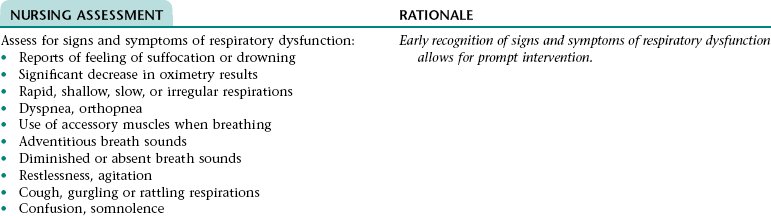
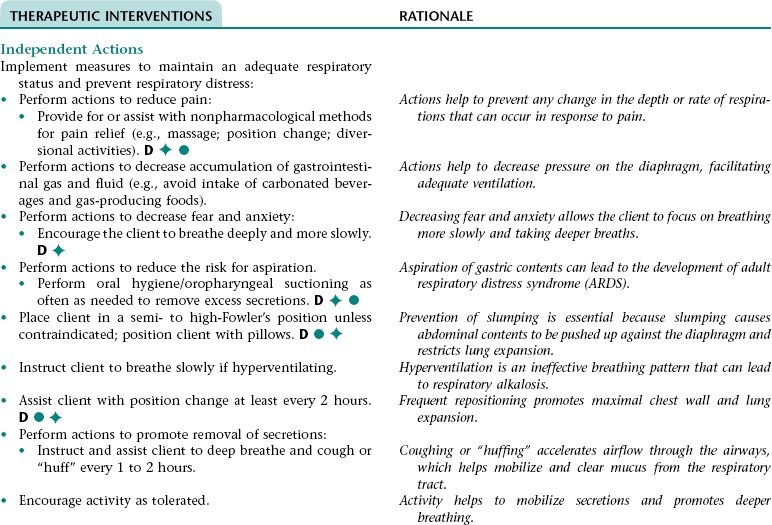
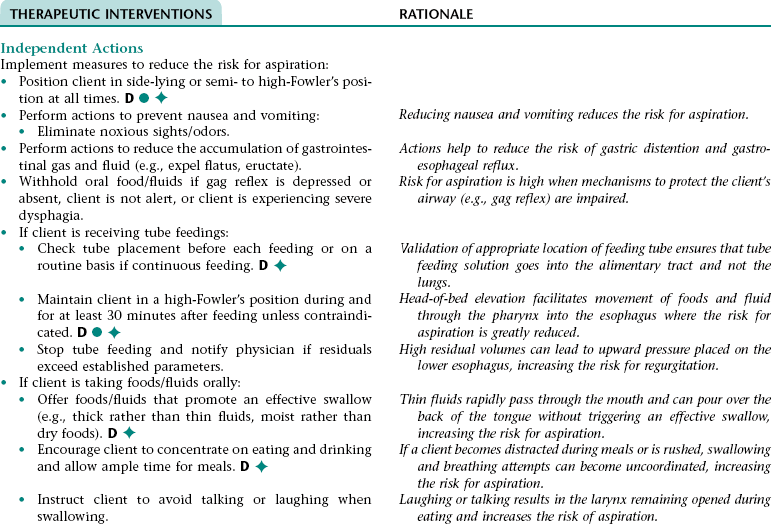
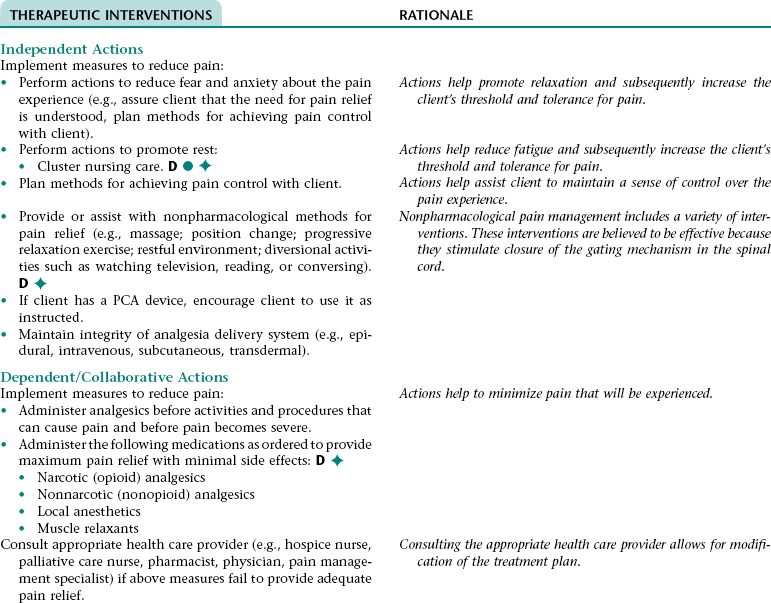
CHAPTER 16 This care plan focuses on care of the adult client who is expected to die soon. The information included is appropriate for clients in acute or extended care settings or in the home. The major goals of nursing care are to prevent or control physiological problems that could reduce the quality of the client’s remaining life; facilitate the client’s psychological adjustment to his/her imminent death; and assist the client to experience a peaceful, dignified death. The nurse also assists the significant others to understand the dying process, support the dying person, meet their own physical and emotional needs, and adjust to their loss of the client. Ineffective breathing pattern NDx related to: • Increased rate of respirations associated with fear, anxiety, and pain • Decreased rate of respirations associated with the depressant effect of some medications (e.g., narcotic [opioid] analgesics, some antiemetics and antianxiety agents) • Decreased depth of respirations associated with recumbent positioning (in this position, full expansion of the lungs is restricted by the bed surface and by the abdominal contents pushing up against the diaphragm), fear, anxiety, weakness, fatigue, and/or abdominal distention • Altered function of the respiratory center (can occur as a result of the underlying disease process) Ineffective airway clearance NDx related to: • Stasis of secretions associated with: • Difficulty coughing up secretions resulting from diminished lung/chest wall expansion and presence of tenacious secretions if fluid intake is inadequate • Fluid accumulation in the alveoli and bronchioles associated with pulmonary edema if present • Airway obstruction associated with the underlying disease process and/or relaxation of the tongue (can occur with decreased level of consciousness and as a result of administration of central nervous system depressants) Impaired gas exchange NDx related to: • Loss of effective lung tissue (can occur as a result of the underlying disease process) • A thickened alveolar-capillary membrane associated with stasis of pulmonary secretions and pulmonary edema if present • Decreased oxygen availability associated with anemia (can result from decreased nutritional status and/or the underlying disease process) NOC OUTCOMES: Respiratory status: ventilation; respiratory status: airway patency; respiratory status: gas exchange; comfortable death; comfort level • Decreased level of consciousness • Absent or diminished gag reflex associated with the underlying disease process and/or the depressant effect of some medications (e.g., narcotic [opioid] analgesics, some antiemetics and antianxiety agents) • Increased risk for gastroesophageal reflux associated with increased gastric pressure resulting from decreased gastrointestinal motility • Impaired swallowing associated with dry mouth and absent or diminished swallowing reflex (can occur as a result of the underlying disease process) • The underlying disease process • Muscle spasms or stiff joints associated with decreased mobility • Reluctance to take pain medication associated with fear of loss of control and/or oversedation, feeling that taking medication is a sign of weakness or that pain has redemptive qualities, and/or need to be stoic Related to: Stimulation of the vomiting center associated with: • Stimulation of the visceral afferent pathways resulting from abdominal distention if present • Stimulation of the cerebral cortex resulting from pain and stress • Stimulation of the chemoreceptor trigger zone by some medications (e.g., morphine sulfate)
End-of-Life Nursing Care
Nursing Diagnosis IMPAIRED RESPIRATORY FUNCTION*
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR ASPIRATION NDx
Nursing Diagnosis ACUTE/CHRONIC PAIN NDx
Nursing Diagnosis NAUSEA NDx
Nursing Diagnosis IMPAIRED COMFORT NDx (ABDOMINAL DISTENTION AND GAS PAIN)
End-of-Life Nursing Care
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access