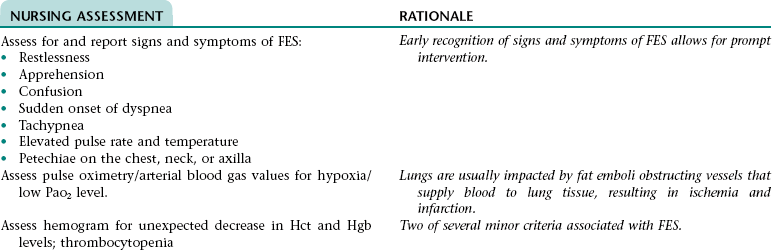
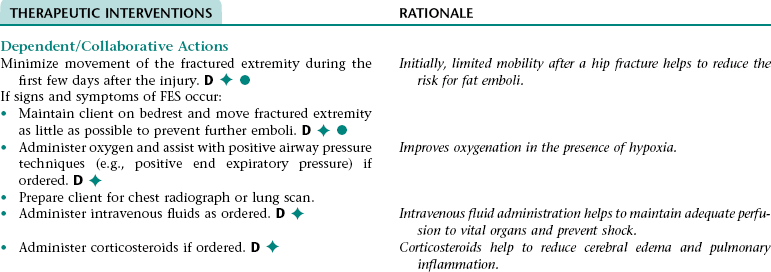
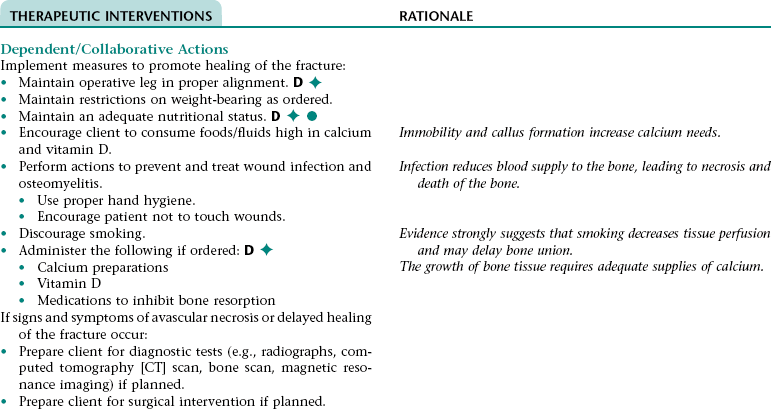
CHAPTER 12 This care plan focuses on the adult client hospitalized for a planned below-the-knee, closed amputation.* Much of the postoperative information is applicable to clients receiving follow-up care in an extended care facility or home setting. 2. Have evidence of normal healing of the surgical wound 3. Achieve expected level of mobility 4. Have no signs and symptoms of postoperative complications 5. Demonstrate appropriate ways to prevent contractures, increase strength, and improve mobility 6. Demonstrate correct transfer and ambulation techniques and proper use of ambulatory aids 7. Identify ways to maintain health of the remaining lower extremity 8. Demonstrate the ability to care for the residual limb 9. Verbalize how to care for the prosthesis and residual limb if a permanent prosthesis is planned 10. Identify ways to manage phantom limb pain if it occurs 11. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 12. Share feelings and thoughts about the change in body image and effects of the amputation on lifestyle and roles 13. Identify community resources that can assist with home management and adjustment to changes resulting from the amputation 14. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including future appointments with health care provider, prosthetist, and physical therapist; medications prescribed; and activity level For a full, detailed care plan on this topic, go to http://evolve.elsevier.com/Haugen/careplanning/. 1. Have evidence of normal healing of the surgical wound 2. Have clear, audible breath sounds throughout lungs 3. Have expected level of mobility 4. Have adequate fracture reduction and healing 6. Have no signs and symptoms of infection or postoperative complications 7. Demonstrate correct transfer and ambulation techniques and proper use of ambulatory aids 8. Demonstrate the ability to correctly perform the prescribed exercises 9. Verbalize an understanding of activity and position restrictions necessary to prevent dislocation of the prosthesis or internal fixation device 10. Identify ways to reduce the risk of falls in the home environment 11. Share thoughts and feelings about the need to transfer to or remain in an extended care or assisted living facility 12. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 13. Identify community resources that can assist with home management and provide transportation 14. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including future appointments with health care provider and physical therapist, medications prescribed, activity level, and wound care. • Lack of understanding of traction device and planned surgical procedure • Unfamiliar environment and separation from significant others • Anticipated postoperative discomfort and loss of control associated with the effects of anesthesia • Financial concerns associated with hospitalization • Potential embarrassment or loss of dignity associated with body exposure • Possibility of changes in usual lifestyle, permanent disability, or death Related to: fracture of the bone, tissue trauma, and muscle spasms Definition: At risk for disruption in circulation, sensation, or motion of an extremity • Trauma to or excessive pressure on the nerves or blood vessels as a result of the injury • Blood accumulation and edema at fracture site • Improper alignment, application of skin traction device, or traction on the injured extremity DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will maintain normal neurovascular function in the injured extremity as evidenced by: Definition: At risk for disruption in circulation, sensation, or motion of an extremity • Trauma to or excessive pressure on the nerves or blood vessels as a result of surgery and the initial injury • Blood accumulation and edema in the surgical area • Improper alignment of operative extremity • Tight or improperly positioned abductor device straps DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will maintain normal neurovascular function in the operative extremity. Definition: Low blood flow shock due to loss of intravascular fluid volume • Improper movement or positioning of operative extremity • Noncompliance with weight-bearing limitations • Delayed healing of the fracture • Venous stasis associated with increased blood viscosity (can result from deficient fluid volume), decreased mobility, and pressure exerted on blood vessels by abductor device • Hypercoagulability associated with increased release of tissue thromboplastin into the blood (occurs as a result of surgical trauma) and hemoconcentration and increased blood viscosity (can occur as a result of deficient fluid volume) • Avascular necrosis related to an inadequate blood supply to the bone (occurs primarily after intracapsular fractures) • Delayed healing of fractured bone related to: • Inadequate reduction and internal fixation of fracture • Diminished blood supply to fracture site • Thin or absent periosteum in neck of femur (decreases the healing potential) • Inadequate nutritional status • Development of infection in the fractured bone and/or surrounding tissue
The Client with Alterations in Musculoskeletal Function
 AMPUTATION
AMPUTATION
OUTCOME/DISCHARGE CRITERIA
OUTCOME/DISCHARGE CRITERIA
RELATED PREOPERATIVE NURSING/COLLABORATIVE DIAGNOSES
FEAR/ANXIETY
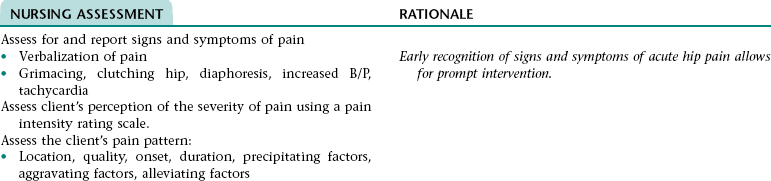
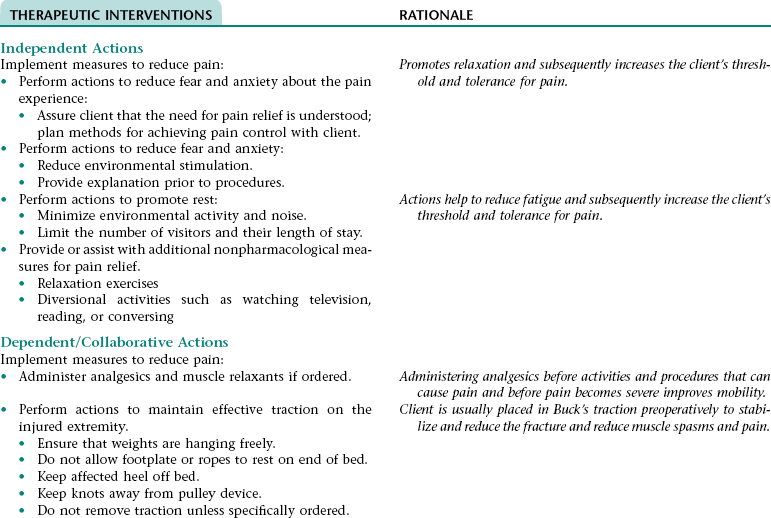
Nursing Diagnosis ACUTE PAIN NDx (HIP)
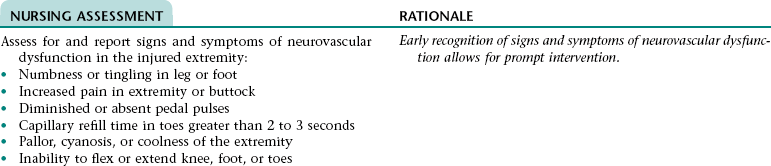
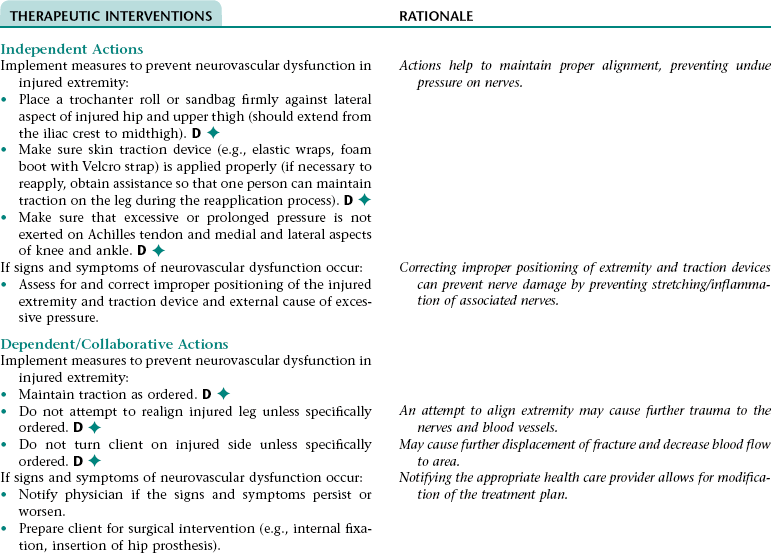
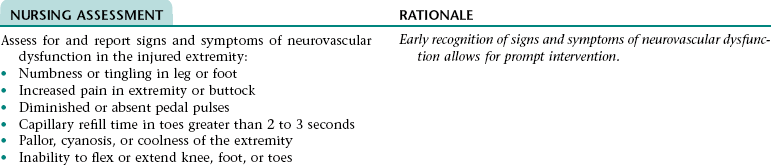
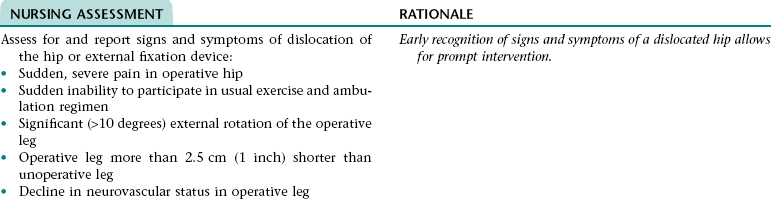
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR PERIPHERAL NEUROVASCULAR DYSFUNCTION NDx (FRACTURED EXTREMITY)
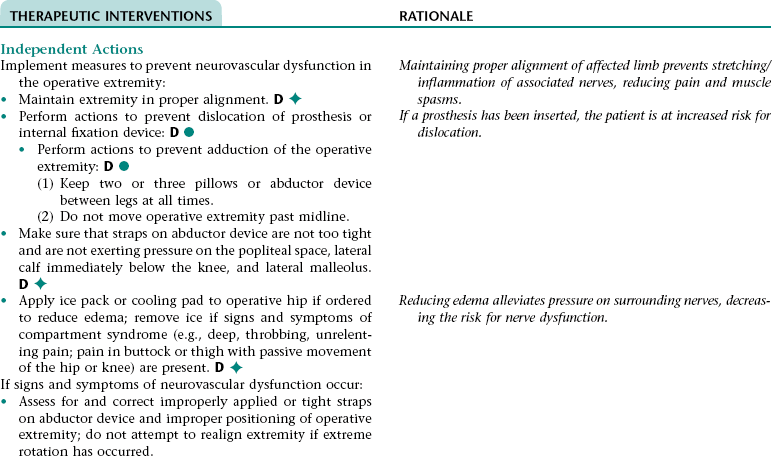
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR PERIPHERAL NEUROVASCULAR DYSFUNCTION NDx (OPERATIVE EXTREMITY)
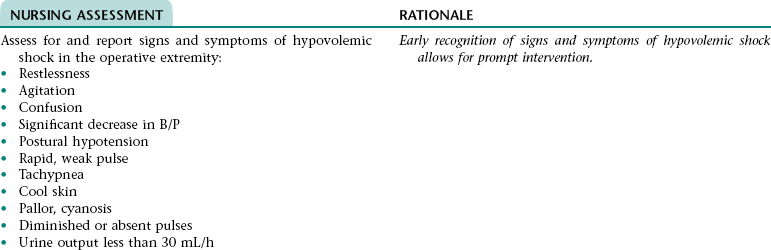
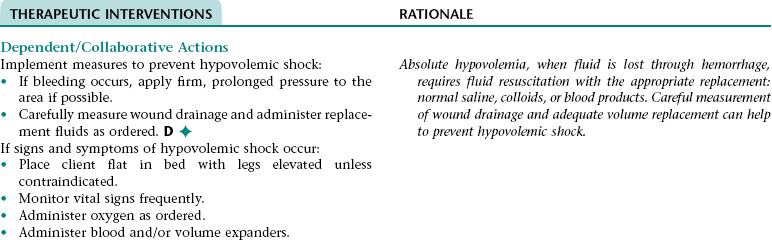
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR HYPOVOLEMIC SHOCK
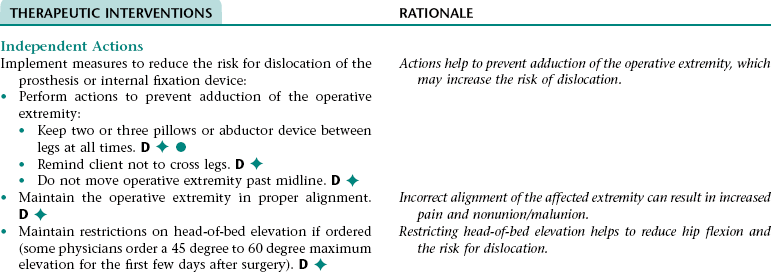
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR DISLOCATION OF PROSTHESIS OR INTERNAL FIXATION DEVICE
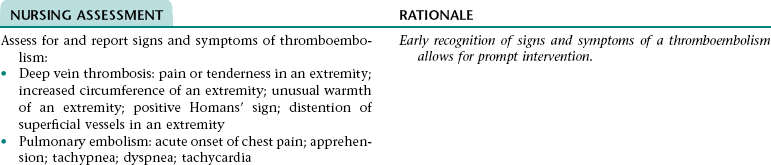
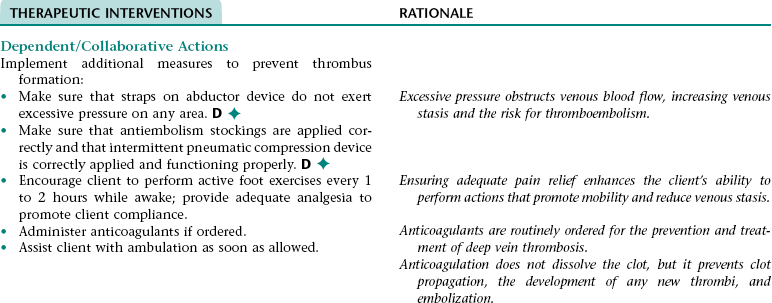
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR THROMBOEMBOLISM
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR FAT EMBOLISM SYNDROME (FES)
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR AVASCULAR NECROSIS/DELAYED HEALING OF FRACTURED BONE
Nursing Diagnosis DEFICIENT KNOWLEDGE NDx, INEFFECTIVE SELF-HEALTH MANAGEMENT NDx, OR INEFFECTIVE HEALTH MAINTENANCE*
NURSING ASSESSMENT
RATIONALE
Assess client’s readiness and ability to learn.
Early recognition of readiness to learn and meaning of illness to client allows for implementation of the appropriate teaching interventions.
Assess meaning of illness to client.
THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
Desired Outcome: The client will demonstrate correct transfer and ambulation techniques and proper use of ambulatory aids.
Independent Actions
Reinforce instructions about correct transfer and ambulation techniques, amount of weight-bearing allowed, and proper use of ambulatory aids (a walker is preferable for most elderly clients because it provides the greatest stability).
Performing transfer techniques and using assistive devices correctly reduce the risk of injury.
Allow time for questions, clarification, and practice of transfer and ambulation techniques.
Allows the nurse to reinforce patient education and to evaluate the need for further instruction.
THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
Desired Outcome: The client will demonstrate correct transfer and ambulation techniques and proper use of ambulatory aids.
Independent Actions
Reinforce instructions about correct transfer and ambulation techniques, amount of weight-bearing allowed, and proper use of ambulatory aids (a walker is preferable for most elderly clients because it provides the greatest stability).
Performing transfer techniques and using assistive devices correctly reduce the risk of injury.
Allow time for questions, clarification, and practice of transfer and ambulation techniques.
Allows the nurse to reinforce patient education and to evaluate the need for further instruction.
THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTIONS
RATIONALE
Desired Outcome: The client will demonstrate the ability to correctly perform the prescribed exercises.
Independent Actions
Reinforce instructions on muscle strengthening and range-ofmotion exercises.
Improves mobility, flexibility, and reduces the risk of muscle atrophy.
Explain importance of performing muscle strengthening and range-of-motion exercises 3 to 4 times a day.
Builds muscle mass, increasing strength and support to joint.
Allow time for questions, clarification, and return demonstration of prescribed exercises.
Allows the nurse to reinforce patient education and to evaluate the need for further instruction.
The Client with Alterations in Musculoskeletal Function
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access