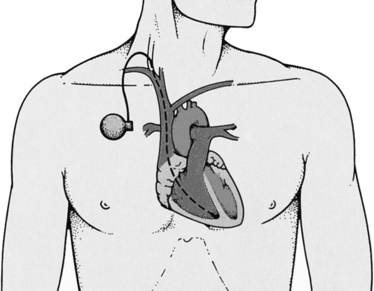
On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define the terms in the vocabulary list. 2. Write the meaning of the abbreviations in the abbreviations list. 3. Discuss three methods that may be used to treat cardiovascular conditions, and identify three areas within the hospital where cardiovascular surgical and treatment procedures may be performed. 4. Identify the three commonly used procedures performed to repair obstructed coronary blood vessels. 5. Identify the name and location of a vein and an artery that may be used for grafts during a coronary artery bypass graft. 6. Discuss the reasoning for cardiovascular treatment procedures being performed in conjunction with diagnostic procedures, and list five treatment procedures performed in interventional radiology. 7. State the purpose of the cardiopulmonary (respiratory care) department pertaining to patient treatment orders, and list at least five cardiopulmonary (respiratory care) treatments. 8. Explain the importance of the health unit coordinator (HUC) including the entire doctor’s order when communicating a cardiopulmonary (respiratory care) order (electronically, by requisition, or by telephone), and list the information that would be needed when sending an order for oxygen. 9. List four types of aerosol delivery devices, and identify at least two types of aerosolized drugs. 10. Explain the procedure and equipment needed to obtain an induced sputum specimen. 11. Discuss the purpose of incentive spirometry, chest percussion therapy, and noninvasive positive pressure ventilation, and explain the use of a mechanical ventilator. 12. State the purpose of the wound care department, and explain the purpose of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. 13. Identify the two basic types of traction and the traction setup used by patients to assist them to move in bed. 14. Identify three divisions that make up the physical medicine department. 15. Describe the purpose of the physical therapy (PT) division of physical medicine, and list four methods that would be used by PT personnel. 16. Describe the purpose of the occupational therapy (OT) division of the physical medicine department, and list three doctor’s orders that would be sent to the OT department. 17. Explain the purpose of speech therapy, and describe the patients who would benefit from speech therapy. 18. Explain the need for dialysis, identify two types of dialysis, and discuss the process of each type. 19. Identify three areas in the hospital that may provide radiation treatments, and explain the HUC’s role regarding doctors’ orders for radiation. Exercise performed by the patient without assistance as instructed by the physical therapist. Tasks that enable individuals to meet basic needs (eating, bathing, and so forth). Liquid suspension of particles in a gas stream for inhalation purposes. Exercise that involves strengthening muscles by forcing them to work very hard for a brief time. Certified Respiratory Therapist (CRT) Constraint-Induced (movement) Therapy (CI therapy) Difficult or labored breathing. Removal of a previously inserted tube (such as an endotracheal tube). Hemodialysis (extracorporeal dialysis) The removal of waste products from the blood through use of a machine through which the blood flows. A concentrated salt solution (>0.9%). A dilute salt solution (<0.9%). A sputum specimen obtained by performing a respiratory treatment to loosen lung secretions. Insertion and placement of a tube within the trachea to maintain an open airway. A gas-driven device that produces an aerosol. Exercise in which the patient is submissive and the physical therapist moves the patient’s limbs. Pressure greater than atmospheric pressure. The range in which a joint can move. A cast that begins at the chest and includes one or both lower limbs. A room where hydrotherapy is performed. A machine that is used to give the patient breaths through the ET or tracheostomy tube. A cardiac pacemaker is an electric apparatus that is used in most cases to increase the heart rate in severe bradycardia by electrically stimulating the heart muscle. A pacemaker may be permanent or temporary, may emit the stimulus at a constant and fixed rate, or may fire only on demand. Permanent pacemakers are implanted under a chest muscle during surgery. With temporary pacemakers, wires from outside the body lead into the heart (Fig. 17-1).
Treatment Orders
Abbreviation
Meaning
Example of Usage on a Doctor’s Order Sheet
AA
active assisted
AA exercises B/L LE
ADLS
activities of daily living
OT for ADLs
ADS
adult distress syndrome
The patient’s dx is ADS
AKA
above-the-knee amputation
AKA protocol
BiPAP
bilevel positive airway pressure
BiW
twice a week
PT 2 × a wk
BKA
below-the-knee amputation
consent for BKA
BLE
both or bilateral lower extremities
HBOT BLE
BUE
both or bilateral upper extremities
strengthening exercises BUE
CABG
coronary artery bypass graft
consent for CABG
CBNT
continuous bronchodilator nebulizer therapy
CP
cold pack
CP L arm
CPAP
continuous positive airway pressure
CPAP 5 cm H2O
CPM
continuous passive motion
CPM
CPR
cardiopulmonary resuscitation
CPR training for parents before child’s discharge
CPT
chest percussion therapy
DC CPT
DPI
dry powder inhaler
instruct patient on use of DPI
EPC
electronic pain control
EPC
ES
electrical stimulation
ES
ET
endotracheal tube
CXR for ET tube placement
FWW
front-wheel walker
provide FWW
HA
heated aerosol
HA T-piece @ 60%
HBOT
hyperbaric O2 therapy
HBOT qd 3 × wk for 8 wk
HD
hemodialysis
HD BiW × 3 h
HP
hot packs
HP to neck
ICD
implantable cardioverter-defibrillator
Have consent signed for ICD
IPPB
intermittent positive pressure breathing
IPPB q4h 0.5 mL Ventolin in 2 mL NS
IS
incentive spirometry
IS tid
ISOM
isometric
ISOM UE bid
lb or #
pounds
bucks traction 5# weight
LE
lower extremities
ROM LE qd
LLE
left lower extremity
passive exercises LLE
LLL
left lower lobe
CPT—LLL only
L/min
liters per minute
↑ O2 to 4 L/min
LUE
left upper extremities
ROM LUE
LUL
left upper lobe
CPT to LUL
MDI
metered-dose inhaler
MDI puffs qid
NC or NP
nasal cannula or nasal prongs
02 40% by NC
NWB
non–weight bearing
Crutch-walking NWB
O2
oxygen
O2 6 L/min by mask
O2 SAT
oxygen Saturation
Place on oximetry to monitor O2 SAT
ORIF
open reduction, internal fixation
ORIF lt femur
OT
occupational therapy or occupational therapist
OT for ADLs
PD
peritoneal dialysis
Tenckhoff cath for PD
PDPV
postural drainage, percussion, and vibration
PDPV to LUL
PEP
positive expiratory pressure
IS PEP
PROM
passive range of motion
PROM LUE bid
PT
physical therapy or physical therapist
To PT for crutch walking
PTA
physical therapy assistant
PTA to assist patient in amb
PTCA
percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
Have consent signed for PTCA
RLE
right lower extremities
ISOM to RLE
RLL
right lower lobe
CPT RLL
RML
right middle lobe
CPT RML
ROM
range of motion
ROM to upper extremities tid
RT
respiratory therapy or respiratory therapist
RT to obtain induced sputum specimen
RUE
right upper extremity
Hot pk to RUE
RUL
right upper lobe
CPT to RUL
SaO2
arterial oxygen saturation (on pulse
oximetry, not ABGs)
ABG now—notify resident of SaO2
SpO2
oxygen saturation via pulse oximetry
SpO2 notify resident if O2 SAT below 90%
SIDS
sudden infant death syndrome
The baby died of SIDS
STM
soft tissue massage
STM lt shoulder 20 min bid
SVN
small volume nebulizer
Δ SVN to bid
TENS
transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
Postop TENS
THR or THA
total hip replacement or arthroplasty
follow THR protocol
TKR or TKA
total knee replacement or arthroplasty
TKA protocol
TT
tilt table
PT for TT
TTOT
transtracheal oxygen therapy
Start TTOT today
Tx
traction
Buck’s Tx
UD
unit dose
UD Ventolin now
USN
ultrasonic nebulizer
USN 15 min tid
WBAT
weight bearing as tolerated
amb, WBAT rt leg
WP
whirlpool
WP to L leg bid
>
greater than
Call hospitalist if pH >7.4
<
less than
Call Dr. Jones if O2 Sats <70%
Cardiovascular
Invasive Cardiovascular Therapies
Insertion of a Cardiac Pacemaker
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Treatment Orders
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access