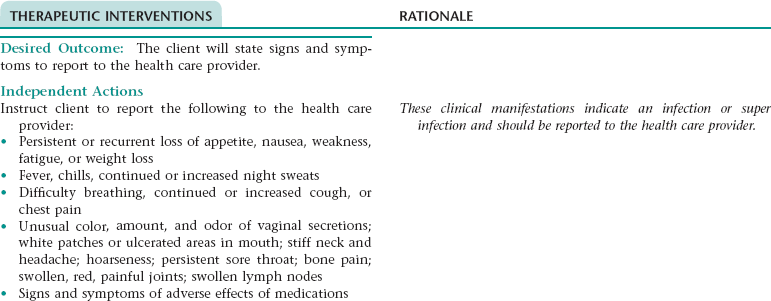
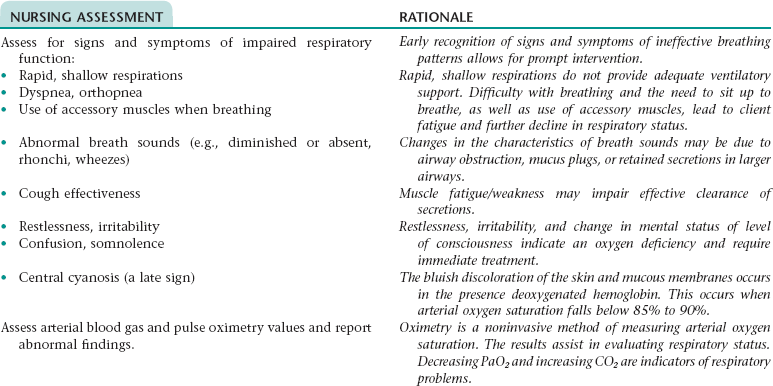
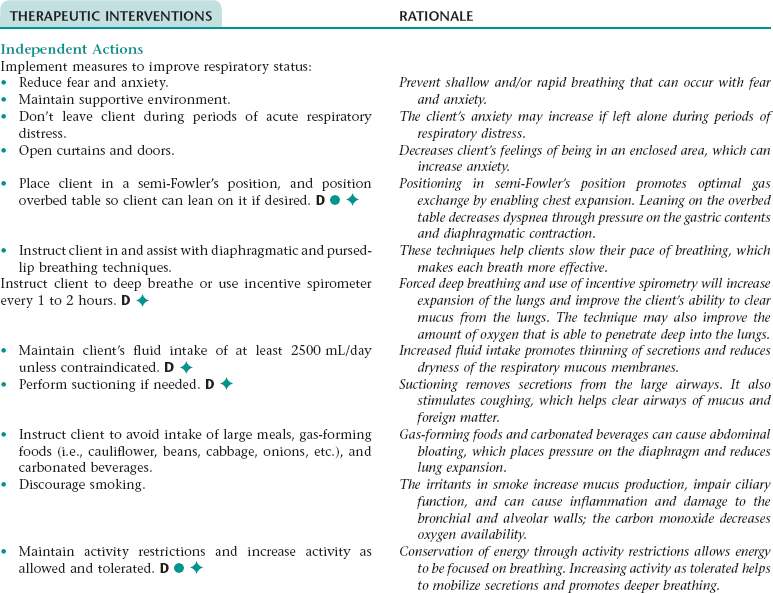
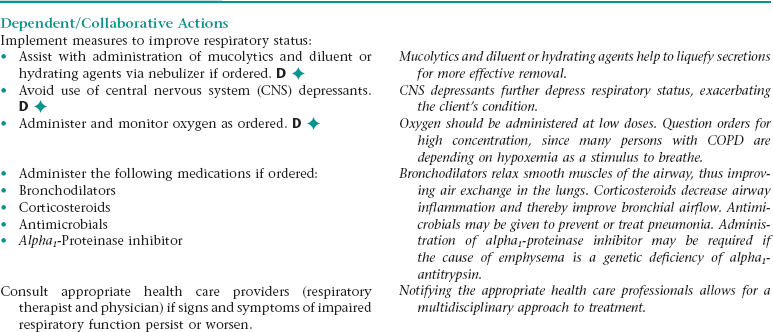
CHAPTER 4 1. Have improved respiratory function 2. Have vital signs within client’s normal range 3. Tolerate expected level of activity 4. Verbalize an understanding of medications ordered including rationale, food and drug interactions, side effects, methods of administering, and importance of taking as prescribed Ineffective breathing pattern NDx • Increased rate of respirations associated with fear and anxiety, and feeling of “air hunger” • Decreased depth of respirations associated with weakness, fatigue, fear, anxiety Ineffective airway clearanceNDx • Narrowing of the airways associated with: • Excessive mucus production, inflammation, and bronchospasm • Bronchial wall remodeling with bronchial hypertrophy and hyperplasia of mucus-secreting cells • Stasis of secretions associated with: NOC OUTCOMES: Respiratory status; airway patency; respiratory status: ventilation; respiratory status: gas exchange • Tissue hypoxia associated with impaired gas exchange • Difficulty resting and sleeping associated with dyspnea, excessive coughing, fear, anxiety, frequent assessment and treatments, and side effects of medication therapy (e.g., some bronchodilators, corticosteroids) • Increased energy expenditure associated with strenuous breathing efforts and persistent coughing 1. Have improved respiratory function 2. Tolerate expected level of activity 3. Have no signs and symptoms of complications 4. Identify ways to prevent or minimize further respiratory problems 5. Verbalize ways to maintain an optimal nutritional status 6. Identify ways to conserve energy and/or reduce dyspnea and fatigue 7. Demonstrate proper chest physiotherapy and use of respiratory equipment 8. Verbalize an understanding of medications ordered including rationale, food and drug interactions, side effects, methods of administering, and importance of taking as prescribed 9. Identify precautions that should be adhered to when using oxygen 10. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 11. Share feelings and thoughts about the effects of COPD on lifestyle and roles 12. Identify resources that can assist with financial needs, home management, and adjustment to changes resulting from COPD 13. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including future appointments with health care provider and graded exercise program. Ineffective breathing pattern NDx • Increased rate of respirations associated with fear and anxiety • Decreased depth of respirations associated with weakness, fatigue, fear, anxiety, and presence of a flattened diaphragm (a result of prolonged hyperinflation of the lungs) Ineffective airway clearance NDx • Narrowing of the airways associated with: • Excessive mucus production and inflammation and hyperplasia of the bronchial walls (especially with chronic bronchitis) • Destruction of the elastic fibers in the walls of the small airways (with emphysema) • Stasis of secretions associated with: • Narrowing or obstruction of the small airways • A decrease in effective lung surface (occurs as a result of collapse or destruction of alveolar walls) NOC OUTCOMES: Respiratory status; airway patency; respiratory status: ventilation; respiratory status: gas exchange • Decreased oral intake associated with: • Dyspnea, weakness, and fatigue • Nausea (can occur in response to noxious stimuli such as the sight of expectorated sputum and as a side effect of some medications) • Early satiety resulting from compression of the stomach by flattened diaphragm • Increased metabolic needs associated with increased energy expenditure resulting from strenuous breathing efforts and persistent coughing • Tissue hypoxia associated with impaired gas exchange • Difficulty resting and sleeping associated with dyspnea, excessive coughing, fear, anxiety, frequent assessment and treatments, and side effects of medication therapy (e.g., some bronchodilators, corticosteroids) • Increased energy expenditure associated with strenuous breathing efforts and persistent coughing NOC OUTCOMES: Activity tolerance; endurance; fatigue level; vital signs; self-care: activities of daily living; energy conservation Definition: At increased risk for the lungs being invaded by pathogens • Stasis of secretions in the lungs (secretions provide a good medium for bacterial growth) • Inhalation of pathogens (especially if client is using respiratory equipment or medication delivery devices that are not being cleaned adequately or routinely) DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will not develop pneumonia as evidenced by: a. Usual breath sounds and percussion note over lungs c. Cough productive of clear mucus only e. WBC count within normal range f. Arterial blood gas values within normal range for client h. Ability to perform ADL without increased dyspnea, chest pain, diaphoresis, dizziness, and a significant change in vital signs Definition: A condition where the right side of the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently • Increased cardiac workload associated with: • Pulmonary hypertension (can result from pulmonary vasoconstriction that occurs in response to hypoxia and the release of vasoactive substances) • Compensatory response to decreased pulmonary blood flow that results from compression of the pulmonary capillaries by hyperinflated alveoli (with emphysema) and loss of large portions of the pulmonary vascular bed (occurs in emphysema as a result of destruction of the alveolar walls) Definition: Failure of the lungs to provide adequate oxygenation to the body • Exacerbation of symptoms (e.g., increased dyspnea, feeling of suffocation), need for hospitalization, and concern about prognosis • Lack of understanding of the diagnosis, diagnostic tests, treatments, and prognosis • Financial concerns about hospitalization and lifelong treatment • Feeling of lack of control over the progression of COPD and its effects on lifestyle and roles
The Client with Alterations in Respiratory Function
ASTHMA
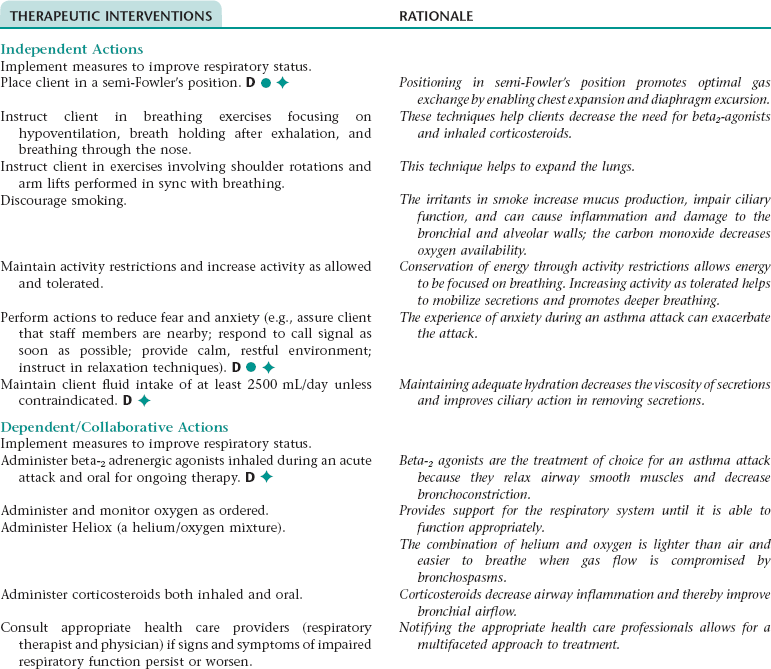
 Asthma is a disorder characterized by intermittent and reversible obstruction of the airways. This airflow obstruction is caused by bronchial hyperresponsiveness and inflammation of the airway mucous membranes. Allergens enter the airway and initiate the inflammatory cascade. Mast cells found in the basement membranes of the bronchial walls degranulate and release inflammation response mediators, which cause increased capillary permeability and vasodilation, and recruitment of eosinophils, lymphocytes, and neutrophils. The response leads to the production of thick, tenacious mucus that blocks the airways. Combined with the bronchial hyperresponsiveness and capillary vasodilation and permeability, intake of air significantly decreases, and air is trapped in the lungs below the obstruction. Chronic inflammation leads to remodeling of the bronchial walls. The bronchial walls hypertrophy, and mucus-producing cells undergo hyperplasia.
Asthma is a disorder characterized by intermittent and reversible obstruction of the airways. This airflow obstruction is caused by bronchial hyperresponsiveness and inflammation of the airway mucous membranes. Allergens enter the airway and initiate the inflammatory cascade. Mast cells found in the basement membranes of the bronchial walls degranulate and release inflammation response mediators, which cause increased capillary permeability and vasodilation, and recruitment of eosinophils, lymphocytes, and neutrophils. The response leads to the production of thick, tenacious mucus that blocks the airways. Combined with the bronchial hyperresponsiveness and capillary vasodilation and permeability, intake of air significantly decreases, and air is trapped in the lungs below the obstruction. Chronic inflammation leads to remodeling of the bronchial walls. The bronchial walls hypertrophy, and mucus-producing cells undergo hyperplasia.
OUTCOME/DISCHARGE CRITERIA
Nursing Diagnosis IMPAIRED RESPIRATORY FUNCTION*
Subjective
Objective
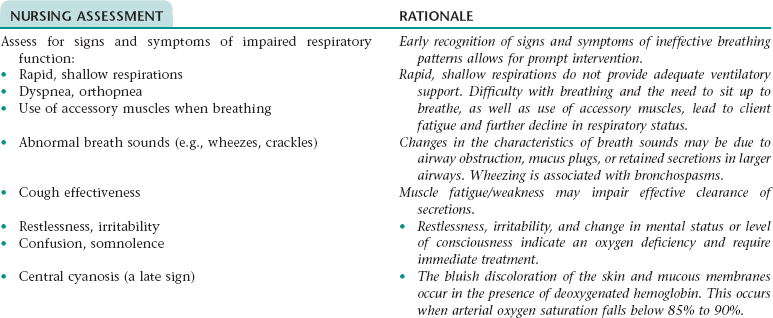
Reports of restlessness; irritability; somnolence; chronic cough; chest tightness
Rapid, shallow respirations; abnormal breath sounds— wheezing; cough; use of accessory muscles when breathing; significant decrease in oximetry results; abnormal arterial blood gas values; reduced activity tolerance
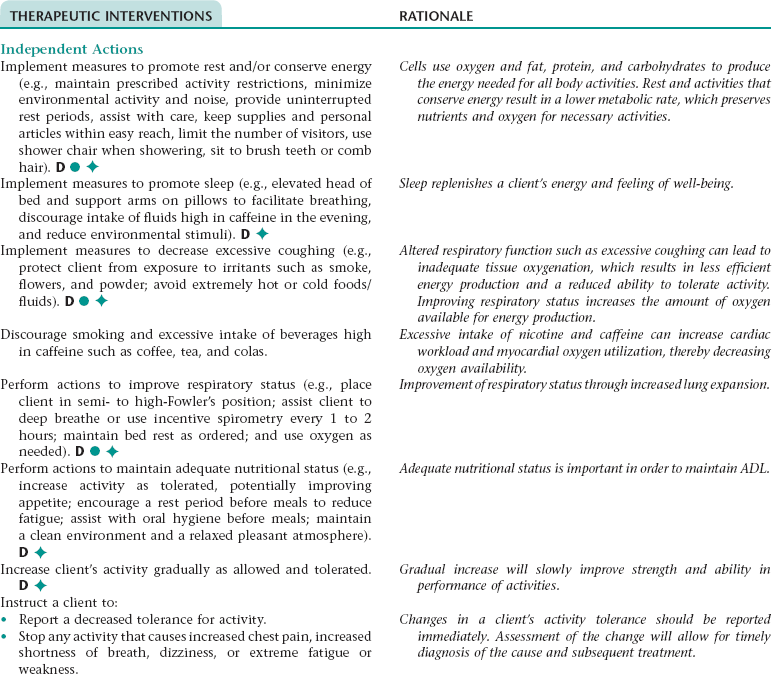
Nursing Diagnosis ACTIVITY INTOLERANCE NDx
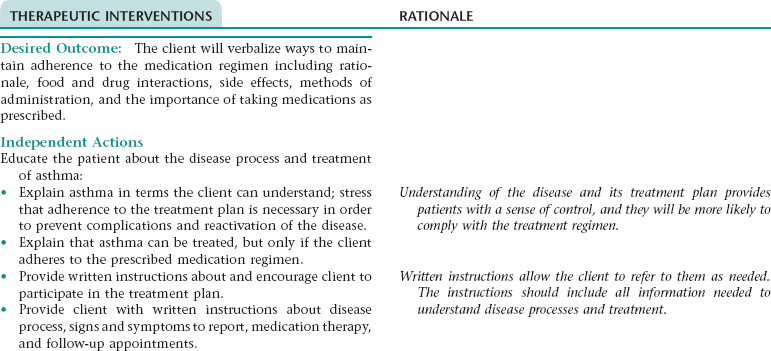
Nursing Diagnosis DEFICIENT KNOWLEDGE NDx; INEFFECTIVE HEALTH MAINTENANCE NDx; OR INEFFECTIVE SELF-HEALTH MANAGEMENT* NDx
NURSING ASSESSMENT
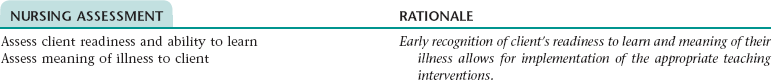
CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE
OUTCOME/DISCHARGE CRITERIA
Nursing Diagnosis IMPAIRED RESPIRATORY FUNCTION*
Subjective
Objective
Reports of confusion; disorientation; restlessness; irritability; somnolence; chest tightness
Rapid, shallow respirations; abnormal breath sounds; chronic cough; use of accessory muscles when breathing; increased anterior-posterior diameter; dyspnea; nasal flaring; central cyanosis (late sign); decreased expiratory and inspiratory pressure; decreased minute ventilation and vital capacity; significant decrease in oximetry results; abnormal arterial blood gas values; reduced activity tolerance
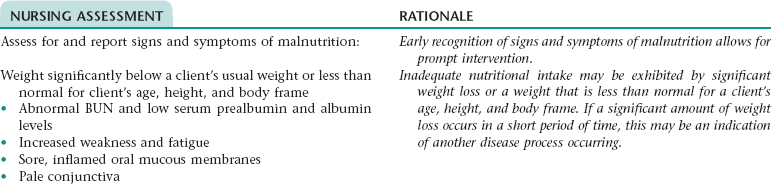
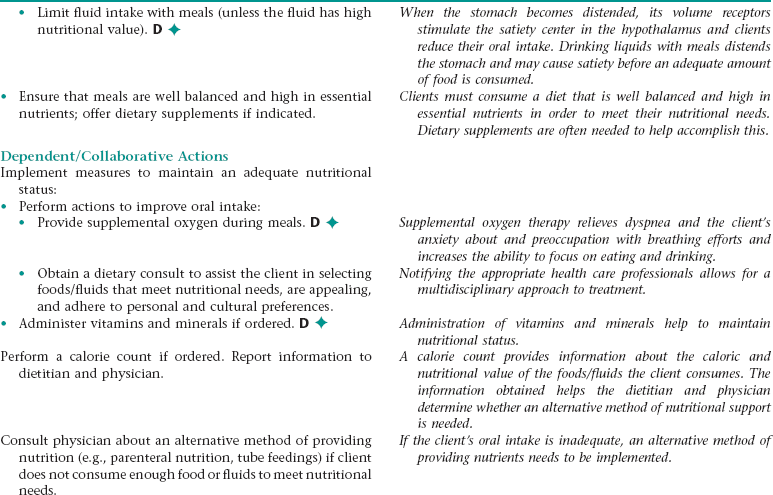
Nursing Diagnosis IMBALANCED NUTRITION: LESS THAN BODY REQUIREMENTS NDx
Subjective
Objective
Report of painful oral mucous membrane
Weight loss; weight less than normal for client’s age, height, and body frame; abnormal blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and low serum prealbumin levels; inflamed mucous membranes; pale conjunctiva; excessive hair loss; poor muscle tone
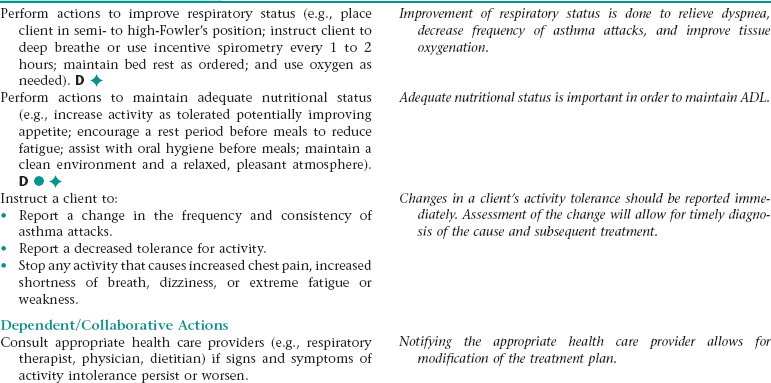
Nursing Diagnosis ACTIVITY INTOLERANCE NDx
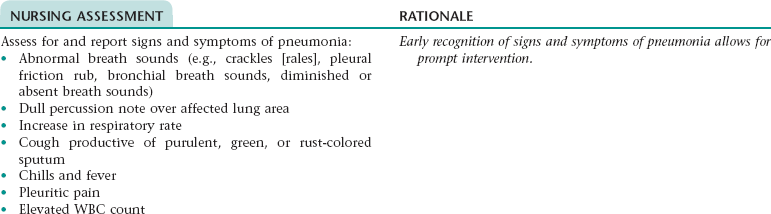
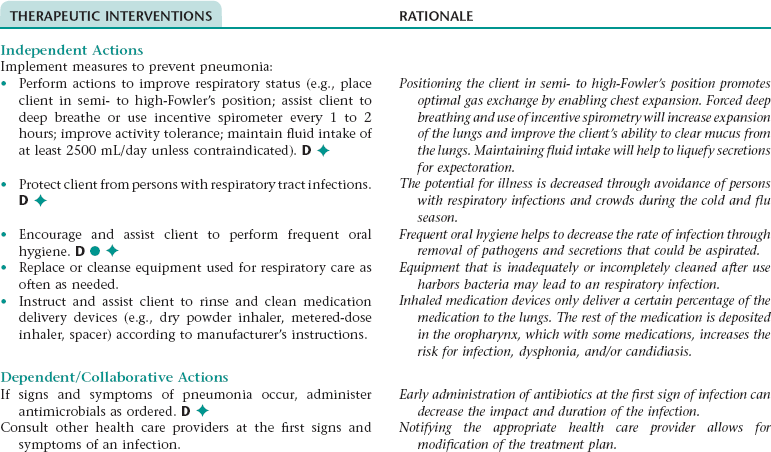
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR INFECTION NDx (PNEUMONIA)
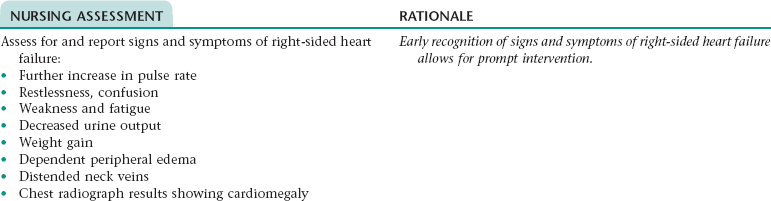
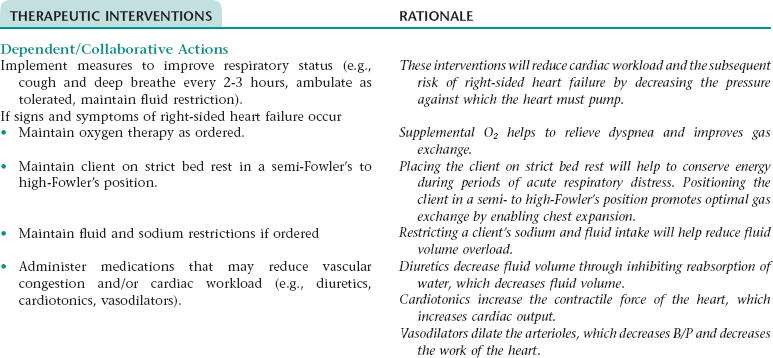
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR RIGHT-SIDED HEART FAILURE
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR RESPIRATORY FAILURE
Nursing Diagnosis FEAR/ANXIETY NDx