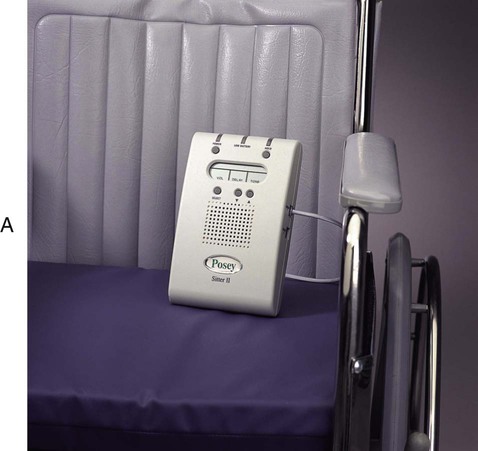
• Define the key terms listed in this chapter. • Identify the causes and risk factors for falls. • Describe the safety measures that prevent falls. • Explain how to use bed rails safely. • Explain the purpose of hand rails and grab bars. • Explain how to use wheel locks safely. • Describe how to use transfer/gait belts. • Explain how to help the person who is falling. • Perform the procedures described in this chapter. • Explain how to promote PRIDE in the person, the family, and yourself. See Focus on Surveys: Assisting With Fall Prevention. • In patient and resident rooms and in bathrooms. • Within the first 72 hours of admission to a hospital or nursing center. • During the night and after meals. • During shift changes. Staff are busy going off and coming on duty. Confusion can occur about who gives care and answers call lights. The accident risk factors described in Chapter 9 can lead to falls. The problems listed in Box 10-1 increase a person’s risk of falling.
Assisting With Fall Prevention
Causes and Risk Factors for Falls