(Apo-Valacyclovir Do not confuse valacyclovir with acyclovir or valganciclovir, or Valtrex with Valcyte. Do not confuse Valcyte with Valium or Valtrex, or valganciclovir with valacyclovir. Dosage and frequency are modified based on creatinine clearance. (Apo-Divalproex Do not confuse Depakene with Depakote. Do not confuse vancomycin with clindamycin, gentamicin, tobramycin, or Vibramycin.
V
valacyclovir
![]() , Valtrex)
, Valtrex)
valganciclovir
Indications/routes/dosage
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis
Dosage in renal impairment
Creatinine Clearance
Induction Dosage
Maintenance Dosage
60 ml/min or higher
900 mg twice daily
900 mg once daily
40–59 ml/min
450 mg twice daily
450 mg once daily
25–39 ml/min
450 mg once daily
450 mg every 2 days
10–24 ml/min
450 mg every 2 days
450 mg twice a wk
valproic acid
![]() , Depacon, Depakene, Depakote, Depakote ER, Depakote Sprinkle, Novo-Divalproex
, Depacon, Depakene, Depakote, Depakote ER, Depakote Sprinkle, Novo-Divalproex ![]() , Stavzor)
, Stavzor)
vancomycin
vandetanib
V
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

 classification
classification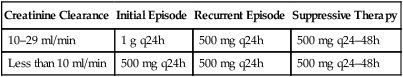
 classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification classification
classification

