V
Varicella-zoster antibody
Interfering factors
NURSING CARE
Nursing actions are similar to those used in venipuncture procedures (see Chapter 2), with the following additional measures.
Posttest
Vasopressin
Also called: Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH), Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP)
Basics the nurse needs to know
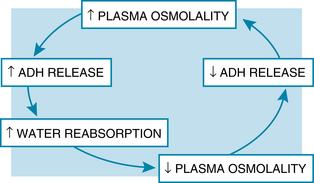
Vasopressin (ADH) is produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. Its major function in the body is to act on the cells in the collecting ducts of the kidney, making them more permeable to water. The result is an increased reabsorption of water. This action is independent of electrolyte levels, and electrolytes are not reabsorbed with the water. The purpose of this action is to maintain normal plasma osmolality. ADH also has a vasopressor effect. It causes arteriole smooth muscles to constrict, thus elevating the blood pressure.
ADH is released from the posterior pituitary gland in response to several stimuli. The major stimulus is an increase in plasma osmolality. Whenever the osmoreceptors in the anterior hypothalamus sense even minor changes in plasma osmolality, neural stimulation of the pituitary gland will result in an increased secretion of ADH, which will result in an increased reabsorption of water at the renal collecting ducts. With the increase in water in the extracellular fluid, blood tonicity will decrease. Because the increase in water results in decreased blood osmolality, the osmoreceptors will cease the neural stimulation necessary for ADH secretion (Figure 104).
Interfering factors
NURSING CARE
Nursing actions related to venipuncture are presented in Chapter 2, with the following additional measures.