CHAPTER 13 1. Have evidence of normal healing of surgical wound 3. Have surgical pain controlled 4. Have no signs and symptoms of infection or postoperative complications 5. Identify ways to decrease the risk of reherniation of the bladder and rectum 6. Identify ways to relieve surgical site discomfort 7. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 8. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including future appointments with health care provider, medications prescribed, and limitations on sexual activity. Definition: Incomplete emptying of the bladder • Edema of the bladder neck and urethra resulting from surgical trauma • Increased tone of the urinary sphincters resulting from sympathetic nervous system stimulation (can result from pain, fear, and anxiety) • Decreased perception of bladder fullness resulting from the depressant effect of anesthesia and some medications (e.g., narcotic [opioid] analgesics) • Relaxation of the bladder muscle resulting from the depressant effect of anesthesia and some medications (e.g., narcotic [opioid] analgesics) and stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system (can result from pain, fear, and anxiety) Definition: At risk for being invaded by pathogenic organisms a. Vaginal/perineal wound infection related to: • Wound contamination associated with introduction of pathogens during or after surgery (a high risk with this surgery because of the close proximity of the incisions to the perianal area) • Decreased resistance to infection associated with factors such as age and an inadequate nutritional status b. Urinary tract infection related to: DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will remain free of wound infection as evidenced by: Definition: Protrusion of the bladder or rectum into the vaginal canal Definition: Inadvertent injury to the bladder, urethra, or ureters during surgery Related to: Accidental tear or ligation during the surgical procedure 1. Have evidence of normal healing of surgical wound 2. Have clear, audible breath sounds throughout lungs 4. Have surgical pain controlled 5. Have no signs and symptoms of postoperative complications 6. Verbalize an understanding of the effects of surgical menopause 7. Identify ways to achieve sexual satisfaction 8. Verbalize an understanding of medications ordered including the rationale for the prescription, food and drug interactions, side effects, schedule for taking, and importance of taking as prescribed 9. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 10. Share feelings about the loss of reproductive ability 11. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including future appointments with health care provider, activity limitations, and wound care. • Anticipated loss of control associated with the effects of anesthesia • Anticipated effects of surgery on femininity and reproductive ability • Fear of rejection by partner • Unfamiliar environment and separation from significant others • Potential embarrassment or loss of dignity associated with body exposure during preoperative care, surgery, and postoperative care • Lack of understanding of the surgical procedure and postoperative expectations and care • Anticipated surgical findings and postoperative discomfort • Financial concerns associated with hospitalization Definition: Incomplete emptying of the bladder a. Obstruction of the urinary catheter b. Impaired urination after removal of catheter associated with: • Decreased perception of bladder fullness associated with the depressant effect of anesthesia and some medications (e.g., narcotic [opioid] analgesics) • Increased tone of the urinary sphincters associated with sympathetic nervous system stimulation resulting from pain, fear, and anxiety • Relaxation of the bladder muscle associated with nerve trauma and/or edema in the bladder area resulting from surgical manipulation; the depressant effect of anesthesia and some medications (e.g., narcotic [opioid] analgesics); stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system (can result from pain, fear, and anxiety) Definition: Inadvertant injury to the bladder or ureters during surgery. Related to: Accidental tear or ligation during the surgical procedure Definition: A clot attached to a vessel wall that detaches and circulates within the blood a. Trauma to the pelvic veins during surgery b. Venous stasis associated with: • Increased blood viscosity (can result from deficient fluid volume) • Pelvic congestion resulting from inflammation in the surgical area • Abdominal distention (the distended intestine may put pressure on the abdominal vessels) • Pressure on the pelvic and calf vessels during surgery if a vaginal approach was used (client is placed in lithotomy position for this approach) c. Hypercoagulability associated with increased release of tissue thromboplastin into the blood (occurs as a result of surgical trauma) and hemoconcentration and increased blood viscosity (can result from deficient fluid volume)
The Client with Alterations in the Breast and Reproductive System
COLPORRHAPHY (ANTERIOR AND POSTERIOR REPAIR)
OUTCOME/DISCHARGE CRITERIA
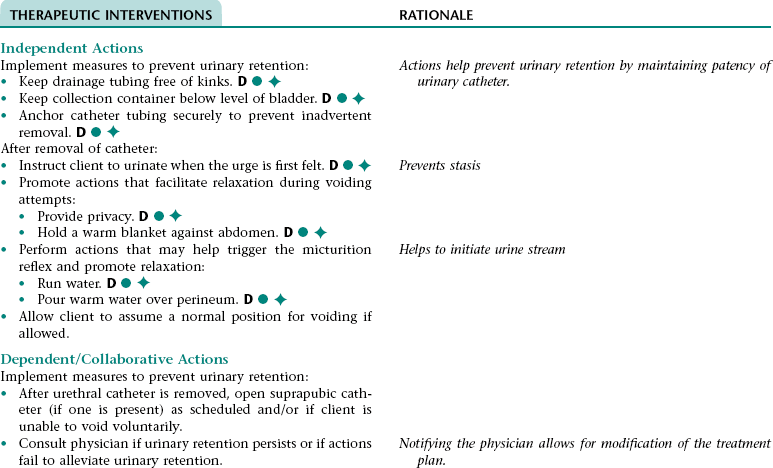
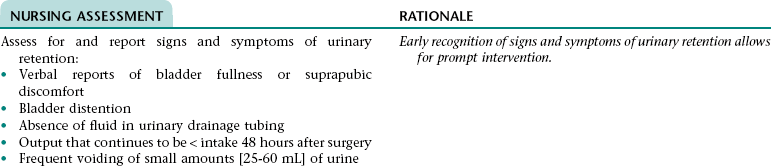
Nursing Diagnosis URINARY RETENTION NDx
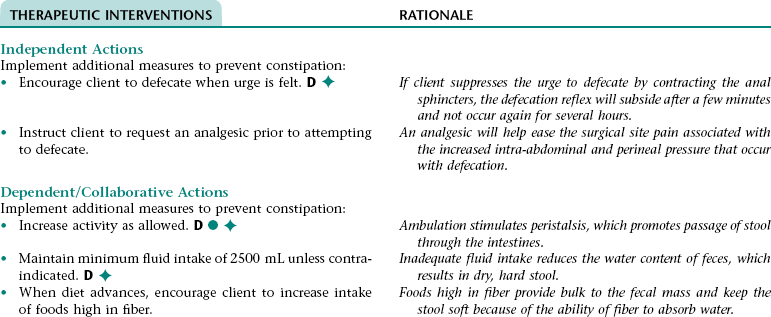
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR CONSTIPATION NDx
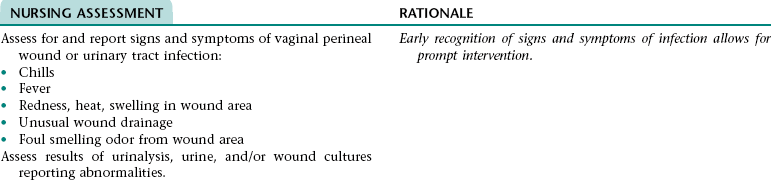
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR INFECTION NDx
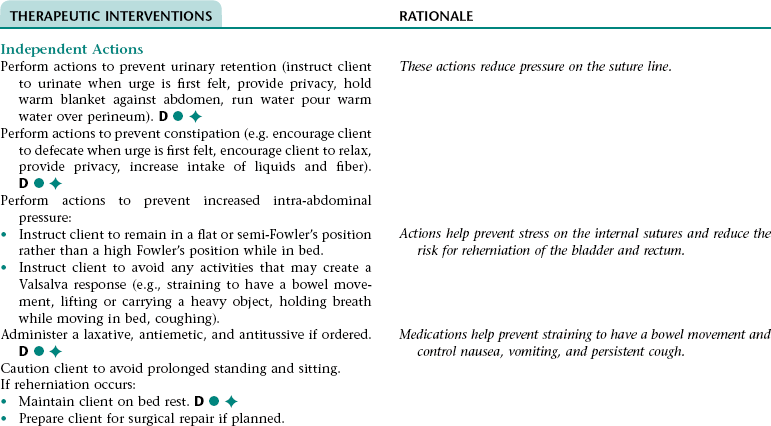
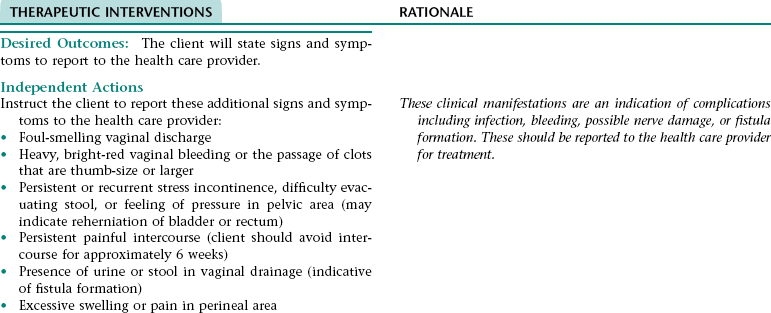
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR REHERNIATION OF THE BLADDER OR RECTUM
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR BLADDER, URETHRAL, OR URETERAL INJURY
Nursing Diagnosis DEFICIENT KNOWLEDGE NDx, INEFFECTIVE FAMILY THERAPEUTIC REGIMEN NDx, OR INEFFECTIVE SELF-HEALTH MANAGEMENT*NDx
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess client’s readiness and ability to learn.
Early recognition of readiness to learn and meaning of illness to client allows for implementation of the appropriate teaching interventions.
Assess meaning of illness to client.
HYSTERECTOMY WITH SALPINGECTOMY AND OOPHORECTOMY
RELATED PREOPERATIVE NURSING DIAGNOSES
FEAR/ANXIETY
Nursing Diagnosis URINARY RETENTION NDx
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR BLADDER OR URETERAL INJURY
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR THROMBOEMBOLISM
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess for signs and symptoms of thromboebolism
DVT: Pain, tenderness, Swelling, unusual warmth, or positive humans’ sign in extremity
Early recognition of signs and symptoms of thromboembolism allows prompt intervention.
Arterial thrombus: Numbness and/or pain in the extremity, diminished or absent pulses, pallor, coolness
Pulmonary embolism: Sudden onset of chest pain, increased dyspnea, increased restlessness, apprehension, significant decrease in SaO2
Nursing Diagnosis DEFICIENT KNOWLEDGE NDx, INEFFECTIVE FAMILY THERAPEUTIC REGIMEN NDx OR INEFFECTIVE SELF-HEALTH MANAGEMENT*NDx