8 Women’s health
ANATOMY AT A GLANCE
The female reproductive system may be divided into an external and an internal component.
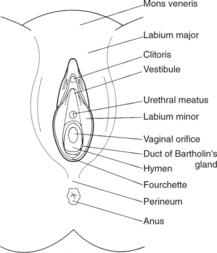
The external organs have the collective name of the vulva, and are shown in Figure 8.1.
The internal organs consist of the
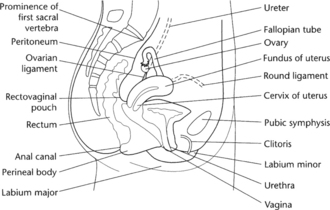
 Vagina: a tubular structure running backwards at an angle of 45 degrees to the vertical situated between the bladder and the rectum.
Vagina: a tubular structure running backwards at an angle of 45 degrees to the vertical situated between the bladder and the rectum. Uterus: a hollow muscular organ which is shaped like a pear 7.5 cm long and 5 cm wide with relatively thick walls (2.5 cm). The cervix is that part of the uterus that protrudes into the vagina.
Uterus: a hollow muscular organ which is shaped like a pear 7.5 cm long and 5 cm wide with relatively thick walls (2.5 cm). The cervix is that part of the uterus that protrudes into the vagina. Uterine (Fallopian) tubes: extend from the uterus towards the ovaries where they terminate in finger-like projections known as fimbriae which lie adjacent to the ovaries.
Uterine (Fallopian) tubes: extend from the uterus towards the ovaries where they terminate in finger-like projections known as fimbriae which lie adjacent to the ovaries. Ovaries: each ovary is approximately 3 cm long and 2 cm wide. Surrounding the medulla is the cortex containing ovarian follicles in various stages of development, each of which contains an ovum.
Ovaries: each ovary is approximately 3 cm long and 2 cm wide. Surrounding the medulla is the cortex containing ovarian follicles in various stages of development, each of which contains an ovum.The relationship of these organs is shown in Figure 8.2.
PHYSIOLOGY YOU NEED TO KNOW
The main functions of the female reproductive system are:
 To incubate the fetus and deliver it into the outside world when it is ready to continue its growth and development as an infant.
To incubate the fetus and deliver it into the outside world when it is ready to continue its growth and development as an infant.Reproductive function ceases at around age 50, the menopause, when menstruation stops. On average, therefore, women live for some 30 years in this post-menopausal state. The menopause is a time in a woman’s life when her hormonal balance is severely disrupted as oestrogen levels fall dramatically. Hot flushes are one very pronounced symptom associated with low oestrogen levels and pulses of LH. The woman experiences acute physical discomfort as she feels very hot and her skin reddens, particularly around the face and neck. Episodes are unpredictable and sudden in onset, although they gradually decline in frequency as the now postmenopausal hormonal balance is established.
ABORTION
PATHOLOGY: Key facts
 Problems with the fetus due to chromosomal or developmental abnormalities which are incompatible with life.
Problems with the fetus due to chromosomal or developmental abnormalities which are incompatible with life. Maternal problems such as a severe infection of the mother, side effects of drugs or hormonal imbalances.
Maternal problems such as a severe infection of the mother, side effects of drugs or hormonal imbalances.WHAT TO LOOK OUT FOR
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is abnormal and the woman should be seen by a midwife or doctor immediately as this may indicate a threatened abortion. At this stage it is still possible to save the pregnancy. Severe bleeding and pain usually indicate that an inevitable abortion has occurred, however, and the pregnancy cannot be saved.
PHARMACOLOGICAL FOCUS
Mifepristone is an anti-progesterone agent. A pregnancy requires progesterone to prevent uterine contractions, therefore reducing progesterone levels makes it easier to induce uterine contractions with prostaglandins, and so expel the fetus.
PRIORITIES FOR NURSING CARE
 Intermittent menstrual-like discharge is to be expected for the next 2 weeks but it should not be bright red in colour; sanitary pads should be used. She should abstain from sexual intercourse while the discharge is present.
Intermittent menstrual-like discharge is to be expected for the next 2 weeks but it should not be bright red in colour; sanitary pads should be used. She should abstain from sexual intercourse while the discharge is present.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree