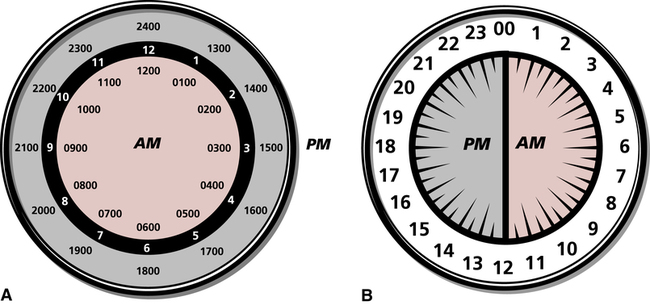
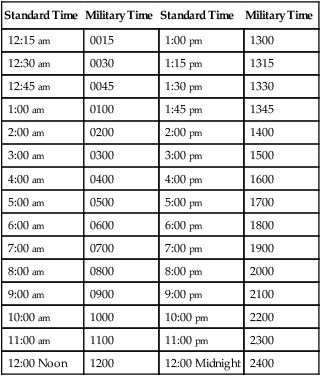
On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Define the terms in the vocabulary list. 2. Write the meaning of the abbreviations in the abbreviations list. 3. List six purposes for maintaining an electronic medical record (EMR) or paper chart for each patient. 4. Demonstrate knowledge of military time by converting military time to standard time and standard time to military time. 5. List five guidelines to be followed by all personnel when entering information into a patient’s EMR. 6. Describe how the patient’s medical records are organized and identified when paper charts are used, and list five guidelines to be followed by all personnel when writing on a patient’s paper chart. 7. Identify four standard patient chart forms that are initiated in the admitting department. 8. State the purpose of seven standard chart forms included in a patient’s electronic or paper admission packet, and list information that is included on the history and physical form. 9. Define what is meant by a supplemental chart form, and provide at least two examples of supplemental chart forms. 10. Explain the importance of accurately charting vital signs in a timely manner, and explain the correction of three types of errors on a graphic record. 11. Describe the purpose of a consent form, and list five guidelines to follow in the preparation of a consent form. 12. List four types of permits or release forms that patients may be required to sign during a hospital stay. 13. Describe the methods for correcting a labeling error and a written entry error on a patient’s paper chart form. 14. List seven health unit coordinator (HUC) duties in monitoring and maintaining the patient’s EMR. 15. List eight HUC duties in maintaining a patient’s paper chart. 16. Explain the purposes and processes of splitting or thinning a patient’s chart and reproducing chart forms. When a patient is discharged, health information management personnel will analyze and check the EMR for completeness and will notify the appropriate nurses and/or doctors when they must go into the computer to complete the records. The patient’s previous EMR will be available on computer to the patient’s doctor, or if the patient is readmitted to the hospital. The Security Rule, a key part of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), protects a patient’s electronically stored information (see Chapter 6). Military time is a system that uses all 24 hours in a day (each hour has its own number) rather than repeating hours and using am and pm. When military time is used, there are always four digits, the first two digits representing hours and the second two representing minutes. For example, 1:45 am is recorded as 0145, and 1:45 pm is recorded as 1345; the colon is not needed when military time is used (Table 8-1). The hours after midnight are recorded as 0100, 0200, and so forth. Thirty minutes after midnight is written as 0030. Twelve noon is recorded as 1200, and the hours that follow are arrived at by adding the hours after noon to 1200. Thus 1:00 pm is 1200 + 100 = 1300, 2 pm is 1200 + 200 = 1400, and so forth. See Figure 8-1 for a comparison of standard and military times. Military time is used with the EMR and paper chart systems and eliminates confusion because hours are not repeated, and am or pm is unnecessary. TABLE 8-1 Standard and Military Time Comparisons As was discussed in Chapter 6, the EMR or paper chart is confidential, and the HUC is a custodian of all patient medical records (electronic or paper) on the unit. Any information provided by the patient to the health care facility and the medical staff is confidential. All health care personnel are required to have a code and a password to gain access to a patient’s EMR. Portions of the patient’s EMR may be available only to the patient’s doctor and nurses. 1. All entries into the EMR must be accurate. 2. Handwritten progress notes, electrocardiograms, consents, anesthesia records, and outside records and reports must be scanned into the EMR. 3. Errors made in care or treatment must be documented and cannot be falsified. 4. All entries into the EMR must include the date and time (military or standard) of the entry. 5. Abbreviations may be used in keeping with the health care facility’s list of “approved abbreviations.” 1. All paper chart form entries must be made in ink. This is to ensure permanence of the record. Black ink is preferred by many health care facilities because it produces a clearer picture when the record is microfilmed, faxed, or reproduced on a copier. 2. Written entries on paper chart forms must be legible and accurate. Entries may be made in script or printed. Diagnostic reports, history and physical examination reports, and surgery reports are usually computer generated. 3. Recorded entries on the paper chart may not be obliterated or erased. The method for correcting errors is outlined later in this chapter. 4. All written entries on paper chart forms must include the date and time (military or standard) of the entry. 5. Abbreviations may be used in keeping with the health care facility’s list of “approved abbreviations.” Forms that constitute the patient’s paper chart are usually kept together in a three-ring binder. The binder may open from the bottom, or it may be a notebook that opens from the side, the top, or the bottom (Fig. 8-2). The chart forms in the binder are sectioned off by dividers placed in the chart according to the sequence set forth by the health care facility (Fig. 8-3).
The Patient’s Electronic Medical Record or Chart
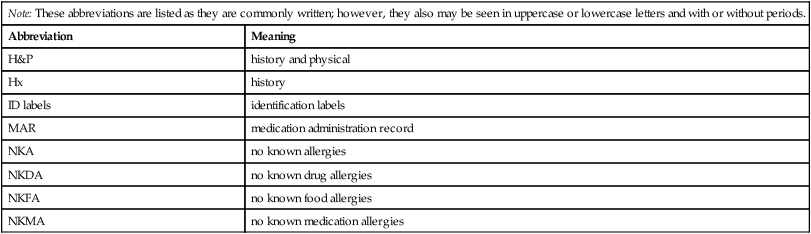
Note: These abbreviations are listed as they are commonly written; however, they also may be seen in uppercase or lowercase letters and with or without periods.
Abbreviation
Meaning
H&P
history and physical
Hx
history
ID labels
identification labels
MAR
medication administration record
NKA
no known allergies
NKDA
no known drug allergies
NKFA
no known food allergies
NKMA
no known medication allergies
Purposes and Use of a Patient’s Electronic Medical Record or Paper Chart
The Patient Electronic Medical Record or Paper Chart as a Legal Document
Military Time
Standard Time
Military Time
Standard Time
Military Time
12:15 am
0015
1:00 pm
1300
12:30 am
0030
1:15 pm
1315
12:45 am
0045
1:30 pm
1330
1:00 am
0100
1:45 pm
1345
2:00 am
0200
2:00 pm
1400
3:00 am
0300
3:00 pm
1500
4:00 am
0400
4:00 pm
1600
5:00 am
0500
5:00 pm
1700
6:00 am
0600
6:00 pm
1800
7:00 am
0700
7:00 pm
1900
8:00 am
0800
8:00 pm
2000
9:00 am
0900
9:00 pm
2100
10:00 am
1000
10:00 pm
2200
11:00 am
1100
11:00 pm
2300
12:00 Noon
1200
12:00 Midnight
2400
Confidentiality
The Electronic Medical Record
Guidelines to Follow When Entering Information into the Patient’s Electronic Medical Record
The Paper Chart
Guidelines to Follow When Writing in a Patient’s Paper Chart
The Chart Binder


![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


The Patient’s Electronic Medical Record or Chart
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access