5 Biology
Biology Basics
Science is a process. For an experiment to be performed, the following steps must be taken:
Water
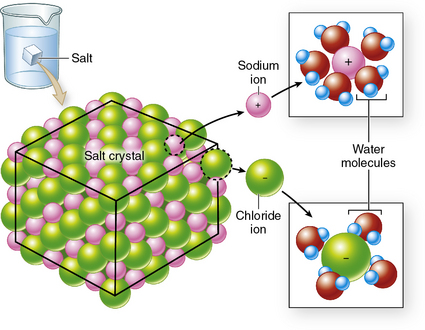
The polarity of water also allows it to act as a versatile solvent. Water can be used to dissolve a number of different substances (Figure 5-1).
Biologic Molecules
Lipids
Lipids are better known as fats, but specifically they are fatty acids, phospholipids, and steroids.
Nucleic Acids
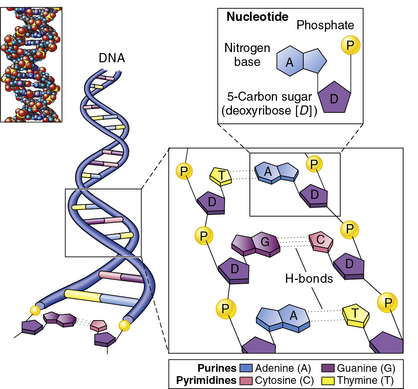
Nucleic acids are components of the molecules of inheritance. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a unique molecule specific to a particular organism and contains the code that is necessary for replication (Figure 5-2). Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is used in transfer and as a messenger in most species of the genetic code.
The Cell
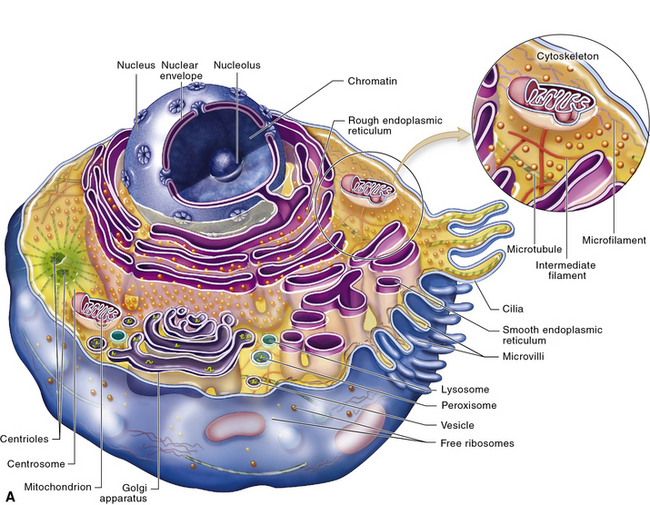
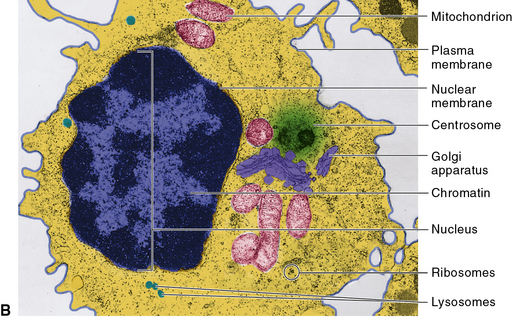
The cell is the fundamental unit of biology. There are two types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Cells consist of many components, most of which are referred to as organelles. Figure 5-3 illustrates a typical cell.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree