Classification of Blood Pressure for Adults Ages 18 Years and Older∗ ∗Not taking antihypertensive drugs and not acutely ill. When systolic and diastolic blood pressures fall into different categories, the higher category should be selected to classify the individual’s blood pressure status. For example, 160/92 mm Hg should be classified as stage 2 hypertension. In addition to classifying stages of hypertension on the basis of average blood pressure levels, clinicians should specify presence or absence of target organ disease and additional risk factors. †Based on the average of two or more readings taken at each of two or more visits after an initial screening. From National Institutes of Health Publication No. 04-5320, 2004. PEDIATRIC VARIATIONS Blood Pressure Levels for the 90th and 95th Percentiles of Blood Pressure for Boys 1 to 17 Years of Age by Percentile of Height
Vital Signs and Pain Assessment
Examination
Techniques
Findings
VITAL SIGNS
Temperature
Take the temperature with an oral, tympanic, axillary, temporal, or rectal thermometer.
EXPECTED: Temperature range of 97.2° F to 99.9° F (36.2° C to 37.7° C).
UNEXPECTED: Fever, hypothermia.
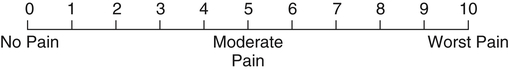
Pulse Rate
Palpate the radial or brachial pulse to count the heart rate for 30 seconds and multiply by 2. Note the contour and amplitude of the pulsation. See Chapter 12 for rhythm assessment.
EXPECTED: Rate 60 to 90 beats/min, average 70, regular rhythm.
UNEXPECTED: Bradycardia, tachycardia, irregular rhythm.
Respiratory Rate
Assess the respiratory rate for 30 seconds and multiply by 2. See Chapter 10 to assess the pattern of respirations.
EXPECTED: Breathing easy, regular, without distress. Pattern even. Rate 12 to 20 respirations/min. Ratio of respirations to heartbeats about 1:4.
UNEXPECTED: Tachypnea, bradypnea, dyspnea.
Blood Pressure
Measure in both arms at least once annually. Patient’s arm should be slightly flexed and positioned or held at the level of the heart.
EXPECTED: Less than 120 mm Hg systolic and less than 80 mm Hg diastolic, with pulse pressure of 30 to 40 mm Hg (sometimes to 50 mm Hg). Reading between arms may vary by as much as 10 mm Hg. Prehypertension is now defined as a blood pressure between 120 and 139 mm Hg systolic or 80 and 89 mm Hg diastolic.
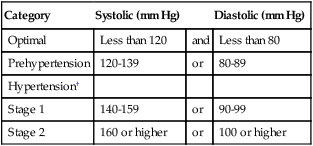
UNEXPECTED: Hypertension (see table below). Unusually low readings should be evaluated for clinical significance.
Category
Systolic (mm Hg)
Diastolic (mm Hg)
Optimal
Less than 120
and
Less than 80
Prehypertension
120-139
or
80-89
Hypertension†
Stage 1
140-159
or
90-99
Stage 2
160 or higher
or
100 or higher
Techniques
Findings
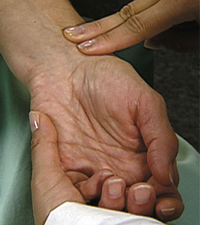
Pain Assessment
Explain how to use the pain assessment tool. See figures below. Ask the patient to indicate the pain level at each site and then to describe the pain characteristics. Observe for pain behaviors.
EXPECTED: The patient does not have pain or the painful condition is well managed.
UNEXPECTED: Pain level greater than 3. Pain characteristics such as stabbing, sharp, dull, or aching. Documented pain rating. Behaviors indicating pain such as guarding, facial grimace or other expression of pain, groaning, or rubbing or holding painful site.
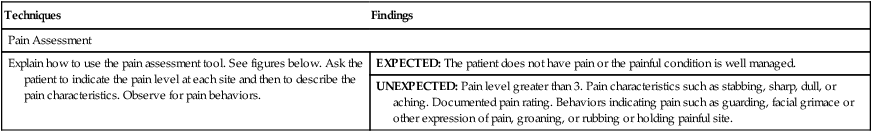
Pain Assessment Tools
EXAMINATION
Techniques
Findings
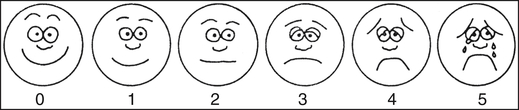
Pulse Rate
Palpate the pulse or use a stethoscope to auscultate the apical pulse
EXPECTED:
Age
Beats/min
Newborn
120-170
1 year
80-160
3 years
80-120
6 years
75-115
10 years
70-110
Respiratory Rate
Observe abdominal rise to count the respiratory rate in infants and toddlers.
EXPECTED:
Age
Respirations/min
Newborn
30-80
1 year
20-40
3 years
20-30
6 years
16-22
10 years
16-20
17 years
12-20
UNEXPECTED: Sustained rate higher or lower than expected range.
Measure the Blood Pressure
Select the appropriate size cuff to measure the infant’s or child’s blood pressure.
EXPECTED:
For children aged ≥1 year, less than 90th percentile for age, sex, and height (see tables on pp. 13-16).
UNEXPECTED: ≥95th percentile for age, sex, and height.
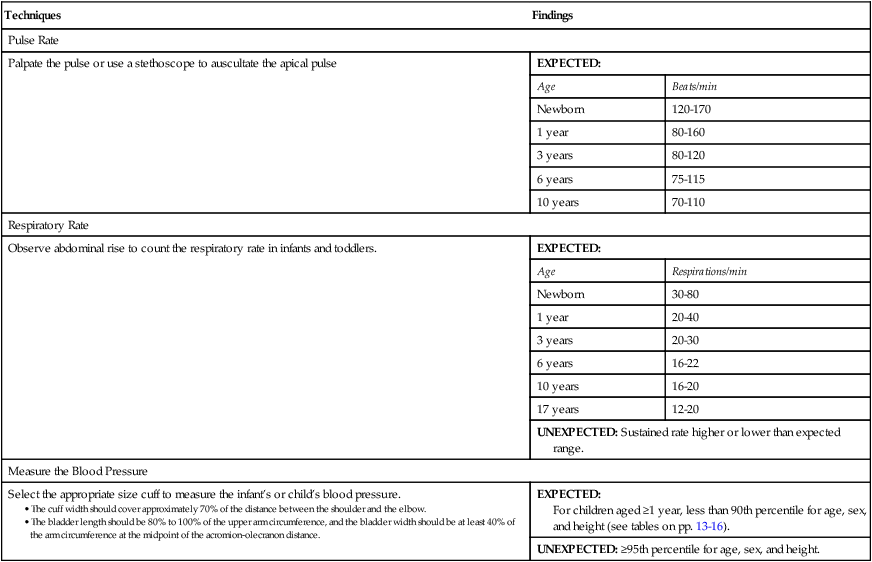
Age, Years
Blood Pressure Percentile∗
Systolic Blood Pressure by Percentile of Height, mm Hg†
Diastolic Blood Pressure by Percentile of Height, mm Hg†
5th
10th
25th
50th
75th
90th
95th
5th
10th
25th
50th
75th
90th
95th
1
90th
94
95
97
99
100
102
103
49
50
51
52
53
53
54
95th
98
99
101
103
104
106
106
54
54
55
56
57
58
58
2
90th
97
99
100
102
104
105
106
54
55
56
57
58
58
59
95th
101
102
104
106
108
109
110
59
59
60
61
62
63
63
3
90th
100
101
103
105
107
108
109
59
59
60
61
62
63
63
95th
104
105
107
109
110
112
113
63
63
64
65
66
67
67
4
90th
102
103
105
107
109
110
111
62
63
64
65
66
66
67
95th
106
107
109
111
112
114
115
66
67
68
69
70
71
71
5
90th
104
105
106
108
110
111
112
65
66
67
68
69
69
70
95th
108
109
110
112
114
115
116
69
70
71
72
73
74
74
6
90th
105
106
108
110
111
113
113
68
68
69
70
71
72
72
95th
109
110
112
114
115
117
117
72
72
73
74
75
76
76
7
90th
106
107
109
111
113
114
115
70
70
71
72
73
74
74
95th
110
111
113
115
117
118
119
74
74
75
76
77
78
78
8
90th
107
109
110
112
114
115
116
71
72
72
73
74
75
76
95th
111
112
114
116
118
119
120
75
76
77
78
79
79
80
9
90th
109
110
112
114
115
117
118
72
73
74
75
76
76
77
95th
113
114
116
118
119
121
121
76
77
78
79
80
81
81
10
90th
111
112
114
115
117
119
119
73
73
74
75
76
77
78
95th
115
116
117
119
121
122
123
77
78
79
80
81
81
82
11
90th
113
114
115
117
119
120
121
74
74
75
76
77
78
78
95th
117
118
119
121
123
124
125
78
78
79
80
81
82
82
12
90th
115
116
118
120
121
123
123
74
75
75
76
77
78
79
95th
119
120
122
123
125
127
127
78
79
80
81
82
82
83
13
90th
117
118
120
122
124
125
126
75
75
76
77
78
79
79
95th
121
122
124
126
128
129
130
79
79
80
82
82
83
83
14
90th
120
121
123
125
126
128
128
75
76
77
78
79
79
80
95th
124
125
127
128
130
132
132
80
80
81
82
83
84
84
15
90th
122
124
125
127
129
130
131
76
77
78
79
80
80
81
95th
126
127
129
131
133
134
135
81
81
82
83
84
85
85
16
90th
125
126
128
130
131
133
134
78
78
79
80
81
82
82
95th
129
130
132
134
135
137
137
82
83
83
84
85
86
87
17
90th
127
128
130
132
134
135
136
80
80
81
82
83
84
84
95th
131
132
134
136
138
139
140
84
85
86
87
87
88
89 ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Vital Signs and Pain Assessment
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access