13 Case study of a patient with heart failure
Introduction
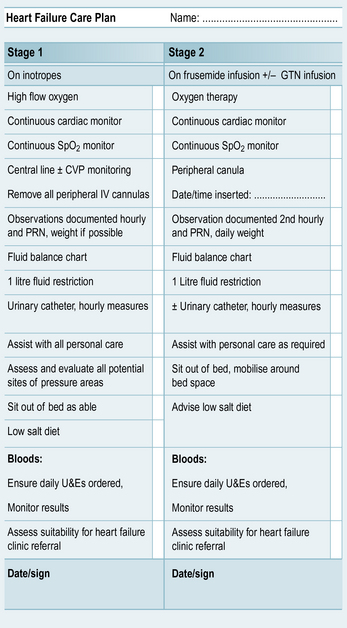
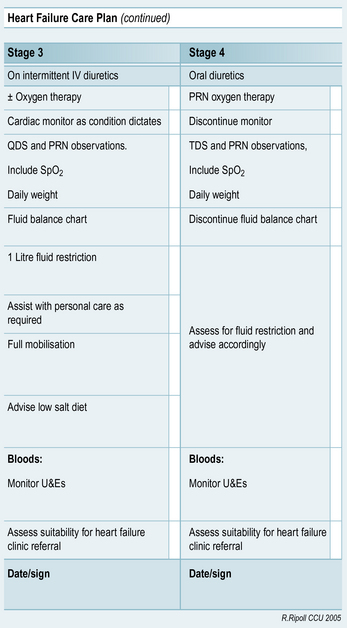
This chapter provides you with an example of the nursing care that a patient with heart failure may require. The heart failure care plan (Fig. 13.1) has been written by a senior charge nurse for coronary care, Rafael Ripoll, and outlines care for the four stages of heart failure. The case history for Martha will then guide you through the assessment, nursing action and evaluation of a patient with heart failure.
A definition of heart failure was given in Chapter 1 and asked you to revise your anatomy and physiology (see Montague et al 2005). Before reading the case study, find out the following:
1. What are some of the symptoms of heart failure?
2. What health education could you provide for a patient with heart failure?
http://www.bhf.org.uk/heart-health/conditions/heart-failure.aspx (accessed July 2011).
Assessment on admission
Martha is breathless and on oxygen therapy 35% via the mask. She has peripheral oedema and is fluid overloaded. Furosemide is being administered intravenously. She is on stage 2 (see Fig. 13.1) of the heart failure care plan but is not receiving glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) due to hypotension.
See Appendix 4 in Holland et al (2008) for possible questions to consider during the assessment stage of care planning.
Many organisations will have a care plan pathway, and Figure 13.1 is an example of one by R. Ripoll (2005 unpublished). This is to ensure that the care of the patient is explicit and standardised. This does not mean that the care becomes less individualised.
Martha’s problems
Based on your assessment of Martha, the following problems should form the basis of your care plan:
Martha’s nursing care plans
1. Problem: Martha is breathless.
Goal: To restore normal breathing pattern.
| Nursing action | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Assess Martha’s breathing, respiratory rate and keep oxygen saturation > 95% Observe for signs of cyanosis Administer prescribed oxygen Inform the nurse in charge of any changes to Martha’s condition | To observe for any signs of deterioration To ensure that Martha does not become hypoxic Oxygen is a drug and must be prescribed |
| Encourage Martha to sit upright supported by pillows | To maximise lung expansion and gaseous exchange To increase comfort |
| Administer any medication as prescribed and ensure that Martha is fully informed about the medication and any side effects For example, explain to Martha why she needs to keep her oxygen mask on | Martha is much more likely to comply with her medication if she understands why she needs to have it |
| Refer Martha to the physiotherapist and liaise | To maximise gaseous exchange To prevent complications from immobility To ensure consistent treatment from nurses and physiotherapists |
2. Problem: Martha is cardiovascularly unstable due to her condition.
| Nursing action | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Martha needs continuous cardiac monitoring of her condition until it has stabilised Ensure that alarm limits are set within appropriate limits Hourly observations of pulse and blood pressure Inform the nurse in charge and doctor regarding any changes in observations and discuss the frequency of observations required | To detect any change in Martha’s condition as soon as possible To be able to respond to these changes and for the team to be informed |
| To check blood urea and electolytes | Abnormal potassium levels will increase the risk cardiovascular instability |
3. Problem: Martha is frightened and distressed.
Goal : To try to relieve Martha’s distress.
| Nursing action | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Spend time with Martha using verbal and non-verbal communication to reassure her | Being alone will increase Martha’s distress |
| Always introduce Martha to the nurse who is relieving you or taking over your shift If you need to go to another area, explain to Martha who will be looking after her Explain to Martha how the call bell system works and make sure that it is in easy reach | Knowing who is looking after her will help Martha to relax Knowing where her nurse is is important as Martha will know that there is someone identified who is looking after her needs If Martha cannot see her nurse she will understand how to summon help |
| Communicate with Martha’s family and significant others with her permisssion | Family and friends may find the environment and equipment daunting Information will help them to understand about Martha’s condition Nurses should never presume that a patient wants her family to know about their condition and it is important to respect Martha’s wishes |
4. Problem: Martha has a urinary catheter.
Goal: To monitor fluid balance accurately and to prevent infection.
| Nursing action | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Explain to Martha why she requires urinary catheter. | |
| Hourly measurements of urine: if below 30 mL/h or above 200 mL/h, report to the nurse in charge and liaise with the doctors when reducing the frequency of the urine output measurements Document urine output on a fluid balance chart | To accurately monitor Martha’s fluid balance. Martha is at risk of fluid overload due to her cardiac condition |
| Provide catheter care and hygiene Check the colour of the urine each shift Report any changes to the nurse in charge Provide privacy when providing catheter care | To prevent infection To detect any signs of infection or trauma To ensure that Martha’s privacy and dignity needs are met |
| Monitor temperature, pulse and blood pressure and respirations four times a day while Martha has an indwelling urinary catheter Take a catheter specimen of urine for microscopy, culture and sensitivity testing if Martha’s temperature is > 37.5°C and inform the nurse/doctor | To detect any infection and treat as soon as possible |
5. Problem: Martha is unable to eat or drink adequately due to her condition.
Goal: For Martha to have adequate fluid and dietary intake.
| Nursing action | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Ensure a malnutrition risk assessment is undertaken in the first 24 hours (see Ch. 9) | To determine Martha’s nutritional status |
| Maintain strict food and fluid balance monitoring Martha may be on fluid restriction Inform Martha about this and provide her with rationale Inform the nurse in charge or doctor if Martha’s diet or fluid intake are below the normal limits | Due to her cardiac failure, Martha is at risk of fluid overload To ensure that Martha receives adequate fluids and nutrition To prevent complications of dehydration To ensure that there is effective communication within the multidisciplinary team |
| Ensure that nutritional supplements are explained to Martha and encourage her to drink them | To keep Martha fully informed |
| Monitor and document observations of her vital signs (see Ch. 7) | To detect any deterioration/improvement |
| Administer intravenous therapy as prescribed and ensure that a cannula care plan is in place for this (see Ch. 9) | To reduce the risk of cannula-associated infection/complications |
| Keep Martha informed of her condition | To promote and enhance communication |
6. Problem: Martha is a life-long smoker and cannot smoke in hospital.
Goal: To help Martha deal with any cravings or withdrawal symptoms.
| Nursing action | Rationale |
|---|---|
| To discuss with Martha how she is feeling and discuss prescribing nicotine supplements with the medical team | To prevent Martha from suffering from nicotine withdrawal symptoms |
| Once Martha is feeling better, discuss how she feels about smoking after discharge and whether she would accept a referral to the cardiac rehabilitation/heart failure team or smoking cessation team Provide verbal and written information for Martha and her husband | To provide health education and promotion to Martha and her family |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree