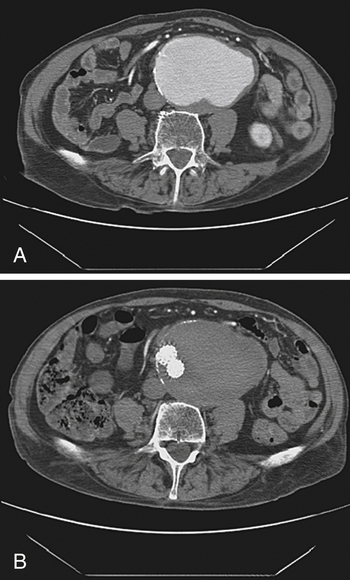
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (Fig. 39-1) classically presents as a pulsatile abdominal mass that may cause abdominal pain. If pain is present, rupture/leak of the aneurysm should be suspected, although an unruptured aneurysm may cause some degree of pain. Ultrasound or computed tomography (CT) scan is used for initial evaluation and diagnostic confirmation in stable patients, as well as for serial monitoring.
Vascular Surgery
4 What are the classic findings in a patient with an abdominal aortic aneurysm? How is it evaluated?
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


