Chapter 28 Veterinary Careers Terminology* *A transition syllable or vowel may be added to or deleted from the word parts to make the combining form. Veterinary care personnel work in a variety of settings, including private practice, public health, research, zoos, circuses, and racetracks (Box 28-1). Those interested in aquatic animals may work in the area of marine biology (Table 28-1). The purpose of animal health care is to prevent illness and provide care for sick and injured animals. Animal health care providers also prevent the spread of disease carried by animals to humans (zoonosis). TABLE 28-1 Veterinary Career Educational Cost and Earnings *http://www.cvm.tamu.edu/vettech/appreq.shtml. Veterinary technicians (VTs) may work in research settings, private clinics, food inspection, and laboratories or perform research under the supervision of a veterinarian, scientist, or senior technologist. The research technician prepares and tests serums (vaccinations) used to prevent animal diseases. Meat and dairy products are inspected for quality and purity by animal technicians. VTs in private practice assist the veterinarian by performing a variety of duties, including obtaining information, preparing animals and equipment, collecting specimens, and assisting with procedures. VTs may also administer medications, prepare laboratory samples, and apply bandages or dressings to wounds (Box 28-2). VTs may be trained to perform extended duties such as teeth cleaning, removal of sutures, and administration of intravenous fluids. One method that the technician may use to administer medications is injection (Fig. 28-1). Medical asepsis is maintained throughout the procedure to prevent the spread of microorganisms. The correct dosage, medication, and route must be determined before giving an injection. The injection sites for animals are determined by the route of administration and type of animal.
Veterinary Careers
 Define at least 10 terms relating to veterinary care.
Define at least 10 terms relating to veterinary care.
 Specify the role of selected veterinary workers, including personal qualities, levels of education, and credentialing requirements.
Specify the role of selected veterinary workers, including personal qualities, levels of education, and credentialing requirements.
 Describe the function of the veterinary team.
Describe the function of the veterinary team.
 Identify the functions that animals serve in the daily life of humans.
Identify the functions that animals serve in the daily life of humans.
 Identify at least three characteristics of a healthy animal.
Identify at least three characteristics of a healthy animal.
 Identify at least five signs of disorders in animals.
Identify at least five signs of disorders in animals.
 Identify at least five methods of restraint for care or examination of animals.
Identify at least five methods of restraint for care or examination of animals.
 Describe at least five disorders affecting animals.
Describe at least five disorders affecting animals.
 Identify at least three methods of assessment of disorders in animals.
Identify at least three methods of assessment of disorders in animals.
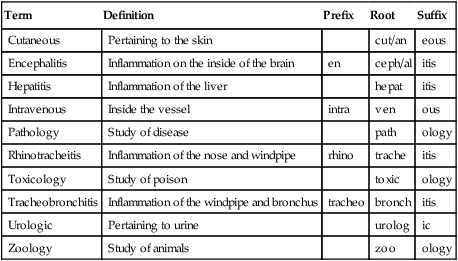
Term
Definition
Prefix
Root
Suffix
Cutaneous
Pertaining to the skin
cut/an
eous
Encephalitis
Inflammation on the inside of the brain
en
ceph/al
itis
Hepatitis
Inflammation of the liver
hepat
itis
Intravenous
Inside the vessel
intra
ven
ous
Pathology
Study of disease
path
ology
Rhinotracheitis
Inflammation of the nose and windpipe
rhino
trache
itis
Toxicology
Study of poison
toxic
ology
Tracheobronchitis
Inflammation of the windpipe and bronchus
tracheo
bronch
itis
Urologic
Pertaining to urine
urolog
ic
Zoology
Study of animals
zoo
ology
Careers
Career
Educational Cost*
Earnings†
Veterinary Technician
Median annual salary: College Station, Tex.—$26,370

![]() Case Study 28-1
Case Study 28-1
Veterinary Technician















