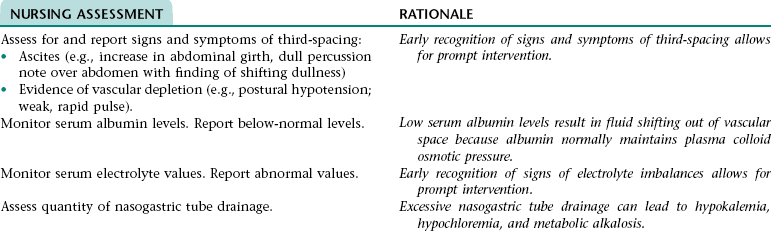
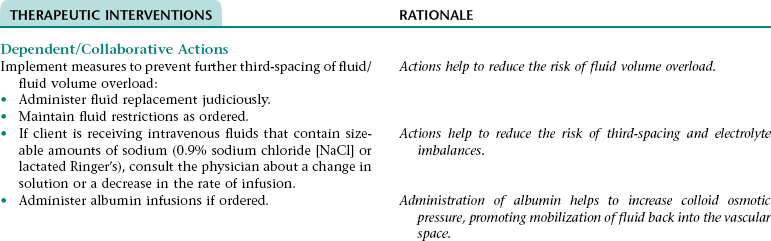
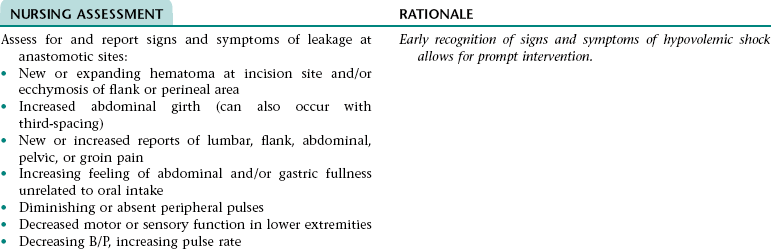
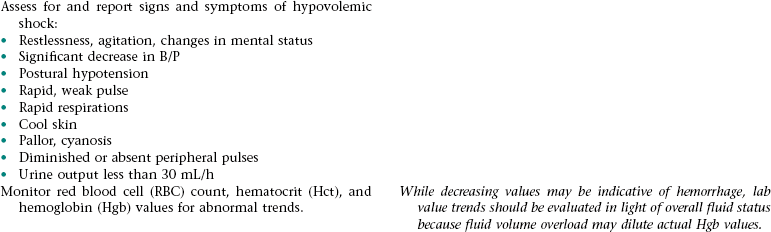
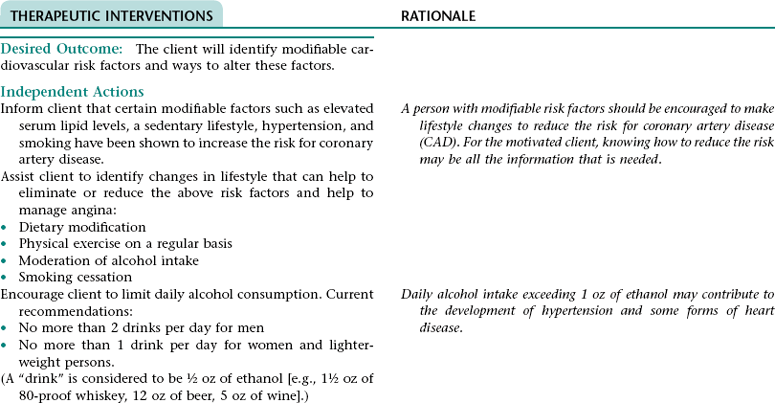
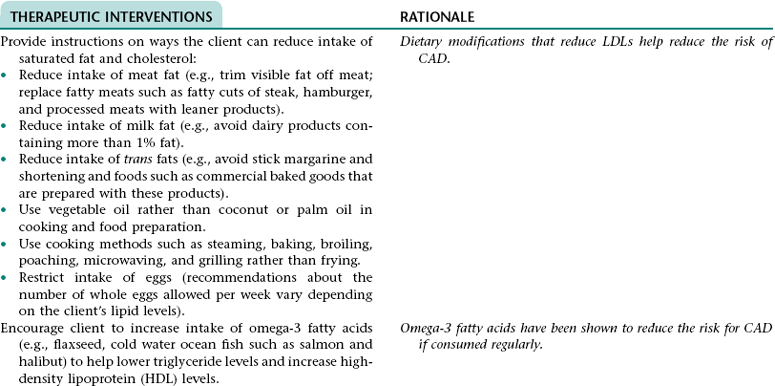
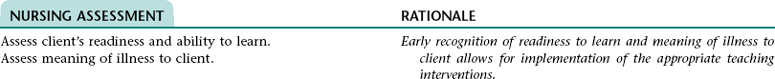CHAPTER 5 2. Tolerate expected level of activity 3. Have surgical pain controlled 4. Have clear, audible breath sounds throughout lungs 5. Have evidence of normal healing of surgical wounds 6. Have no signs and symptoms of postoperative complications 7. Identify ways to prevent or slow the progression of atherosclerosis 8. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 9. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including future appointments with health care provider, medications prescribed, activity level, and wound care. • Unfamiliar environment and separation from significant others • Lack of understanding of diagnostic tests, surgical procedure, and postoperative care • Anticipated loss of control associated with effects of anesthesia risk of disease if blood transfusions are necessary • Anticipated postoperative discomfort and potential change in sexual functioning • Third-spacing of fluid related to: • Increased capillary permeability in surgical area associated with the inflammation that occurs after extensive dissection of tissue during major abdominal surgery • Increased vascular hydrostatic pressure associated with excess fluid volume if present • Hypoalbuminemia associated with the escape of proteins from the vascular space into the peritoneum (a result of increased capillary permeability in the surgical area) • Excess fluid volume NDx related to: • Fluid retention associated with increased secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH; output of ADH is stimulated by trauma, pain, and anesthetic agents) and/or renal insufficiency (can occur if there is inadequate blood flow to the kidneys during or after surgery) • Reabsorption of third-space fluid (occurs about the third postoperative day) • Deficient fluid volume NDx related to restricted oral fluid intake before, during, and after surgery; blood loss; and loss of fluid associated with nasogastric tube drainage • Hypokalemia, hypochloremia, and metabolic alkalosis related to loss of electrolytes and hydrochloric acid associated with nasogastric tube drainage DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will experience resolution of third-spacing as evidenced by: The client will not experience excess fluid volume as evidenced by: a. B/P and pulse rate within normal range for client and stable with position change b. Balanced intake and output within 48 hours after surgery c. Absence of cardiac dysrhythmias, muscle weakness, paresthesias, twitching, spasms, and dizziness d. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum electrolytes, and arterial blood gas values within normal range Definition: A sudden disruption in the arterial blood supply to an extremity Related to: Dislodgment of necrotic debris or clot from surgical site Definition: Abnormal cardiac rhythms Related to: Altered nodal function and myocardial conductivity associated with: • Myocardial hypoxia resulting from: • Altered respiratory function • Diminished myocardial blood flow that can result from preexisting coronary artery disease, hypotension (can occur as a result of hypovolemia, vasodilation associated with rapid warming, and effects of some medications), and sympathetic nervous system-mediated vasoconstriction that results from pain, stress, and hypothermia. • Myocardial damage if a perioperative myocardial infarction has occurred Definition: Inflammation of the colon resulting from impaired blood flow • Decreased libido associated with operative site discomfort and fear of surgical site bleeding • Impotence associated with prolonged reduction in blood flow in the mesenteric or internal iliac arteries (can occur as a result of prolonged aortic clamp time during surgery, persistent hypovolemia, embolization, or graft occlusion) and/or nerve damage (can occur during surgery) 1. Perform activities of daily living and ambulate without angina 2. Have angina controlled by oral medication 3. Have no signs and symptoms of complications 4. Verbalize a basic understanding of angina pectoris 5. Identify factors that may precipitate angina attacks and ways to control these factors 6. Identify modifiable cardiovascular risk factors and ways to alter these factors 7. Verbalize an understanding of the rationale for and components of a diet designed to lower serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels 8. Demonstrate accuracy in counting pulse 9. Verbalize an understanding of medications ordered including rationale, food and drug interactions, side effects, schedule for taking, and importance of taking as prescribed 10. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 11. Identify community resources that can assist in making necessary lifestyle changes and adjusting to the effects of angina pectoris 12. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including future appointments with health care provider. DESIRED OUTCOMES: The client will maintain adequate cardiac output as evidenced by: a. B/P within client’s normal range b. Apical pulse regular and between 60 and 100 beats/min c. Absence of S3, S4 heart sounds (gallop) d. Absence of fatigue and weakness e. Unlabored respirations at 12 to 20 breaths/min f. Clear, audible breath sounds h. Absence of dizziness and syncope j. Capillary refill time less than 2 to 3 seconds k. Urine output of at least 30 mL/h NOC OUTCOMES: Circulation status; cardiac pump effectiveness; tissue perfusion: cardiac; tissue perfusion: peripheral Definition: Irreversible myocardial damage Related to: Persistent ischemia or complete occlusion of a coronary artery 1. Have fewer or no dysrhythmias 2. Have adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion 3. Tolerate expected level of activity 4. Have no signs and symptoms of complications 5. Verbalize a basic understanding of cardiac dysrhythmias 6. Demonstrate accuracy in counting pulse 7. Verbalize an understanding of medications ordered including rationale, food and drug interactions, side effects, schedule for taking, and importance of taking as prescribed 8. Verbalize an understanding of ways to avoid precipitating or exacerbating dysrhythmias 9. State signs and symptoms to report to the health care provider 10. Verbalize an understanding of and a plan for adhering to recommended follow-up care including activity restrictions and future appointments with health care provider. • A slow heart rate (if client has a bradydysrhythmia) • Decreased ventricular filling and emptying associated with a rapid and/or irregular heart rate • Tissue hypoxia if cardiac output is decreased • Difficulty resting and sleeping associated with frequent assessments and treatments, fear, and anxiety
The Client with Alterations in Cardiovascular Function
OUTCOME DISCHARGE CRITERIA
Related Preoperative Nursing/Collaborative Diagnoses ANXIETY NDx/FEAR NDx
Nursing/Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR IMBALANCED FLUID NDx AND RISK FOR ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE NDx
Subjective
Objective
Excessive fluid volume: Not applicable
Excessive fluid volume: Weight gain of 2% or greater in a short period; elevated B/P (B/P may not be elevated if cardiac output is poor or fluid has shifted out of the vascular space); presence of an S3 heart sound; intake greater than output; change in mental status; crackles (rales); dyspnea, orthopnea; edema, distended neck veins; elevated CVP (use internal jugular vein pulsation method to estimate CVP if monitoring device is not present)
Deficient fluid volume: Verbal report of thirst
Deficient fluid volume: Hypotension; tachycardia; decreased urine output; tenting skin turgor; dry mucous membranes; thick, tenacious pulmonary secretions
Hypokalemia: Complaints of muscular weakness, leg cramps; paresthesia; palpitations
Hypokalemia: Decreased or absent deep tendon reflexes; anorexia; nausea; vomiting; rhabdomyolysis; orthostatic hypotension; ventricular arrhythmias; cardiac arrest
Hypochloremia: Complaints of muscle cramps, weakness, and/or twitching; irritability
Hypochloremia: Tetany; hyperactive deep tendon reflexes; arrhythmias; seizures, coma
Metabolic alkalosis: Complaints of muscle cramps, weakness, and/or twitching; irritability; complaints of numbness and tingling of fingers, nose, and/or mouth
Metabolic alkalosis: Apathy; confusion; slow, shallow respirations; hyperactive reflexes; seizures; stupor; anorexia; nausea; vomiting
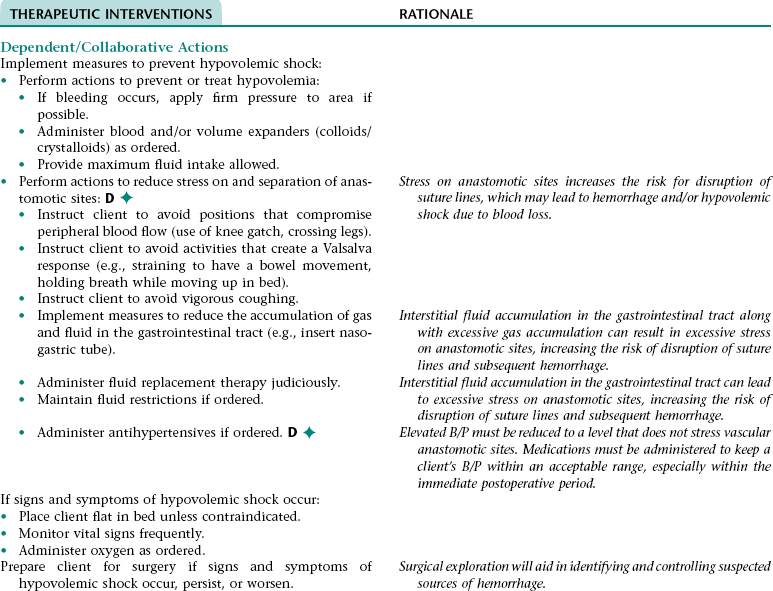
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR HYPOVOLEMIC SHOCK
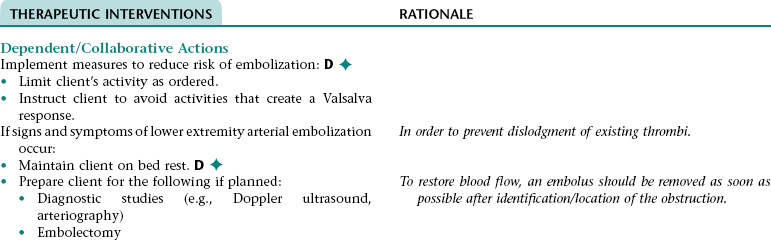
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR LOWER EXTREMITY ARTERIAL EMBOLIZATION
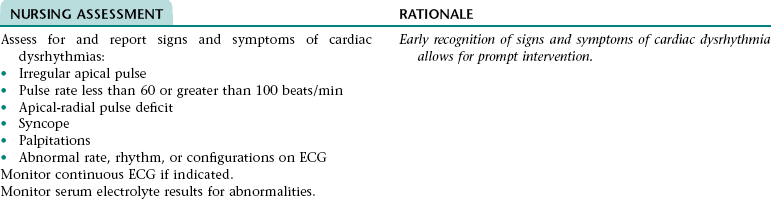
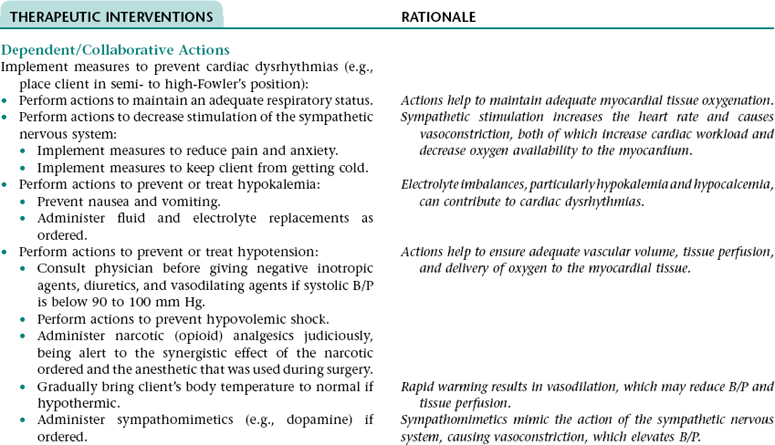
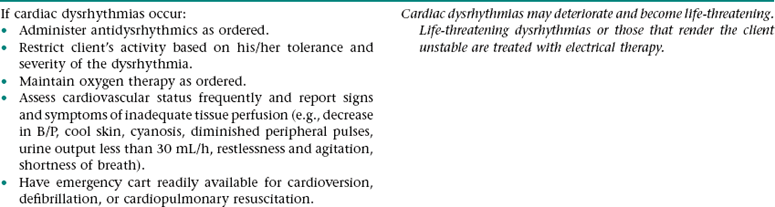
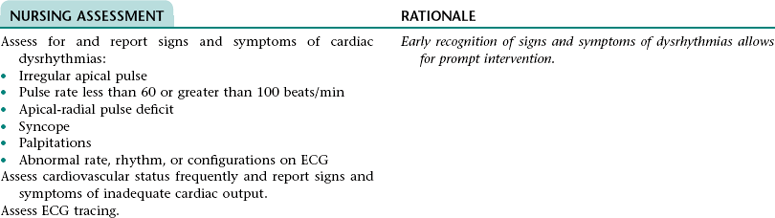
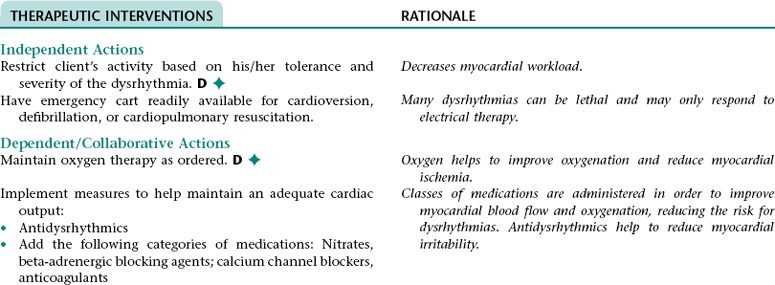
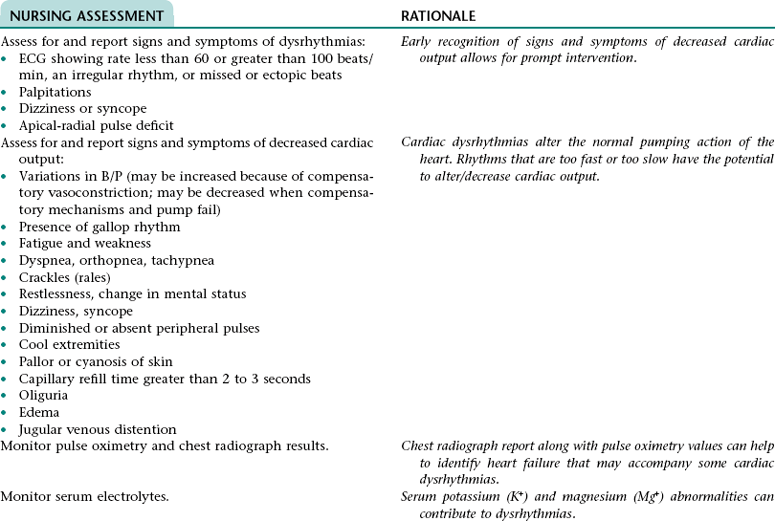
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR CARDIAC DYSRHYTHMIAS
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR ISCHEMIC COLITIS
Collaborative Diagnosis IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCTION
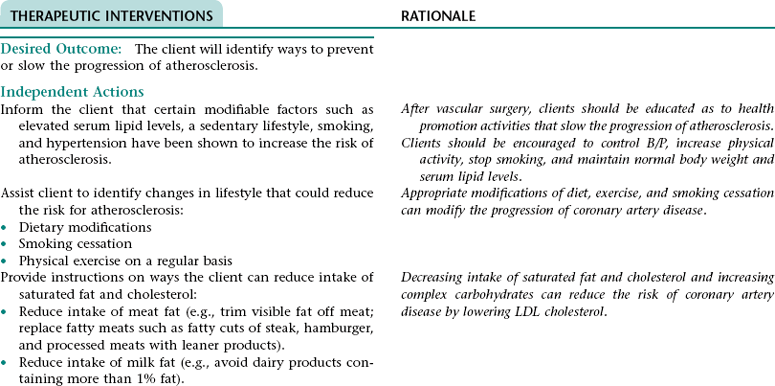
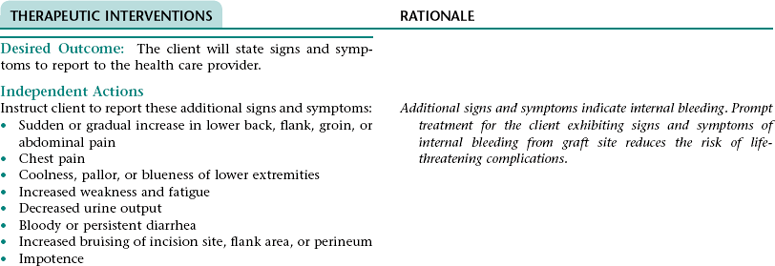
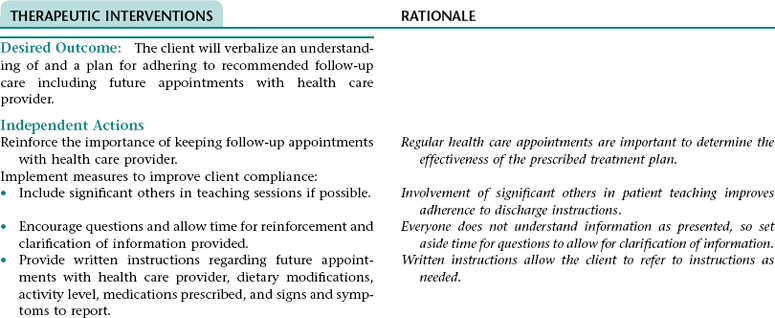
Nursing Diagnosis DEFICIENT KNOWLEDGE NDx; INEFFECTIVE HEALTH MAINTENANCE NDx; OR INEFFECTIVE SELF-HEALTH MANAGEMENT* NDx
ADDITIONAL NURSING DIAGNOSIS
SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION
OUTCOME DISCHARGE CRITERIA
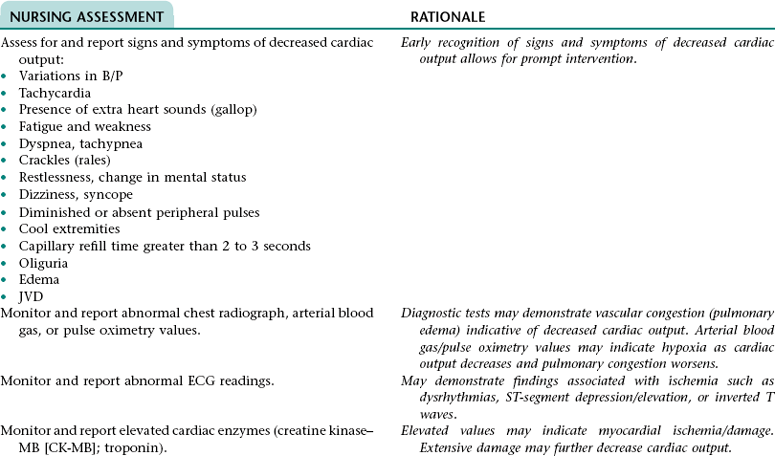
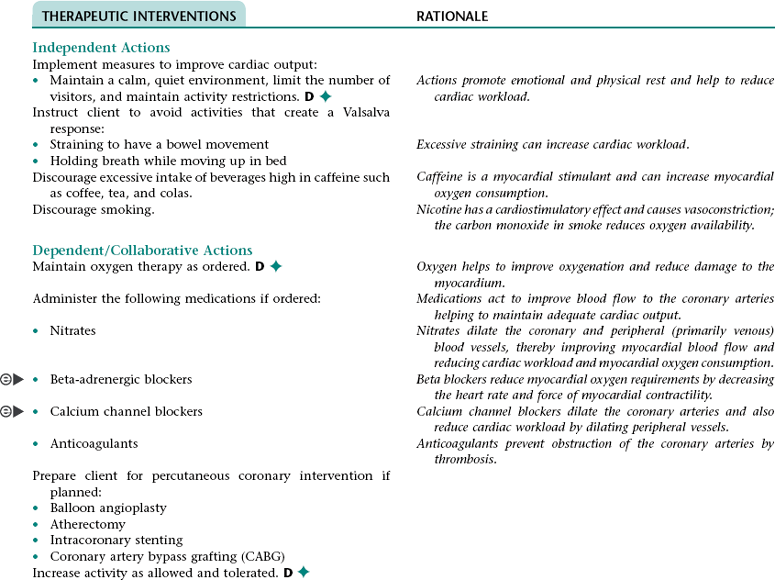
Nursing Diagnosis ACTUAL/RISK FOR DECREASED CARDIAC OUTPUT NDx
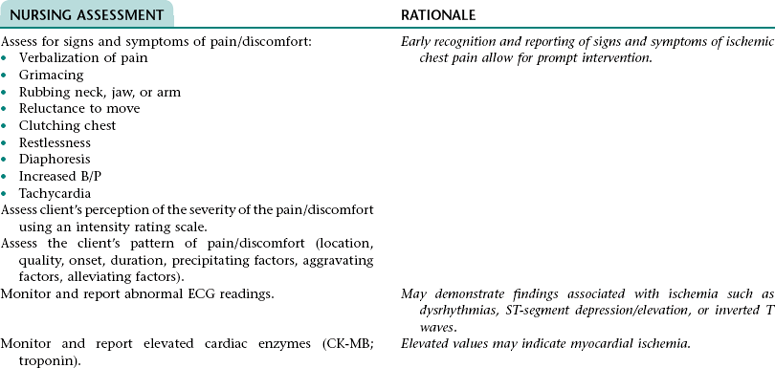
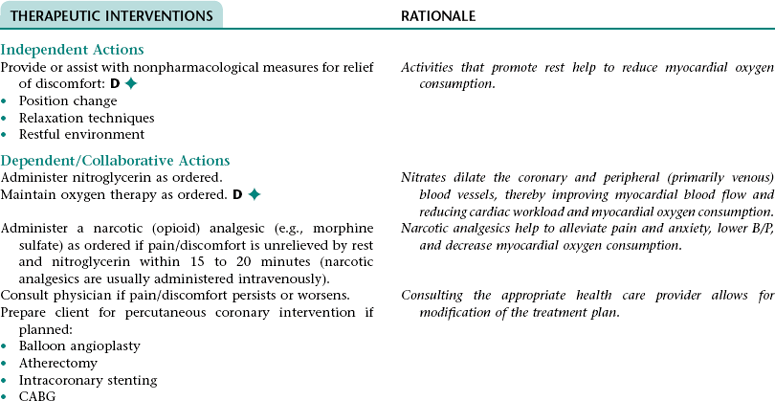
Nursing Diagnosis ACUTE PAIN NDx (RADIATING OR NONRADIATING CHEST PAIN/DISCOMFORT)
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR CARDIAC DYSRHYTHMIAS
 Related to: Myocardial irritability associated with myocardial hypoxia
Related to: Myocardial irritability associated with myocardial hypoxia
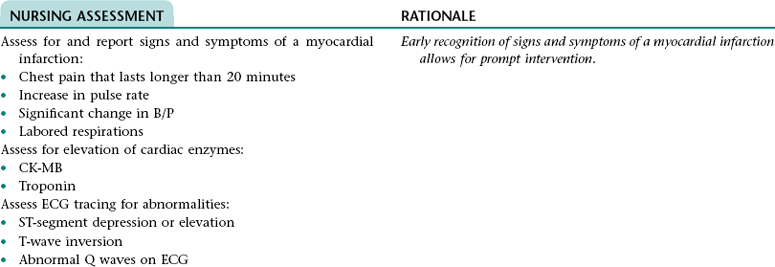
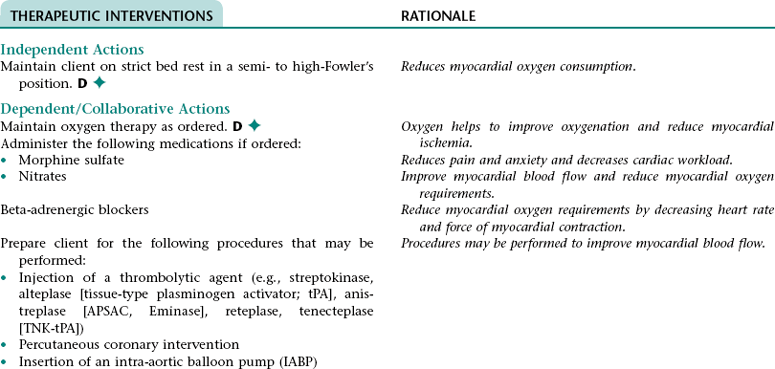
Collaborative Diagnosis RISK FOR MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
Nursing Diagnosis DEFICIENT KNOWLEDGE NDx; INEFFECTIVE FAMILY THERAPEUTIC REGIMEN MANAGEMENT NDx; OR INEFFECTIVE SELF-HEALTH MANAGEMENT NDx*
OUTCOME DISCHARGE CRITERIA
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR DECREASED CARDIAC OUTPUT NDx
Nursing Diagnosis RISK FOR ACTIVITY INTOLERANCE NDx
Subjective
Objective
Verbal reports of exertional discomfort; fatigue; weakness
Abnormal blood pressure response to activity (e.g., excessive rise in blood pressure–systolic >180 or diastolic >110 mm Hg; excessive hypotension—drop in systolic blood pressure of 10 mm Hg from baseline blood pressure); abnormal heart rate response to activity (e.g., inappropriate bradycardia—drop in heart rate >10 beats per minute; increased heart rate >100 beats per minute); EKG changes reflecting arrhythmias or ischemia ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree