeding in patients with factor IX deficiency due to hemophilia B. Indicated to correct or prevent a dangerous bleeding episode or to perform surgery. ■ Prophylaxis to prevent spontaneous bleeding in patients with proven specific congenital deficiency (hemophilia B).
Factor IX (human):
Preferred for surgical coverage; treatment of crush injuries and/or large IM hemorrhages requiring several days of replacement therapy; and treatment in neonates, individuals with severe hepatocellular dysfunction, or those with a history of thrombotic complications associated with factor IX complex.
Factor IX complex:
Prevention/control of bleeding in patients with hemophilia A who have inhibitors to factor VIII. ■ Reversal of coumarin effect (fresh-frozen plasma preferred unless risk of hepatitis transfer would be life threatening). ■ Hemorrhage caused by hepatitis-induced lack of production of liver-dependent coagulation factors. ■ Proplex T is used for prevention or control of bleeding episodes in patients with factor VII deficiency.
Contraindications
Factor IX complex:
Known liver disease with suspicion of intravascular coagulation or fibrinolysis. ■ Factor VII deficiency except for Proplex T.
Mononine:
Known hypersensitivity to mouse protein. ■ No other known contraindications for AlphaNine SD or Bebulin VH. ■ AlphaNine SD, Bebulin VH, and Mononine are not indicated for replacement of any other coagulation factors.
Precautions
Used when plasma infusions would result in hypervolemia and/or proteinemia or when blood volume or RBC replacement is not indicated. ■ Use extreme caution in newborns, infants, postoperative patients, and patients with liver disease. Factor IX (human) (e.g., AlphaNine SD, Mononine) would be preferred because studies show no incidence of thrombin generation. ■ Fresh-frozen plasma may be required in addition to factor IX complex when prompt reversal is required. ■ Danger of thromboembolic episodes (DIC, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis) increases with plasma levels over 50%. ■ Large or frequently repeated doses of factor IX complex may cause intravascular hemolysis in patients with type A, B, or AB blood.
Monitor:
Monitor the patient’s levels of coagulation factors before, after, and between administrations. Do not overdose; see Side Effects. ■ AIDS or hepatitis is possible for the recipient. Health care professionals should exercise caution in handling. Possibility markedly reduced with additional preparation process of AlphaNine SD and Mononine. ■ Observe for signs and symptoms of postoperative thrombosis or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Risk multiplies with repeated administrations except for AlphaNine, AlphaNine SD, and Mononine.
Patient education:
Alert to possible risk of HIV virus and hepatitis. ■ Report early signs of hypersensitivity promptly (burning or pain along injection site, hives, rash, tightness of chest, wheezing). ■ Notify physician if medication seems less effective. May be developing antibodies to factor IX. ■ Carry identification card. ■ Proper preparation and administration imperative if given in home.
Maternal/child:
Category C: safety for use during pregnancy not established; use only if clearly indicated; see Precautions. ■ Use extreme caution in neonates with hepatitis; high rate of morbidity.
Drug/lab interactions
Concurrent use of aminocaproic acid (Amicar) may increase risk of thrombosis.
Side effects
Burning or pain along injection site, changes in BP, chills, fever, flushing, headache, nausea, tingling, urticaria, vomiting.
Major:
Anaphylaxis, DIC, hepatitis, myocardial infarction, postoperative thrombosis (rare with pure factor IX [Human] products), pulmonary embolism. Consider risk potential of contracting AIDS and hepatitis; markedly reduced with pure factor IX (Human) products (AlphaNine, AlphaNine SD, and Mononine).
Antidote
Temporarily discontinue or decrease rate of administration for minor side effects. For major symptoms, discontinue, and notify physician. Treat hypersensitivity reactions as indicated; a different lot may not cause reaction. For thrombosis or DIC, anticoagulation with heparin may be indicated.
Factor IX (recombinant)
(FAK-tor 9 [re-KOM-be-nant])
Alprolix, BeneFIX, IDELVION, IXINITY, RIXUBIS
Antihemorrhagic
Usual dose (international units [IU])
Available recombinant factor IX products include:
Alprolix (recombinant):
A coagulation factor IX Fc fusion protein consisting of the human coagulation factor IX sequence covalently linked to the Fc domain of human immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1). Does not contain proteins derived from animal or human sources.
BeneFIX (recombinant), IXINITY (recombinant), RIXUBIS (recombinant):
Coagulation factor IX proteins produced by a genetically engineered mammalian cell line derived from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. No human or animal proteins are added during any stage of manufacturing.
IDELVION (recombinant):
A coagulation factor IX, albumin fusion protein (rIX-FP) comprising genetically fused recombinant coagulation factor IX and recombinant albumin. Does not contain proteins derived from animal or human sources.
Adults and pediatric patients:
Completely individualized based on the degree of deficiency, the location and extent of bleeding, the patient’s clinical condition and age, and the pharmacokinetic parameters of factor IX, such as incremental recovery and half-life. Base dose and frequency on individual clinical response. Units required to raise blood level percentages are somewhat increased with recombinant products compared with other factor IX products and can be calculated using the following formulas:
Number of factor IX IU required = Body weight (in kg) × Desired factor IX increase (% of normal or IU/dL) × Reciprocal of observed recovery (IU/kg per IU/dL)
The observed recovery for the various products is as follows:
Alprolix:
One IU of recombinant product/kg of body weight increases the circulating level of factor IX by 1% (IU/dL).
BeneFIX:
One IU of recombinant product/kg of body weight increases the circulating level of factor IX by 0.8% (IU/dL) for adults and by 0.7% (IU/dL) in pediatric patients under 15 years of age.
IDELVION:
One IU of recombinant product/kg of body weight is expected to increase the circulating level of factor IX by 1.3% (IU/dL) in patients 12 years of age or older and by 1% (IU/dL) in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age.
IXINITY:
One IU of recombinant product/kg of body weight increases the circulating level of factor IX by 0.98% (IU/dL).
RIXUBIS:
One IU of recombinant product/kg of body weight increases the circulating level of factor IX by 0.9% (IU/dL) for patients 12 years of age or older and by 0.7% (IU/dL) in pediatric patients under 12 years of age.
In the presence of an inhibitor, higher doses may be required. See examples of dose calculation in prescribing information.
The following chart may be used to guide dosing in the prevention of bleeding episodes.
| Factor IX (Recombinant) Dosing Guidelines for Prevention and Control of Bleeding in Adults and Pediatric Patients | |||
| Type of Bleeding Episodes | Circulating Factor IX Activity Required (% of normal or IU/dL) | Dosing Interval (hours) | Duration of Therapy (days) |
| Minor Uncomplicated or early bleeds: hemarthroses, superficial muscle (except iliopsoas) with no neurovascular compromise, other soft tissue or oral bleeding | Alprolix 30 to 60 | 48 hours | Repeat every 48 hours if there is further evidence of bleeding |
| BeneFIX 20 to 30 | 12 to 24 hours | 1 to 2 days | |
| IDELVION* 30 to 60 | 48 to 72 hours | At least 1 day until bleeding stops and healing is achieved A single dose should be sufficient for the majority of bleeds | |
| IXINITY 30 to 60 | 24 hours | 1 to 3 days until healing is achieved | |
| RIXUBIS 20 to 30 | 12 to 24 hours | At least 1 day until healing is achieved | |
| Moderate Intramusclar or soft tissue with dissection, mucous membranes, dental extractions, hematuria, hemarthrosis of longer duration, recurrent hemarthrosis, deep lacerations | Alprolix 30 to 60 | 48 hours | Repeat every 48 hours if there is further evidence of bleeding |
| BeneFIX and RIXUBIS 25 to 50 | 12 to 24 hours | Treat until bleeding stops and healing begins, about 2 to 7 days | |
| IDELVION* 30 to 60 | 48 to 72 hours | At least 1 day until bleeding stops and healing is achieved A single dose should be sufficient for the majority of bleeds | |
| IXINITY 40 to 60 | 24 hours | 2 to 7 days until healing is achieved | |
| Major Life-threatening or limb-threatening hemorrhage, iliopsoas and deep muscle with neurovascular injury or substantial blood loss, pharyngeal, retropharyngeal, retroperitoneal, CNS | Alprolix 80 to 100 | Consider a repeat dose after 6 to 10 hours and then every 24 hours for the first 3 days | Due to the long half-life of Alprolix, the dose may be reduced and frequency may be extended after Day 3 to every 48 hours or longer until bleeding stops and healing is achieved |
| BeneFIX and RIXUBIS 50 to 100 | 12 to 24 hours | 7 to 10 days until bleeding stops and healing is achieved | |
| IDELVION* 60 to 100 | 48 to 72 hours | 7 to 14 days until bleeding stops and healing is achieved Maintenance dose weekly | |
| IXINITY 60 to 100 | 12 to 24 hours | 2 to 14 days until healing is achieved | |
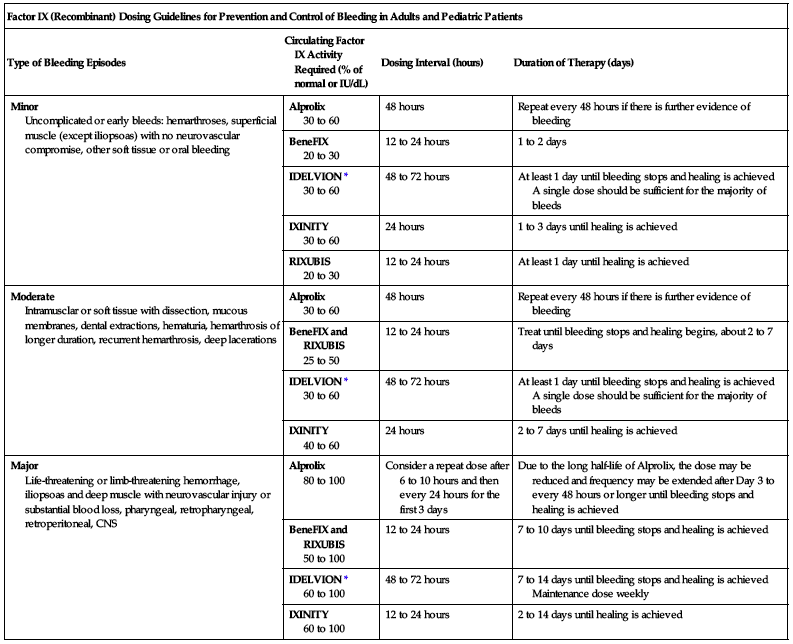
*Adapted from the WFH Guidelines for the Management of Hemophilia.
Source: Roberts and Eberst and Srivastava et al. 2013.
Dosing for perioperative management is provided in the following chart.
| Factor IX (Recombinant) Dosing for Perioperative Management in Adults and Pediatric Patients | |||
| Type of Surgery | Circulating Factor IX Level Required (% or IU/dL) | Dosing Interval (hours) | Duration of Therapy (days) |
| Minor (e.g., tooth extraction) | Alprolix 50 to 80 | A single infusion may be sufficient | Repeat as needed after 24 to 48 hours until bleeding stops and healing is achieved |
| BeneFIX 20 to 30 | 12 to 24 hours | 1 to 2 days until bleeding stops and healing is achieved | |
| IDELVION* 50 to 80 | 48 to 72 hours | At least 1 day or until healing is achieved A single dose should be sufficient for the majority of minor surgeries | |
| IXINITY Preoperative: 50 to 80 Postoperative: 30 to 80 | 24 hours | 1 to 5 days depending on type of procedure | |
| RIXUBIS 30 to 60 | 24 hours | At least 1 day until healing is achieved | |
| Major (e.g., intracranial, intra-abdominal, intrathoracic, joint replacement, pharyngeal, retropharyngeal, retroperitoneal) | Alprolix 60 to 100 (initial level) | Consider a repeat dose after 6 to 10 hours and then every 24 hours for the first 3 days | Due to the long half-life of Alprolix, the dose may be reduced and frequency in the postsurgical setting may be extended after Day 3 to every 48 hours or longer until bleeding stops and healing is achieved |
| BeneFIX 50 to 100 | 12 to 24 hours | 7 to 10 days until bleeding stops and healing is achieved | |
| IDELVION* 60 to 100 (initial level) | 48 to 72 hours | 7 to 14 days or until bleeding stops and healing is achieved Repeat dose every 48 to 72 hours for the first week or until healing is achieved Maintenance dose 1 to 2 times per week | |
| IXINITY Preoperative: 60 to 80 Postoperative: 40 to 60 Postoperative: 30 to 50 Postoperative: 20 to 40 | 8 to 24 hours | 1 to 3 days 4 to 6 days 7 to 14 days | |
| RIXUBIS 80 to 100 | 8 to 24 hours | 7 to 10 days until bleeding stops and healing is achieved | |
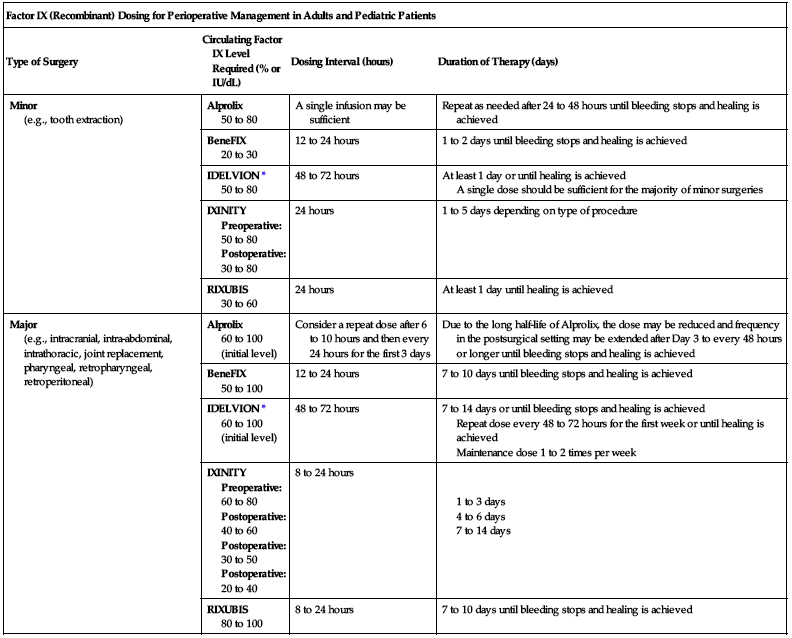
*Adapted from the WFH Guidlines for the Management of Hemophilia.
Routine prophylaxis dosing is as follows:
Alprolix dosing for routine prophylaxis in adults and pediatric patients:
Routine starting regimens are either 50 IU/kg once weekly or 100 IU/kg once every 10 days. Adjust dose based on patient response.
IDELVION dosing for routine prophylaxis in patients 12 years of age or older:
Recommended dose is 25 to 40 IU/kg every 7 days. Patients who are well-controlled on this regimen may be switched to a 14-day interval at 50 to 75 IU/kg.
IDELVION dosing for routine prophylaxis in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age:
RIXUBIS dosing for routine prophylaxis in adults:
Dose for previously treated patients is 40 to 60 IU/kg twice weekly for patients 12 years of age and older and 60 to 80 IU/kg twice weekly for patients under 12 years of age. Dose titration may be necessary based on individual patient’s age, bleeding pattern, and physical activity.
Dose adjustments
Adjust dose and frequency of repeated infusions by using factor IX activity and pharmacokinetic parameters such as half-life and incremental recovery, as well as by taking the clinical situation into consideration. ■ Patients at the lower end of the observed factor IX recovery range may require upward dose adjustment; see Monitor. ■ Dose adjustment may be necessary in pediatric patients under 12 years of age; see Maternal/Child.
Dilution
Actual number of international units contained is shown on each bottle or vial. Alprolix is supplied in a kit that includes single-use vials containing 500, 1,000, 2,000, or 3,000 IU/vial. BeneFIX is supplied in a kit that includes single-use vials containing 250, 500, 1,000, 2,000, or 3,000 IU/vial. IDELVION is available in a kit that includes single-use vials containing 250, 500, 1,000, or 2,000 IU/vial. IXINITY is available in single-use vials containing 500, 1,000, or 1,500 IU/vial. RIXUBIS is available in single-use vials containing 250, 500, 1,000, 2,000, or 3,000 IU/vial. Sterile technique imperative. Confirm expiration date. Plastic syringes may be indicated to prevent binding to glass surfaces. Factor IX and diluent should be at room temperature. Provided diluent, dilution, and transfer equipment are specific to each product; consult manufacturer’s detailed preparation and reconstitution process in prescribing information. When diluted, solution should be clear and colorless. (IDELVION may be yellow to colorless.) Multiple vials may be drawn in the same larger syringe per manufacturer’s specific directions. Most products must be used within 3 hours of reconstitution. IDELVION must be used within 4 hours of reconstitution.
Filters:
Supplied by manufacturer if indicated. If more than one vial is required for a dose, multiple vials may be drawn into the same syringe; see Dilution.
Storage:
Alprolix:
Refrigerate kit at 2° to 8° C (36° to 46° F). Store in original package and protect from light. Do not refrigerate after reconstitution.
BeneFIX:
If product is labeled for RT storage, it may be stored at CRT or refrigerated at 2° to 8° C (36° to 46° F). If product is labeled for refrigeration, store at 2° to 8° C (36° to 46° F).
IDELVION:
Store in original carton to protect from light in the refrigerator or at RT (2° to 25° C [36° to 77° F]). Do not freeze. Do not refrigerate after reconstitution.
IXINITY:
Store at 2° to 25° C (36° to 77° F) in original carton to protect from light. Do not refrigerate after reconstitution.
RIXUBIS:
Refrigerate at 2° to 8° C (36° to 46° F) for up to 24 months.
All products:
Avoid freezing. Do not use after the expiration date. Discard unused product. All products except IDELVION: Must be used within 3 hours of reconstitution. IDELVION must be used within 4 hours of reconstitution. Alprolix, BeneFIX, and RIXUBIS may be stored at room temperature not exceeding 30° C (86° F) for up to 6 months (12 months for RIXUBIS) before expiration (mark date removed from refrigerator on carton). Do not return to the refrigerator.
Compatibility
Alprolix, IXINITY:
Manufacturer states, “Do not administer in the same tubing or container with other medications.”
BeneFIX:
Do not administer in the same tubing or container with other medicinal products. Do not allow blood to enter the syringe; if red blood cell agglutination is observed, discard everything and start over with new product and supplies.
IDELVION:
Manufacturer states, “Do not mix or administer in the same tubing or container with other medicinal products.”
RIXUBIS:
Specific information not available. Consider specific use; consult pharmacist and note compatibility under BeneFIX.
Rate of administration
Alprolix, IDELVION, IXINITY, RIXUBIS:
Administer as an IV bolus infusion. Rate of administration should be determined by patient’s comfort level and no faster than 10 mL/min.
BeneFIX:
Administer over a period of several minutes. Adapt to the comfort level of each individual patient.
All products:
Record the name and batch number of the product in the patient record.
Actions
An antihemorrhagic. A purified protein produced by recombinant DNA technology for use in the treatment of factor IX deficiency. Its primary amino acid sequence is identical to a form of plasma-derived factor IX, and it has structural and functional characteristics similar to those of endogenous factor IX. Inherently free from the risk of transmission of human bloodborne pathogens such as HIV, hepatitis viruses, and parvovirus. Factor IX is the specific clotting factor deficient in patients with hemophilia B and in patients with acquired factor IX deficiencies. Factor IX (recombinant) increases plasma levels of factor IX and can temporarily correct the coagulation defect in these patients, restoring hemostasis. Normalizes aPTT. Average half-life of Alprolix is 86 hours. Half-life of BeneFIX ranges from 11 to 36 hours. The fusion of the recombinant coagulation factor IX with recombinant albumin extends the half-life of factor IX with IDELVION. The half-life of IDELVION ranges from 104 to 118 hours in adults and from 87 to 93 hours in pediatric patients less than 18 years of age (depending on dose). IXINITY half-life ranges from 17 to 31 hours. RIXUBIS half-life ranges from 16 to 42 hours.
Indications and uses
All products:
Control and prevention of bleeding episodes in adult and pediatric patients with hemophilia B (congenital factor IX deficiency or Christmas disease). ■ Perioperative management in adult and pediatric patients with hemophilia B. IXINITY use is limited to patients 12 years of age or older.
Alprolix, IDELVION, RIXUBIS:
Routine prophylaxis to prevent or reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes in adults and pediatric patients with hemophilia B.
Limitations of use:
All products:
Not indicated for induction of immune tolerance in patients with hemophilia B; see Precautions.
BeneFIX:
Not indicated for treatment of other factor deficiencies (e.g., factors II, VII, VIII, and X), hemophilia A patients with inhibitors to factor VIII, reversal of coumarin-induced anticoagulation, or bleeding due to low levels of liver-dependent coagulation factors.
Contraindications
Alprolix:
Known history of hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis) to the product or its excipients.
BeneFIX, IDELVION, IXINITY, RIXUBIS:
Known history of hypersensitivity to the products or their excipients, including hamster protein.
RIXUBIS:
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and/or signs of fibrinolysis.
Precautions
All products:
For IV bolus infusion only; see Rate of Administration. Safety and effectiveness of continuous infusion have not been established. ■ Usually administered under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of hemophilia B. ■ Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported. Risk may be highest during the early phases of initial exposure in previously untreated patients. An association between the occurrence of factor IX inhibitor and allergic reactions has been reported. ■ Thromboembolic episodes (e.g., disseminated intravascular coagulation [DIC], myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, arterial or venous thrombosis) have been reported with factor IX concentrates. Most have been reported in patients receiving factor IX complex concentrates or factor IX via continuous infusions. ■ Because of potential thromboembolic problems, use caution in patients with liver disease, patients with signs of fibrinolysis, patients in the perioperative or postoperative period, neonates, or patients at risk for thromboembolic phenomena or DIC. Benefit must be weighed against risk. ■ Factor IX inhibitors may develop; see Monitor. ■ Nephrotic syndrome has been reported following attempted immune tolerance induction in hemophilia B patients with factor IX inhibitors. Safety for use in immune tolerance induction not established.
Monitor:
All products:
To ensure desired factor IX activity levels are achieved and maintained, precise monitoring using the one-stage factor IX activity assay is recommended, especially during surgical intervention. Adjust dose and frequency as required. Do not overdose; see Side Effects. ■ Monitor vital signs. ■ Monitor for S/S of hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., angioedema, chest pain, dizziness, dyspnea, fever, flushing, hypotension, nausea, pruritus, rash, rigors, urticaria, wheezing). ■ Monitor for early signs of thrombotic events and consumptive coagulopathy; see Precautions. ■ Monitor for development of factor IX inhibitors. Failure to attain the expected factor IX activity plasma levels or to control bleeding with an appropriate dose may indicate development of factor IX inhibitors. Assays used to determine if factor IX inhibitor is present should be titered in Bethesda units (BUs). ■ Patients dosed with high-purity factor IX products who develop inhibitors are at increased risk for anaphylaxis with repeat doses. Evaluate patients who experience a hypersensitivity reaction for the presence of an inhibitor.
Patient education:
All products:
Read manufacturer-supplied patient product information. ■ Hypersensitivity reactions can occur. Promptly report difficulty breathing, hives, itching, tightness of the chest, and/or wheezing. If self-administering, discontinue use and contact physician immediately. ■ Contact provider for lack of clinical response. May indicate development of inhibitors.
Maternal/child:
All products:
Use during pregnancy only if clearly indicated and/or the potential benefit justifies the potential risk. ■ Use caution during breast-feeding. ■ Pediatric patients may have higher factor IX body weight–adjusted clearance, shorter half-life, and lower recovery. Higher dose per kilogram of body weight or more frequent dosing may be needed. ■ Safety and effectiveness of IXINITY for use in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age not established.
Elderly:
All products:
Numbers in clinical studies insufficient to determine whether the elderly respond differently than do younger subjects.
Drug/lab interactions
Specific information not available. Factor IX activity measurements in the clinical lab may be affected by the type of activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) reagent or laboratory standard used.
Side effects
Alprolix:
Headache and oral paresthesia were most common. Breath odor, dizziness, dysgeusia, fatigue, hypotension, infusion site pain, obstructive uropathy, and palpitations have been reported. No inhibitors were detected and no events of anaphylaxis were reported during clinical studies.
BeneFIX:
Dizziness, headache, injection site pain, injection site reaction, nausea, and rash were most common. Blurred vision, cellulitis at IV site, chest tightness, drowsiness, dry cough, factor IX inhibition, fever, flushing, hives, hypoxia, phlebitis at IV site, renal infarct, shaking, taste perversion, and vomiting have been reported. Hypersensitivity reactions (including bronchospastic reactions and/or hypotension and anaphylaxis) and the development of high-titer inhibitors requiring alternate treatments to factor IX therapy are the most serious.
IDELVION:
Most commonly reported reaction is headache. Dizziness, eczema, hypersensitivity reactions, and rash have been reported.
IXINITY:
Most commonly reported reaction is headache. Apathy, asthenia, depression, dysgeusia, influenza, injection site discomfort, lethargy, and pruritic rash have been reported.
RIXUBIS:
Dysgeusia, pain in extremity, and positive furin antibody test were most common during clinical studies.
All products:
Anaphylaxis, angioedema, dyspnea, hypotension, inadequate factor IX recovery, inhibitor development, and thrombosis may occur.
Post-marketing:
BeneFIX:
Anaphylaxis, angioedema, dyspnea, hypotension, and thrombosis.
RIXUBIS:
Hypersensitivity (including dyspnea, pruritus), rash, and urticaria.
Antidote
Temporarily discontinue or decrease rate of administration for minor side effects. If any major symptoms appear, discontinue drug, notify physician, and consider alternative hemostatic measures. Treat hypersensitivity reactions as indicated. For thrombosis or DIC, anticoagulation with heparin may be indicated.
Factor XIII concentrate (human)
(FAK-tor THIR-teen HUE-man)
Corifact
Antihemorrhagic
Usual dose (international units [IU])
Dose must be individualized based on body weight, laboratory values, and patient’s clinical condition.
Initial dose in adult and pediatric patients:
40 international units/kg.
Subsequent doses in adult and pediatric patients:
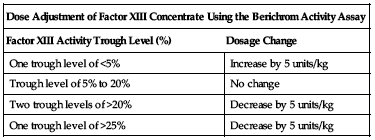
Should be guided by the most recent trough factor XIII (coagulation factor XIII) activity level. Dose every 28 days (4 weeks) to maintain a trough factor XIII activity level of approximately 5% to 20%. Recommended dosing adjustments of ±5 units/kg should be based on trough factor XIII activity levels as shown in the chart in Dose Adjustments and on the patient’s clinical condition.
Dose adjustments
Guide dose adjustments based on a specific assay used to determine factor XIII levels (e.g., Berichrom Activity Assay).
| Dose Adjustment of Factor XIII Concentrate Using the Berichrom Activity Assay | |
| Factor XIII Activity Trough Level (%) | Dosage Change |
| One trough level of <5% | Increase by 5 units/kg |
| Trough level of 5% to 20% | No change |
| Two trough levels of >20% | Decrease by 5 units/kg |
| One trough level of >25% | Decrease by 5 units/kg |
Dilution
Available as a single-use vial containing 1,000 to 1,600 units of factor XIII as a lyophilized concentrate. Actual units of potency stated on vial label. Sterile diluent and Mix2Vial filter transfer set provided. Sterile technique imperative. Confirm expiration date. Record the batch number of the product in the patient’s medical record with each infusion. Bring factor XIII concentrate and diluent to RT. Place vial, diluent, and Mix2Vial transfer set on a flat surface. Remove flip caps on vial and diluent, and wipe stoppers with provided alcohol swab; allow to dry. Peel away the lid on the Mix2Vial transfer set, but leave it in the clear package. Hold the diluent vial tightly on a flat surface and pick up the Mix2Vial transfer set by its clear package. Push the plastic spike at the blue end of the Mix2Vial transfer set through the center of the diluent vial stopper. Carefully remove only the clear packaging from the transfer set. Invert the diluent vial with the Mix2Vial transfer set attached, and push the plastic spike of the transparent adapter firmly through the center of the factor XIII concentrate. Diluent will automatically transfer into the vial. With all parts still attached, gently swirl to fully dissolve. Do not shake. Solution should be colorless to slightly yellowish and slightly opalescent. Grasp the factor XIII side with one hand and the diluent side with the other and unscrew the set into 2 pieces. Draw air into an empty 20-mL sterile syringe. With the factor XIII vial upright, screw the syringe to the Mix2Vial transfer set. Inject air into the factor XIII vial. Keep the syringe plunger pressed, and invert the system upside down to draw the concentrate into the syringe by pulling the plunger back slowly. Keep the plunger facing down and remove syringe from transfer set. Attach the syringe to a suitable IV administration set. If the same patient is to receive more than one vial, contents of multiple vials may be pooled. Use a separate, unused Mix2Vial transfer set for each vial. Must be used within 4 hours of reconstitution.
Filters:
Mix2Vial filter transfer set provided.
Storage:
Protect from light; refrigerate vials and diluent in carton at 2° to 8° C (36° to 46° F). Do not freeze. Stable for 24 months up to the expiration date on the carton under refrigeration. May be stored at RT not to exceed 25° C (77° F) for up to 6 months; however, it cannot be returned to refrigeration. Mark date removed from refrigeration. Do not use beyond expiration date on carton and vial labels or beyond end of RT storage, whichever comes first. Must be used within 4 hours of reconstitution. Do not refrigerate or freeze the reconstituted solution. Contains no preservatives; a single-use vial; discard partially used vials.
Compatibility
Manufacturer states, “Do not mix with other medicinal products, and administer through a separate infusion line.”
Rate of administration
Initial dose:
Do not exceed 4 mL/min.
Actions
A heat-treated, lyophilized factor XIII (coagulation factor XIII) concentrate made from pooled human plasma. Several manufacturing steps are used to inactivate or remove both enveloped and nonenveloped viruses. Factor XIII circulates in blood and is present in platelets, monocytes, and macrophages. Activated factor XIII (factor XIIIa) promotes cross-linking of fibrin during coagulation and is essential to the physiologic protection of the clot against fibrinolysis. Cross-linked fibrin is the end result of the coagulation cascade and provides tensile strength to a primary hemostatic platelet plug. Half-life is approximately 6.6 ± 2.29 days. The increase in plasma levels of factor XIII after administration lasts approximately 28 days.
Indications and uses
Routine prophylactic treatment of congenital factor XIII deficiency in adult and pediatric patients. To be effective, a trough factor XIII activity level of approximately 5% to 20% should be maintained.
Limitation of use:
There are no controlled trials demonstrating a direct benefit on treatment of bleeding episodes.
Contraindications
Known anaphylactic or severe hypersensitivity reactions to human plasma–derived products or to any components of the product.
Precautions
For IV use only. ■ Hypersensitivity reactions have occurred; emergency equipment, medications, and supplies must be available. ■ Neutralizing inhibitory antibodies against factor XIII have been detected in patients receiving factor XIII. ■ Thromboembolic complications have been reported. Assess benefit versus risk in pregnant women because of their hypercoagulable state and potential for increased risk of thromboembolic events. ■ Made from human plasma and may contain infectious agents (e.g., HIV, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C). Numerous steps in the manufacturing process are used to reduce the potential for infection. ■ Consider appropriate vaccination against hepatitis A and B.
Monitor:
Monitor trough factor XIII activity levels as outlined in Usual Dose and Dose Adjustments. ■ Monitor for S/S of hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., chest pain, dizziness, dyspnea, fever, flushing, hypotension, nausea, pruritus, rash, rigors, urticaria). ■ Monitor for possible development of inhibitory antibodies (e.g., response to treatment is inadequate, expected plasma factor XIII activity levels are not attained, or breakthrough bleeding occurs). ■ Monitor for thromboembolic complications (e.g., chest pain, dyspnea, edema, hemoptysis, leg pain, or positive Homans’ sign). ■ Monitor for S/S of viral infection (e.g., chills, drowsiness, fever, runny nose followed by joint pain and rash or abdominal pain, dark urine, jaundice, nausea, vomiting).
Patient education:
Manufactured from pooled human plasma. Possibility of viral transmission exists. Promptly report S/S of viral infections (e.g., chills, drowsiness, fever, runny nose followed by joint pain and rash or abdominal pain, dark urine, jaundice, nausea, vomiting). ■ Promptly report difficulty breathing, pruritus, or rash. ■ Promptly report breakthrough bleeding.
Maternal/child:
Category C: use only if clearly needed; see Precautions. ■ Use only if clearly needed in breast-feeding women. ■ No apparent differences in the safety profile in pediatric patients compared with adults. Pediatric patients less than 16 years of age had a shorter half-life and faster clearance compared with adults.
Elderly:
Numbers in clinical studies insufficient to determine whether elderly patients respond differently than younger subjects.
Drug/lab interactions
Specific information not available.
Side effects
The most commonly reported side effects included arthralgia, chills, elevated thrombin-antithrombin levels, fever, headache, hypersensitivity reactions (including allergy, erythema, pruritus, and rash), and increased hepatic enzymes. Other reported side effects included abdominal pain, diarrhea, epistaxis, flu-like syndrome, hematoma, URT infection, and vomiting.
Post-marketing:
Hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis), factor XIII inhibition (neutralizing antibodies), thrombotic events (e.g., embolism, thrombosis), viral infection (possible).
Antidote
Keep physician informed of side effects; most will be treated symptomatically. Discontinue administration and treat hypersensitivity reactions as indicated. A different lot may not cause a reaction. For thrombosis, anticoagulation may be indicated. Resuscitate as necessary.
Famotidine
(fah-MOH-tih-deen)
Famotidine PF, Pepcid
Antiulcer agent (H2 antagonist)
Gastric acid inhibitor
pH 5.7 to 6.4
Usual dose
20 mg (2 mL) every 12 hours. Increase frequency of dose, not amount, if necessary for pain relief. In hypersecretory states (e.g., Zollinger-Ellison syndrome), higher doses may be required. Adjust dose to individual patient needs.
Pediatric dose
Age 1 to 16 years:
Starting dose is 0.25 mg/kg every 12 hours. Treatment duration and dose must be individualized based on clinical response, pH determination, and/or endoscopy. Doses up to 0.5 mg/kg every 12 hours may be required for gastric acid suppression. Another source suggests 0.6 to 0.8 mg/kg/24 hr (0.3 to 0.4 mg/kg every 12 hours or 0.2 to 0.27 mg/kg every 8 hours). May need to reduce interval to every 8 hours because of increased elimination. Maximum dose is 40 to 80 mg/24 hr based on diagnosis.
Neonate (unlabeled):
0.5 mg/kg/dose/24 hr.
Dose adjustments
Reduce dose by one-half or increase the dosing interval to 36 to 48 hours in patients with moderate or severe renal dysfunction (CrCl less than 50 mL/min). Adjust based on patient response. Half-life may exceed 20 hours if CrCl less than 10 mL/min.
Dilution
IV injection:
Available in vials containing 10 mg/mL and as premixed solution 20 mg/50 mL. Each 20-mg vial must be diluted with 5 to 10 mL of NS or other compatible infusion solutions for injection (e.g., D5W, D10W, LR, SWFI).
Intermittent infusion:
Each 20 mg may be diluted in 100 mL of D5W or other compatible infusion solution and given piggyback.
Storage:
Refrigerate vials before dilution. Manufacturer recommends use of diluted solutions within 48 hours. However, studies suggest diluted solutions are physically and chemically stable at RT for 7 days. Store premixed Galaxy containers at CRT; avoid excessive heat. If solution freezes, bring to RT; allow sufficient time to solubilize.
Compatibility (underline indicates conflicting compatibility information)
Consider any drug NOT listed as compatible to be INCOMPATIBLE until consulting a pharmacist; specific conditions may apply.
May form a precipitate with sodium bicarbonate in concentrations greater than 0.2 mg/mL.
One source suggests the following compatibilities:
Solutions:
Selected TNA and TPN solutions and fat emulsion IV.
Additive:
Cefazolin (Ancef), fat emulsion IV, flumazenil (Romazicon), vancomycin.
Y-site:
Acyclovir (Zovirax), allopurinol (Aloprim), amifostine (Ethyol), aminophylline, amiodarone (Nexterone), ampicillin, ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn), anidulafungin (Eraxis), atropine, aztreonam (Azactam), bivalirudin (Angiomax), calcium gluconate, caspofungin (Cancidas), cefazolin (Ancef), cefotaxime (Claforan), cefotetan (Cefotan), cefoxitin (Mefoxin), ceftaroline (Teflaro), ceftazidime (Fortaz), ceftriaxone (Rocephin), cefuroxime (Zinacef), chlorpromazine (Thorazine), cisatracurium (Nimbex), cladribine (Leustatin), dexamethasone (Decadron), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), dextran 40, digoxin (Lanoxin), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine, docetaxel (Taxotere), dopamine, doripenem (Doribax), doxorubicin (Adriamycin), doxorubicin liposomal (Doxil), droperidol (Inapsine), enalaprilat (Vasotec IV), epinephrine (Adrenalin), erythromycin (Erythrocin), esmolol (Brevibloc), etoposide phosphate (Etopophos), fenoldopam (Corlopam), filgrastim (Neupogen), fluconazole (Diflucan), fludarabine (Fludara), folic acid, furosemide (Lasix), gemcitabine (Gemzar), gentamicin, granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hetastarch in electrolytes (Hextend), hydrocortisone sodium succinate (Solu-Cortef), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), imipenem-cilastatin (Primaxin), insulin (regular), isoproterenol (Isuprel), labetalol, lidocaine, linezolid (Zyvox), lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium sulfate, melphalan (Alkeran), meperidine (Demerol), methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol), metoclopramide (Reglan), midazolam (Versed), morphine, nafcillin (Nallpen), nicardipine (Cardene IV), nitroglycerin IV, nitroprusside sodium, norepinephrine (Levophed), ondansetron (Zofran), oxacillin (Bactocill), oxaliplatin (Eloxatin), paclitaxel (Taxol), palonosetron (Aloxi), pemetrexed (Alimta), phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine), phenytoin (Dilantin), phytonadione (vitamin K1), potassium chloride (KCl), potassium phosphates, procainamide (Pronestyl), propofol (Diprivan), remifentanil (Ultiva), sargramostim (Leukine), sodium bicarbonate, telavancin (Vibativ), teniposide (Vumon), theophylline, thiamine (vitamin B1), thiotepa, ticarcillin/clavulanate (Timentin), tirofiban (Aggrastat), verapamil, vinorelbine (Navelbine).
Rate of administration
IV injection:
Each 20 mg or fraction thereof over at least 2 minutes.
Intermittent infusion:
Each 20-mg dose over 15 to 30 minutes.
Actions
A histamine H2 antagonist, it inhibits both daytime and nocturnal basal gastric acid secretion. It also inhibits gastric acid secretion stimulated by food and pentagastrin. Onset of action occurs within 30 minutes and lasts for 10 to 12 hours. No cumulative effect with repeated doses. 30 to 60 times more potent than cimetidine. Elimination half-life is 2.5 to 3.5 hours. Eliminated by renal and other metabolic routes. Crosses placental barrier. Secreted in breast milk.
Indications and uses
Short-term treatment of active duodenal ulcers, benign gastric ulcers, and pathologic hypersecretory conditions in hospitalized patients or in patients unable to take oral medication. ■ Used orally for short-term treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), including erosive or ulcerative esophagitis.
Unlabeled uses:
GI bleeding. ■ Stress ulcer prophylaxis.
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to H2 receptor antagonists (e.g., cimetidine [Tagamet], famotidine [Pepcid IV], ranitidine [Zantac]) or their components; cross-sensitivity has occurred.
Precautions
Use with caution in patients with moderate or severe renal dysfunction; see Dose Adjustments. ■ CNS adverse effects have been reported in patients with impaired renal function. ■ Gastric malignancy may be present even though patient is asymptomatic. ■ Effects maintained with oral dosage. Total treatment usually discontinued after 4 to 8 weeks.
Monitor:
Use antacids concomitantly to relieve pain. ■ See Precautions.
Patient education:
Stop smoking or at least avoid smoking after last dose of the day. ■ Gastric pain and ulceration may recur after medication is stopped.
Maternal/child:
Category B: use during pregnancy only when clearly needed. ■ Advisable to discontinue breast-feeding. ■ Plasma clearance is reduced and half-life is increased in pediatric patients under 3 months of age compared to older pediatric patients with pharmacokinetic parameters similar to adults.
Elderly:
Response similar to that seen in younger patients; however, greater sensitivity in the elderly cannot be ruled out. ■ Consider risk of renal dysfunction; reduced doses and monitoring of renal function may be indicated; see Dose Adjustments.
Drug/lab interactions
May inhibit gastric absorption of ketoconazole (Nizoral). ■ May decrease cyclosporine serum levels when famotidine is given concurrently with ketoconazole and cyclosporine.
Side effects
Constipation, diarrhea, dizziness, and headache are the most common side effects. Hypersensitivity reactions (bronchospasm, fever, pruritus, rash, eosinophilia) can occur. Abdominal discomfort, agitation, alopecia, anorexia, anxiety, arthralgias, confusion, decreased libido, depression, dry mouth, dry skin, elevated ALT, flushing, grand mal seizure, hallucinations, insomnia, interstitial pneumonia, malaise, muscular pain, nausea and vomiting, orbital edema, palpitations, paresthesias, somnolence, taste disorder, thrombocytopenia, tinnitus, and toxic epidermal necrolysis/Stevens-Johnson syndrome (very rare) have been reported. Convulsions in patients with impaired renal function have been reported rarely.
Antidote
Notify physician of all side effects. May be treated symptomatically or may respond to decrease in frequency of dosage. Resuscitate as necessary for overdosage.
Fat emulsion, intravenous  *
*
Clinolipid 20%, Intralipid 10%, 20%, & 30%, Liposyn II 10% & 20%, Liposyn III 10%, 20%, & 30%
Nutritional supplement (fatty acid)
pH 6 to 9
Usual dose
Dose depends on energy expenditure and on patient’s clinical status, body weight, tolerance, and ability to metabolize. Some solutions may contain aluminum; see Precautions.
Total parenteral nutrition component:
Intralipid and liposyn:
500 mL of 10% or 20% on the first day. Increase dose gradually each day. Clinolipid suggests a dose of 1 to 1.5 Gm/kg/day (equal to 5 to 7.5 mL/kg/day). Do not exceed 60% of the patient’s total caloric intake or 2.5 Gm/kg/day (Clinolipid and Intralipid) or 3 Gm/kg/day (Liposyn). Amino acids and carbohydrates should account for the remaining caloric input.
Prevention of fatty acid deficiency:
Intralipid and liposyn:
500 mL of 10% or 250 mL of 20% twice a week should supply the recommended 4% of caloric intake as linoleate. 8% to 10% of the caloric input should supply adequate amounts of essential fatty acids (EFA); see Dose Adjustments.
Pediatric dose
Some solutions may contain aluminum; see Precautions.
Total parenteral nutrition component:
Intralipid and liposyn:
0.5 to 1 Gm/kg of body weight. Increase dose gradually each day. Do not exceed 60% of total caloric intake. Amino acids and carbohydrates should account for the remaining caloric input. Maximum dose recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics is 3 Gm fat/kg/24 hr. Another source suggests maximum may be as high as 4 Gm fat/kg/24 hr.
Premature infants:
Intralipid and liposyn:
Treatment of premature and low-birth-weight infants must be based on careful benefit-risk assessment. Strict adherence to the recommended total daily dose is mandatory. Hourly infusion rate should be as slow as possible. Never exceed 1 Gm/kg in 4 hours. Begin with 0.5 Gm fat/kg/24 hr (5 mL/kg/24 hr of 10% solution). May be increased based on infant’s ability to eliminate fat. See comments under Pediatric Dose, Rate of Administration, Precautions, and Maternal/Child.
Prevention of fatty acid deficiency:
Intralipid and liposyn:
5 to 10 mL/kg/day of a 10% solution or 2.5 to 5 mL/kg/day of a 20% solution. 8% to 10% of caloric input should be supplied by IV fat emulsion. Essential fatty acid deficiency accompanied by stress may require an increased dose to correct the deficiency.
Dose adjustments
Lower initial starting doses and smaller incremental advances are suggested in patients with elevated triglyceride levels. Checking of triglycerides is recommended before each incremental advance. ■ If essential fatty acid deficiency occurs together with stress, dose may need to be increased. ■ Reduce dose in patients who develop serum triglyceride concentrations above 400 mg/dL to prevent consequences associated with hypertriglyceridemia.
Dilution
Follow manufacturer’s specific instructions for preparation of each individual brand. Must be given as prepared by manufacturer; check labels for aluminum content; see Precautions. Use only freshly opened solutions; discard remainder of partial dose. Do not use if there appears to be an oiling out of the emulsion. Intralipid 30% is not to be given by direct IV infusion. Packaged for bulk use in a pharmacy admixture program. Must be specifically combined with dextrose solutions and amino acids (TPN) so total fat content does not exceed 20%. When combined with dextrose, check mixture closely for the presence of precipitates. Prepared for an individual patient in the pharmacy.
Filters:
Do not use filters of less than 1.2 microns with lipid emulsions. Clinolipid: Use of a 1.2-micron inline filter during administration (alone or as part of an admixture) is recommended. Intralipid and Liposyn: A 1.2-micron inline filter may be used during administration (alone or as part of an admixture). FDA suggests the use of a 1.2-micron filter for admixtures containing lipids (e.g., 3 in 1).
Storage:
Must be stored at temperatures not exceeding 25° C (77° F). Specific storage conditions required (see literature). Do not freeze. Manufacturer recommends admixtures (3 in 1) be refrigerated for no more than 24 hours after mixing and completely infused within 24 hours after removal from refrigeration.
Compatibility
Consider any drug NOT listed as compatible to be INCOMPATIBLE until consulting a pharmacist; specific conditions may apply.
Lipids may extract phthalates from phthalate-plasticized PVC (DEHP). Non-phthalate infusion sets recommended; available with most commercial products.
Manufacturer recommends not mixing with any electrolyte or other nutrient solution. Infuse separately; do not disturb emulsion; no additives or medications are to be placed in bottle or tubing with the exception of heparin 1 to 2 units/mL (may be added before administration [activates lipoprotein lipase]). In actual practice, carbohydrates, amino acids, and fat emulsion are mixed in specific percentages and in a specific order to meet individual total parenteral nutritional needs but should be prepared in the pharmacy. Any addition of supplemental vitamins, minerals, or electrolytes (e.g., calcium, magnesium, phosphates) may cause a precipitate unless a specific order is followed. Precipitates are difficult to detect in lipids.
Rate of administration
Lipids may extract phthalates from phthalate-plasticized PVC (DEHP). Non-phthalate infusion sets recommended; available with most commercial products.
May be administered via a Y-tube or three-way stopcock near the infusion site. Rates of both solutions (fat emulsion and amino acid products) should be controlled by infusion pumps. Keep fat emulsion line higher than all other lines (has low specific gravity and could run up into other lines).
Do not hang flexible plastic containers in series connection, do not pressurize to increase flow rates without first fully evacuating residual air from the container, and do not use vented IV administration sets. All may result in air embolism.
Adult:
10%:
1 mL/min or 0.1 Gm fat/min for the first 15 to 30 minutes. If no untoward effects, the dose may be increased to 2 mL/min. The daily dose should not exceed 2.5 Gm fat/kg (25 mL of 10% solution per kg) (Clinolipid, Intralipid) or 3 Gm fat/kg (Liposyn). On the first day of therapy, a maximum of 500 mL of 10% solution is recommended.
20%:
0.5 mL/min or 0.1 Gm fat/min for the first 15 to 30 minutes. If no untoward effects, the rate may be increased to 1 mL/min. The daily dose should not exceed 2.5 Gm fat/kg (12.5 mL of 20% solution per kg) (Clinolipid, Intralipid) or 3 Gm fat/kg (Liposyn). On the first day of therapy, a maximum of 500 mL of 20% solution is recommended.
Premature infants:
Intralipid and liposyn:
0.5 Gm fat/kg/24 hr (5 mL of 10% or 2.5 mL of 20% per 24 hours). Hourly infusion rate should be as slow as possible. Adjust rate and/or increase amount based on the infant’s ability to eliminate fat. Never exceed 1 Gm/kg in 4 hours. See comments under Usual Dose and Maternal/Child.
Pediatric:
Intralipid and liposyn: 10%:
0.1 mL/min for the first 10 to 15 minutes. Reduce initial rate to 0.05 mL/min for a 20% solution. If no untoward effects, rate may be increased to administer 1 mL/kg/hr of 10% solution or 0.5 mL/kg/hr of 20%. One source suggests a maximum rate of 0.17 Gm/kg/hr. An infusion pump is recommended. Do not exceed a rate of 50 mL/hr (20%) or 100 mL/hr (10%).
Actions
An isotonic nutrient that serves as an important substrate for energy production. Used as a source of calories and essential fatty acids. Fatty acids are important for membrane structure and function as precursors for bioactive molecules (e.g., prostaglandins) and as regulators of gene expression. Total caloric value (fat, phospholipid, and glycerol) is 1.1 cal/mL for the 10% emulsion and 2 cal/mL for the 20% emulsion. Various formulations contain various components (e.g., Intralipid: soybean oil, egg yolk phospholipids, glycerin, and water; Liposyn: safflower oil, soybean oil, various linoleic acid components and glycerin; Clinolipid: refined olive oil, refined soybean oil, linoleic acid, and phospholipids. The fatty acids, phospholipids, and glycerol found in lipid emulsions are metabolized by cells to carbon dioxide and water. This metabolism results in the generation of energy. Increases heat production and oxygen consumption. Decreases respiratory quotient. Some lipids are excreted through the biliary system.
Indications and uses
To provide additional calories and essential fatty acids for patients requiring parenteral nutrition whose caloric requirements cannot be met by glucose or who will be receiving parenteral nutrition over extended periods (over 5 days usually). ■ To prevent essential fatty acid deficiency.
Limitation of use:
Clinolipid
is not indicated for use in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
Severe disorders of fat metabolism, such as pathologic hyperlipemia, lipoid nephrosis, and acute pancreatitis with hyperlipemia. ■ Severe egg allergies. Clinolipid: Known hypersensitivity to egg or soybean proteins or any ingredients; hyperlipidemia concentrations above 1,000 mg/dL.
Precautions
Isotonic; may be administered by a peripheral vein or central venous infusion; when administered with dextrose and amino acids, choice of peripheral or central vein is based on osmolarity of the final infusate. ■ Fatty acids displace bilirubin bound to albumin. Use caution in jaundiced or premature infants. ■ Deaths in preterm infants have been reported; see Maternal/Child. ■ Use caution in pulmonary disease, liver disease, anemia, or blood coagulation disorders or when there is any danger of fat embolism. ■ Patients requiring parenteral nutrition may be at higher risk for infection. ■ Hypersensitivity reactions are possible. ■ Fat overload syndrome has been reported (rare); see Monitor. ■ Parenteral nutrition–associated liver disease has been reported with use for extended periods of time, especially in preterm infants. May present as cholestasis or steatohepatitis. ■ Some solutions may contain aluminum. In impaired kidney function, aluminum may reach toxic levels. Premature neonates are particularly at risk because of their immature kidneys and requirement for calcium and phosphate, which also contain aluminum. Research indicates that patients with impaired renal function who receive more than 4 to 5 mcg/kg/day of parenteral aluminum are at risk for developing CNS or bone toxicity associated with aluminum accumulation. ■ See Maternal/Child.
Monitor:
Monitor lipids routinely; lipemia should clear daily. ■ Correct severe water and electrolyte disorders, severe fluid overload states, and severe metabolic disorders before administration. ■ Obtain baseline values and monitor blood glucose, fluid and electrolyte status, hemogram, blood coagulation, liver and kidney function, triglycerides, CBC and platelet count, and serum osmolarity as indicated, especially in neonates. Discontinue use for significant abnormality. ■ Monitor for S/S of hypersensitivy (e.g., bronchospasm, chills, dyspnea, fever, hypotension, rash). ■ Monitor for S/S of infection. ■ Monitor for S/S of fat overload syndrome. Reduced or limited ability to metabolize and clear lipids may result in a sudden deterioration of patient condition accompanied by anemia, coagulation disorders, deteriorating liver function, fever, hepatomegaly, hyperlipidemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and CNS manifestations (e.g., coma). ■ Monitor for S/S of essential fatty acid deficiency. ■ See Maternal/Child.
Maternal/child:
Category C: use in pregnancy only when clearly needed; safety not established. ■ Use caution if emulsion is administered to a woman who is breast-feeding. ■ Use extreme caution in neonates; death from intravascular fat accumulation in the lungs has occurred. Strict adherence to dose and rate of administration is imperative. Premature and small-for-gestational-age infants have poor clearance. Administration of less than the maximum recommended dose should be considered in these patients to decrease the likelihood of intravenous fat overload. Monitor serum triglycerides and/or plasma free fatty acid levels to assess infant’s ability to eliminate infused fat from the circulation; must clear between daily infusions. Frequent, even daily, platelet counts are recommended in neonatal patients receiving TPN with IV fat emulsion. Clinolipid: Safety and effectiveness for use in pediatric patients, including preterm infants, has not been established. Use in pediatric patients is not recommended.
Elderly:
Clinolipid:
No overall differences in safety and/or effectiveness.
Drug/lab interactions
Intralipid and liposyn:
No specific information available; see Dilution. Clinolipid: Drug interaction studies not performed. ■ Olive and soybean oils contain vitamin K1. May decrease the anticoagulant activity of coumarin derivatives (e.g., warfarin). ■ May interfere with certain lab tests if samples are taken before the lipids are eliminated from the serum (5 to 6 hours).
Side effects
Intralipid and liposyn:
Back pain, chest pain, cyanosis, dizziness, dyspnea, flushing, headache, hypercoagulability, hyperlipemia, hypersensitivity reactions, hyperthermia, nausea and vomiting, sepsis (from contamination of IV catheter), sleepiness, sweating, thrombophlebitis (from concurrent hyperalimentation fluids), thrombocytopenia in neonates (rare), and transient increase in liver enzymes may occur.
Clinolipid:
Abnormal liver function tests, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hypoproteinemia, nausea, and vomiting were most common. Hypersensitivity and infectious complications (e.g., fever of unknown origin, septicemia, UTI) have been reported.
All formulations with long-term therapy:
Abnormal liver function tests, hepatomegaly, jaundice due to central lobular cholestasis, leukopenia, overloading syndrome, splenomegaly, thrombocytopenia, and deposition of brown pigment in the reticuloendothelial tissue of the liver may occur.
Post-marketing:
Diarrhea, pruritus.
Antidote
Notify physician of all side effects. Many will be treated symptomatically. Treat hypersensitivity reactions promptly and resuscitate as necessary. For accidental overdose, stop the infusion. Obtain blood sample for inspection of plasma, triglyceride concentration, or measurement of plasma light-scattering activity by nephelometry. Repeat blood samples until the lipid has cleared. Stop infusion immediately for any signs of acute respiratory distress. May represent pulmonary embolus or interstitial pneumonitis, which may be caused by an unseen precipitate of electrolytes (e.g., calcium and phosphates) in the solution. Lipids administered and fatty acids produced are not dialyzable.
Fenoldopam mesylate
(feh-NOL-doh-pam MES-ih-layt)
Corlopam
Antihypertensive
Vasodilator
Usual dose
Initiate dosing at 0.01 to 0.3 mcg/kg/min as a continuous infusion. Titrate in increments of 0.05 to 0.1 mcg/kg/min every 15 minutes or longer until target blood pressure is reached. The maximum infusion rate reported in clinical studies was 1.6 mcg/kg/min. Doses lower than 0.1 mcg/kg/min and slow up-titration have been associated with less reflex tachycardia. Maintenance infusions may be continued for up to 48 hours. Transition to oral therapy with another agent can begin any time after blood pressure is stable during fenoldopam infusion. Avoid hypotension and rapid decreases in BP.
Pediatric dose
Initiate dosing at 0.2 mcg/kg/min as a continuous infusion. Titrate dose by 0.3 to 0.5 mcg/kg/min every 20 to 30 minutes to a maximum dose of 0.8 mcg/kg/min. Higher doses generally produced no further decreases in mean arterial pressure (MAP) but did worsen tachycardia. See Maternal/Child.
Dose adjustments
Dose adjustment is not required in end-stage renal disease; in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD); in severe hepatic failure; or by age, gender, or race. Effects of hemodialysis have not been evaluated. ■ Caution and lower-end dosing suggested in elderly patients. Consider decreased organ function and concomitant disease or drug therapy.
Dilution
Each 10 mg (1 mL) must be diluted with 250 mL of NS or D5W and given as a continuous infusion. (10 mg in 250 mL, 20 mg in 500 mL, or 40 mg in 1,000 mL all yield 40 mcg/mL.) Use of an infusion pump is recommended.
Pediatric dilution:
Mix to yield a final concentration of 60 mcg/mL (6 mg in 100 mL, 15 mg in 250 mL, or 30 mg in 500 mL of D5W or NS). Use of an infusion pump capable of delivering low infusion rates is required.
Storage:
Store unopened ampules or vials at 2° to 30° C (35.6° to 86° F). Discard diluted solution if not being administered to a patient after 4 hours at RT or after 24 hours refrigerated.
Compatibility (underline indicates conflicting compatibility information)
Consider any drug NOT listed as compatible to be INCOMPATIBLE until consulting a pharmacist; specific conditions may apply. Consider specific use and need for continuous adjustment.
One source suggests the following compatibilities:
Y-site:
Alfentanil, amikacin, aminocaproic acid (Amicar), amiodarone (Nexterone), ampicillin/sulbactam (Unasyn), argatroban, atracurium (Tracrium), atropine, aztreonam (Azactam), butorphanol (Stadol), calcium gluconate, cefazolin (Ancef), cefepime (Maxipime), cefotaxime (Claforan), cefotetan (Cefotan), ceftazidime (Fortaz), ceftriaxone (Rocephin), cefuroxime (Zinacef), chlorpromazine (Thorazine), ciprofloxacin (Cipro IV), cisatracurium (Nimbex), clindamycin (Cleocin), dexmedetomidine (Precedex), digoxin (Lanoxin), diltiazem (Cardizem), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), dobutamine, dolasetron (Anzemet), dopamine, doxycycline, droperidol (Inapsine), enalaprilat (Vasotec IV), ephedrine, epinephrine (Adrenalin), erythromycin (Erythrocin), esmolol (Brevibloc), famotidine (Pepcid IV), fentanyl, fluconazole (Diflucan), gentamicin, granisetron (Kytril), heparin, hetastarch in electrolytes (Hextend), hydrocortisone sodium succinate (Solu-Cortef), hydromorphone (Dilaudid), isoproterenol (Isuprel), labetalol, levofloxacin (Levaquin), lidocaine, linezolid (Zyvox), lorazepam (Ativan), magnesium, mannitol (Osmitrol), meperidine (Demerol), metoclopramide (Reglan), metronidazole (Flagyl IV), micafungin (Mycamine), midazolam (Versed), milrinone (Primacor), morphine, nalbuphine, naloxone, nicardipine (Cardene IV), nitroglycerin IV, norepinephrine (Levophed), ondansetron (Zofran), pancuronium, phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine), piperacillin/tazobactam (Zosyn), potassium chloride, procainamide (Pronestyl), promethazine (Phenergan), propofol (Diprivan), propranolol, quinupristin/dalfopristin (Synercid), ranitidine (Zantac), remifentanil (Ultiva), rocuronium (Zemuron), sufentanil (Sufenta), sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, theophylline, ticarcillin/clavulanate (Timentin), tobramycin, vancomycin, vecuronium, verapamil.
Rate of administration
Do not give as a bolus injection; must be given as an infusion. See Usual Dose and Pediatric Dose for recommended initial infusion rate, titration, and maximum recommended infusion rate. Use of an infusion pump is recommended. To calculate the infusion rate in mL/hr, use the following formula:
Infusion rate (mL/hr)=[Dose (mcg/kg/min)×Weight (kg)×60 min/hr]Concentration (mcg/mL)
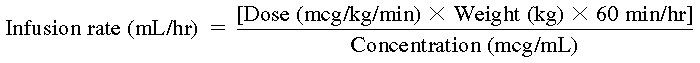
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


